Difference between revisions of "Forest NucPhys I"
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
= The Nuclear Force= | = The Nuclear Force= | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[NuclearForce_Forest_NucPhys_I]] | ||
| + | |||
==Deriving the Coulomb Force== | ==Deriving the Coulomb Force== | ||
Revision as of 03:28, 8 April 2009
Advanced Nuclear Physics
- References:
- Introductory Nuclear Physics
- Kenneth S. Krane: ISBN 9780471805533
Catalog Description:
PHYS 609 Advanced Nuclear Physics 3 credits. Nucleon-nucleon interaction, bulk nuclear structure, microscopic models of nuclear structure, collective models of nuclear structure, nuclear decays and reactions, electromagnetic interactions, weak interactions, strong interactions, nucleon structure, nuclear applications, current topics in nuclear physics. PREREQ: PHYS 624 OR PERMISSION OF INSTRUCTOR.
PHYS 624-625 Quantum Mechanics 3 credits. Schrodinger wave equation, stationary state solution; operators and matrices; perturbation theory, non-degenerate and degenerate cases; WKB approximation, non-harmonic oscillator, etc.; collision problems. Born approximation, method of partial waves. PHYS 624 is a PREREQ for 625. PREREQ: PHYS g561-g562, PHYS 621 OR PERMISSION OF INSTRUCTOR.
NucPhys_I_Syllabus
Introduction
The interaction of charged particles (electrons and positrons) through the exchange of photons is described by a fundamental theory known as Quantum ElectroDynamics(QED). QED has perturbative solutions which are limited in accuracy only by the order of the perturbation you have expanded to. As a result, the theory is quite useful in describing the interactions of electrons that are prevalent in Atomic physics.
Nuclear physics describes how Atomic nuclei interact via the strong forces as well as how the strong force binds the constituents of a nucleus (protons and neutrons, a.k.a. nucleons). Particle physics studies the interactions of fundamental particles, particles without substructure like quarks, photons, and electrons. Both Nuclear and Particle physics rely on the "Standard Model", a field theory description of the strong, weak and electromagnetic forces. Quantum ChromoDynamic (QCD) is one component to the Standard Model which represents the fundamental theory developed to describe the interactions of the quarks and gluons inside a nucleon, analogous to how QED describes the electromagnetic forces of electrons within the atom. The electroweak and Higgs field are the remaining components to the Standard model.
Ideally, QCD is a field theory which could be used to describe how quarks interact to for nucleons and then describe how those nucleons interact to form a nucleus and eventually lead to a description of how the nucleus interacts with other nuclei.
Unfortunately, QCD does not have a complete solution at this time. At very high energies, QCD can be solved perturbatively. This is an energy at which the strong coupling constant is less than unity where
The objectives in this class will be to discuss the basic aspects of the nuclear phenomenological models used to describe the nucleus of an atom in the absence of a QCD solution.
Nomenclature
| Variable | Definition |
| Z | Atomic Number = number of protons in an atom |
| A | Atomic Mass |
| N | number of neutrons in an atom = A-Z |
| Nuclide | A specific nuclear species |
| Isotope | Nuclides with same Z but different N |
| Isotones | Nuclides with same N but different Z |
| Isobars | Nuclides with same A |
| Nuclide | A specific nuclear species |
| Nucelons | Either a neutron or a proton |
| J | Nuclear Angular Momentum |
| angular momentum quantum number | |
| s | instrinsic angular momentum (spin) |
| total angular momentum = | |
| Spherical Harmonics, = angular momentum quantum number, = projection of on the axis of quantization | |
| Planks constant/2 |
Notation
= An atom identified by the Chemical symbol with protons and neutrons.
Notice that and are redundant since can be identified by the chemical symbol and can be determined from both and the chemical symbol (N=A-Z).
- example
Historical Review
Rutherford Nuclear Atom (1911)
Rutherford interpreted the experiments done by his graduate students Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden involving scattering of alpha particles by the thin gold-leaf. By focusing on the rare occasion (1/20000) in which the alpha particle was scattered backward, Rutherford argued that most of the atom's mass was contained in a central core we now call the nucleus.
Chadwick discovers neutron (1932)
Prior to 1932, it was believed that a nucleus of Atomic mass was composed of protons and electrons giving the nucleus a net positive charge . There were a few problems with this description of the nucleus
- A very strong force would need to exist which allowed the electrons to overcome the coulomb force such that a bound state could be achieved.
- Electrons spatially confined to the size of the nucleus ( would have a momentum distribution of . Electrons ejected from the nucleus by radioactive decay ( decay) have energies on the order of 1 MeV and not 20.
- Deuteron spin: The total instrinsic angular momentum (spin) of the Deuteron (A=2, Z=1) would be the result of combining two spin 1/2 protons with a spin 1/2 electron. This would predict that the Deuteron was a spin 3/2 or 1/2 nucleus in contradiction with the observed value of 1.
The discovery of the neutron as an electrically neutral particle with a mass 0.1% larger than the proton led to the concept that the nucleus of an atom of atomic mass was composed of protons and neutrons.
