Difference between revisions of "Neutron TGEM Detector Abdel"
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[File:GEM_2003_AnsysE-field.png | 200 px]] | [[File:GEM_2003_AnsysE-field.png | 200 px]] | ||
[[File:AnimGEM_2003_AnsysE-field.gif | 200 px]] | [[File:AnimGEM_2003_AnsysE-field.gif | 200 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Garfield simulation for GEM foils== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ;Single GEM | ||
| + | |||
| + | Garfield simulates a single GEM that has the standard structure | ||
| + | |||
| + | pitch = 0.14 ! Distance between holes, in mm | ||
| + | kapton = 0.050 ! Thickness of the kapton layer, in mm | ||
| + | metal = 0.005 ! Thickness of the meta layers, in mm | ||
| + | r_o = 0.050 ! Hole outer diameter, in mm | ||
| + | r_i = 0.070 ! Hole diameter in the centre, in mm | ||
=Summary Sorma 2012= | =Summary Sorma 2012= | ||
Revision as of 18:58, 31 May 2012
Garfield
Electric Field distribution
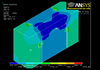
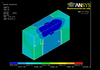
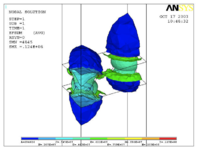
The figures represent the simulation of the electric field by using 1/4 hole in THGEM card that is made of FR4 and covered with resistive paste.
The figures represent in order : the THGEM hole model design, electric field simulation of the recent THGEM hole model that has a diameter 0.5mm and 0.9mm rim diameter(we are testing in the lab now), and the last figure represents the THGEM hole simulation after changing the hole's inside shape from the cylindrical shape to cone shape for the top and the bottom part of the hole (so it looks like the hour clock or sand clock shape). The new change in shape will change the E-field strength around and inside the hole to higher values, also it changes the electric field lines distribution outside the hole. The new simulated hole model consists of two cones that have the 0.5 diameter area in contact, each has a an inner diameter of 0.5mm and an outer diameter is 0.8mm, the rim still has 0.9mm diameter without any change.
Garfield simulation for GEM foils
- Single GEM
Garfield simulates a single GEM that has the standard structure
pitch = 0.14 ! Distance between holes, in mm kapton = 0.050 ! Thickness of the kapton layer, in mm metal = 0.005 ! Thickness of the meta layers, in mm r_o = 0.050 ! Hole outer diameter, in mm r_i = 0.070 ! Hole diameter in the centre, in mm
Summary Sorma 2012
Due to the demand on robust, economical, large active area compatible and gamma discriminating detectors, we started our work to build then measure the efficiency of Thick Gaseous Electron Multiplier Preamplifiers (THGEM) as a Neutron Sensitive Detector in the range of 1-14 MeV. The THGEM is constructed using an FR4 substrate that has been coated with a resistive paste or a thin layer of copper. A staggered array of millimeter size holes are machined in the THGEM. The resistive paste is removed from the perimeter of the holes in order to reduce the spark discharge probability. By doping the resistive paste with a neutron sensitive material A determination of the neutron sensitive material type and optimal doping strategy to produces a high detection efficiency.
ACNS 2012
A neutron detector is being constructed that uses Thick Gaseous Electron Multiplier preamplifiers (THGEM) and a thin film of a fissionable material. The THGEM is constructed using an FR4 substrate that has been coated with a resistive paste to reduce disharge events uncorrelated with an incident neutron. A staggered array of millimeter size holes are machined in the THGEM. The detector includes a segmented charge collector which is used to determine the potisiton of the neutron as it enters the detector's acceptance. The detector's efficiency for neutrons having energies between 1 and 14 MeV will be quantified using an accelerator based neutron source.
The Gaol in participating in ACNS school
Being a neutron detector research student, I am always interested in all neutron science developments and applications. A recent goal of my work is developing a fast response neutron detector using THGEM (thick gaseous electron multiplier) preamplifier, and neutron imaging using segmented charge collector technology. Such a combination between two technologies requires a knowledge of the latest neutron detectors' uses and of other instrumentation used in experiments. Participating in your school is a step to gain experience in this field, and offers a golden opportunity to communicate with specialists and scientists who have remarkable achievements in this field.
ISU research symposium
http://www.isu.edu/bulletinboard/student/xcall-03_19_2012_so.html
Due to the demand on robust, economical, large active area and gamma discriminating detectors, we started our work to build then measure the efficiency of Thick Gaseous Electron Multiplier Preamplifier (THGEM) as a Neutron Sensitive Detector in the range of 1-14 MeV. The THGEM is constructed using an FR4 substrate that has been coated with a resistive paste or a thin layer of copper. A staggered array of millimeter size holes are machined in the THGEM. The resistive paste is removed from the perimeter of the holes in order to reduce the spark discharge probability. Basically , the incident particle causes an ionization within the active area, most of the free electrons will drift through the holes by the the electric field causing an electron multiplication. The project THGEM model has a hole diameter of 0.5mm and rim size of 0.2mm, which allows the voltage between the top and bottom side of the Preamplifier to go up to 2kV. We are expecting a gain of 105 electron when a gas chamber filled 90/10% Ar/CO2 gas mixture has four THGEM Preamplifiers, each has a voltage close to 2kV. By doping the resistive paste with a neutron sensitive material A determination of the neutron sensitive material type and optimal doping strategy to produce a high detection efficiency.
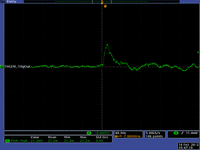
THGEM test 2/15/12
Four THGEM Card Model were tested and the pulses below were observed.
The distances in of : Cathode is 11.5mm, THGEM card distance is 4.6mm, readout distance : 6.9mm
Nothing is observed on the readout card!
3/28/12
- Conical copper THGEM cards are in the machine shop and may be done by next week
- 5 resistive paste cards are in the LDS
- Succeeded to run Garfield example GEM.C (error message: couldn't reach a Garfield text file)
To Do:
- Tomorrow install 4 THGEM cards into test chamber with advisor
- Document Garfield results from GEM.C
U-238 fission cross section in EPS format for Dr. Forest
File:ENDF GEAN4 U238 fxsection.eps
5/11/12 3-THGEM copper card detector testing results
- There was not any signal observed from the detector for cosmic rays or for the gamma source, the maximum voltage applied on each card (top and bottom) was 1.7 kV, and the trasmission voltage was 0.9 kV (between the cards), the distance between the cards was 2.3 mm, the same distance used to separate the cathode from the first THGEM card.
- Strong sparking was observed when the applied voltage on the cards was equal or more than 1.8 kV (as the THGEM cards and the cathode were placed with the same distances mentioned before), the sparking wass not in the holes area but on the other areas around the holes on the surface of the THGEM card. The spark was strong enough to damage a 1kV rated capacitor (for the fifth time by today morning), to damage a 50 ohm terminator (0.5 W), and to cause an offset on the scilloscope channel if it was connected. (it is not recommended to connect the oscilloscope over night with the detector even if the voltage is 1.7 kV!)
- The cathode distance varied from 6.9 to 2.3 mm, but the changing the distance did not forbid creating the sparks in the holes area (for the largest seperation distance), or around the holes (for the smallest one).
- The next step (if you agree) is to reproduce the results of the published paper for using the THGEM copper cards to build an alpha detector, simultaneously I repeat the testing steps using 3 resistive paste card detector in the old gas chamber, then compare the results with the THGEM copper cards' results .
References
Electric field Simulation
- Rim size dependence
File:THGEM Efield simulation.pdf
- 2010 THGEM design(s)
File:THGEM 2009 design gas efficiency.pdf
Simulations_of_Particle_Interactions_with_Matter
Voss and 3 russian references for Dy(n,x) cross sections
Media:Shalem_MSthesis_march2005.pdf
http://arxiv.org/abs/0903.3819 Dy photon gammas spectrum
http://www.ippe.obninsk.ru/podr/cjd/kobra13.php?SubentID=30974002
http://www.americanelements.com/thoxst.html
http://arxiv.org/pdf/physics/0404119
NIM_A535_2004_93[1]
File:NIM A590 2008 pg134 Eberhardt.pdf Prep Targets
Neutron cross sections for different elements Media:Neutron_cross_sections.pdf
http://www-nds.iaea.org/RIPL-2/
Media:n gamma cross sections at 25 keV.jpg
Media:n alpha cross section at 14.2 MeV.jpg
Media:ne cross section at 14 MeV.jpg
Media:high enegy fission x-section.jpg
Media:N_gamma_x-section_at_400_keV.jpg
Media:x-sections of reactions at 14 MeV.jpg
Media:n p x-section at 14.3MeV.jpg
Media: n gamma x-section at 14.5 MeV.jpg
Media: elastic x-section at 0.5 MeV.jpg
Media: n gamma x-section at 1 MeV.jpg
Media: n 2n x-section at 14.3 MeV.jpg
Donald James Hughes, Neutron cross sections, 2nd edition 1958, u.s.a atomic energy commission.Media:Neutron cross sections.pdf
File:NSAE 151 2005 319-334 Y.D. Lee.pdf
TGEM-2009 File:TGEM 2009.pdf
12 Volt power supply system.
http://www.lnf.infn.it/esperimenti/imagem/doc/NIMA_46128.pdf
http://electrontube.com.Media: rp097mono HV divier.pdf
http://www.cerac.com/pubs/proddata/thf4.htm#anchor550078
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PC_board
GEANT4_Paticles_Models[2]
Resistors online store : http://www.justradios.com/rescart.html
RETGEMs
Media:Jinst8_02_p02012_THGEM_spark.pdf
- Thick GEM COBRA
Media: Nucl_Phys_B_Bidault_ novel UV photon detector.pdf
Media:Mauro micro pattern gaseuos detectors.pdf
Media:Development and First Tests of GEM-Like Detectors With Resistive Electrodes.pdf
http://www.supplydivision.co.uk/genitem.htm
Thick_GEM_versus_thin_GEM_in_two_phase_argon_avalanche_detectors (HV circuit)[3]
Stainless Steel deflection [4]
Data Sheets
radioactive surface cleaner NoCount MDSD File:Radioactive surface cleaner.pdf.
Th-Xsection references
File:Th-232 fxsection Behrens 0.7-1.4MeV.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection Blons 1975 1.2-1.8MeV.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection ermagambetov 0-3MeV.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection Henkel 0-9MeV.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection Ohsawa original.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection pankratov 3-35MeV.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection protopopov distancefromthesource.pdf
File:Th-232 fxsection rago 12.5-18MeV.pdf
U-238-Xsection and coating references
relative cross section and calibration samples characteristics for a well determined number of fissions per second
File:Eismont relative absolute nf induced intermediate energy.pdf
- U_238 cross section error analysis
INTERNATIONAL EVALUATION OF NEUTRON CROSS-SECTION STANDARDS, INTERNATIONAL ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY,VIENNA, 2007 File:U238-xsection.pdf
U_238 (0.5-4MeV) and Th_232 (1-6MeV) fission cross section with statistical error.File:Th-232 U238 xsetion data ebars.txt
File:Pankratov fxsection Th232 U233 U235 Np237 U238 5-37MeV.pdf
Thorium Coating
ThF4 target for sputtering coatings
http://www.cerac.com/pubs/proddata/thf4.htm
Machining Uranium
Uranium will ignite in powder form
http://www.springerlink.com/content/rr072r52163x0833/
- coating Uranium
http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=16864172
Calorimeters/Detectors: DU sheet is in wide-scale use as an absorber material in high-energy physics research at large accelerator laboratories. The high atomic number and density of DU presents a large number of atoms per unit volume to interact with the particles emerging from collisions in these detectors. Also the slight background radiation from DU enables in situ calibration of the electronic read out devices within such detectors, thereby improving the accuracy of measurement.
http://www.2spi.com/catalog/chem/depleted-uranium-products.html
- IAEA Photonuclear Data Library [5]
- Data Acquisition
Warren_logbook[6]
Warren_Thesis [7]
Related To Gaseous Detectors
Breakdown and Detector Failure (10/21/10)
- Different kind of micro-pattern detectors
- References
1- A. Bressan, M. Hocha : NIM A 424 (1999) 321—342 File:High rate behavior and discharge limits in micro-pattern detectors .pdf
2- Fonte and Peskov IEEE 1999 :File:Fundamental limitations of high rate gaseous detectors.pdf
3- B. Schmidt: NIM A 419 (1998) 230—238 File:Microstrip gas chambers Recent developments radiation damage.pdf
Ideas
1.) Can we mix resistive paste (Encre MINICO) with TH-232. We construct a "bed of nails" to place a predrilled G-10 board with a copper border. The nails fill in the holes of the G-10 to keep the paste out. Ecre MINICO is a resistive paste used for transistors.
a.) Get some resistive paste.
http://www.leggesystems.com/p-253-elimstat-uxm-ccp.aspx
Resistive glue to compare
http://www.ellsworth.com/conformal.html?tab=Products
http://www.ellsworth.com/display/productdetail.html?productid=764&Tab=Products
http://www.ellsworth.com/display/productdetail.html?productid=2067&Tab=Products
http://www.cotronics.com/vo/cotr/ea_electricalresistant.htm
b.) mix with a metal similar to Th-232.
c.) construct bed of 0.4 mm nails. Look for 0.4 mm diameter pins.
7/31/2009
New vendor for carbon paste.
http://www.electrapolymers.com/productItem.asp?id=33
The data sheet does not show any information about the thickness of the paste.
The company has a distributor in the usa (877)-867-9668. A phone call is expected on Sat. 8/3/2009 about the availability of the product.
TGEM Mask Design
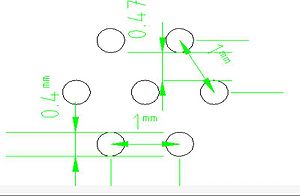
Coating U-238 or Th-232 is essential for neutron detection in the range 2-14 MeV, but THGEM contains holes that should be protected from any coating material. So, a mask is designed to cover these holes. The holes are in drilled to be on the corners of hexagonal of 1mm side length as in the figure:
The mask is made of stainless steel, 10 um laser tolerance with cut the plate to get the shape in the figure:
Please look at the following files for more details:
Make number bold black font. Add color so it is clear that they are holes in a material.
P_D
Performance of THGEM as a Neutron Detector
Vendor
Thick Film Screen Printers
http://www.sciquip.com/browses/browse_Cat.asp?Category=Screen+Printers
http://www.marubeni-sunnyvale.com/screen_printing.html
tektronix oscilloscope
134.50.3.73