Powell discovers pion (1947)
Although Cecil Powell is given credit for the discovery of the pion, Cesar Lattes is perhaps more responsible for its discovery. Powell was the research group head at the time and the tradition of the Nobel committe was to award the prize to the group leader. Cesar Lattes asked Kodak to include more boron in their emulsion plates making them more sensitive to mesons. Lattes also worked with Eugene Gardner to calcualte the pions mass.
Lattes exposed the plates on Mount Chacaltaya in the Bolivian Andes, near the capital La Paz and found ten two-meson decay events in which the secondary particle came to rest in the emulsion. The constant range of around 600 microns of the secondary meson in all cases led Lattes, Occhialini and Powell, in their October 1947 paper in 'Nature ', to postulate a two-body decay of the primary meson, which they called p or pion, to a secondary meson, m or muon, and one neutral particle. Subsequent mass measurements on twenty events gave the pion and muon masses as 260 and 205 times that of the electron respectively, while the lifetime of the pion was estimated to be some 10-8 s. Present-day values are 273.31 and 206.76 electron masses respectively and 2.6 x 10-8 s. The number of mesons coming to rest in the emulsion and causing a disintegration was found to be approximately equal to the number of pions decaying to muons. It was, therefore, postulated that the latter represented the decay of positively-charged pions and the former the nuclear capture of negatively-charged pions. Clearly the pions were the particles postulated by Yukawa.
In the cosmic ray emulsions they saw a negative pion (cosmic ray) get captured by a nucleus and a positive pion (cosmic ray) decay. The two pion types had similar tracks because of their similar masses.
Nuclear Properties
NuclearProperties_Forest_NucPhys_I
The nucleus of an atom has such properties as spin, mangetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments. Nuclides also have stable and unstable states. Unstable nuclides are characterized by their decay mode and half lives.
Decay Modes
| Mode | Description |
| Alpha decay | An alpha particle (A=4, Z=2) emitted from nucleus |
| Proton emission | A proton ejected from nucleus |
| Neutron emission | A neutron ejected from nucleus |
| Double proton emission | Two protons ejected from nucleus simultaneously |
| Spontaneous fission | Nucleus disintegrates into two or more smaller nuclei and other particles |
| Cluster decay | Nucleus emits a specific type of smaller nucleus (A1, Z1) smaller than, or larger than, an alpha particle |
| Beta-Negative decay | A nucleus emits an electron and an antineutrino |
| Positron emission(a.k.a. Beta-Positive decay) | A nucleus emits a positron and a neutrino |
| Electron capture | A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino - The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state |
| Double beta decay | A nucleus emits two electrons and two antineutrinos |
| Double electron capture | A nucleus absorbs two orbital electrons and emits two neutrinos - The daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state |
| Electron capture with positron emission | A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one positron and two neutrinos |
| Double positron emission | A nucleus emits two positrons and two neutrinos |
| Gamma decay | Excited nucleus releases a high-energy photon (gamma ray) |
| Internal conversion | Excited nucleus transfers energy to an orbital electron and it is ejected from the atom |
Time
Time scales for nuclear related processes range from years to seconds. In the case of radioactive decay the excited nucleus can take many years () to decay (Half Life). Nuclear transitions which result in the emission of a gamma ray can take anywhere from to seconds.
Units and Dimensions
| Variable | Definition |
| 1 fermi | m |
| 1 MeV | = eV = J |
| 1 a.m.u. | Atomic Mass Unit = 931.502 MeV |
Resources
The following are resources available on the internet which may be useful for this class.
in particular
The Lund Nuclear Data Search Engine
Several Table of Nuclides
BNL
LANL
Korean Atomic Energy Research Institute
National Physical Lab (UK)
Table of Isotopes at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Quantum Mechanics Review
Quantum_Mechanics_Review_Forest_NucPhys_I
Nuclear Properties
NuclearProperties_Forest_NucPhys_I
The Nuclear Force
Deriving the Coulomb Force
- Poisson's Equation
The Deuteron
Nucleon- Nucleon scattering
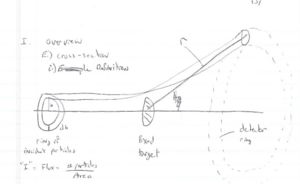
Cross section
- Total cross section
- =
- current density = # scattered particles per Area.
Particles are scattered in all directions. Typically you measure the number of scattered particle with a detector of fixed surface area that is located a fixed distance away from the scattering point thereby subtending a solid angle as shown below.
- Solid Angle
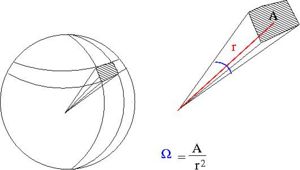
- = surface area of a sphere covered by the detector
- ie;the detectors area projected onto the surface of a sphere
- A= surface area of detector
- r=distance from interaction point to detector
- sterradians
- if your detector was a hollow ball
- sterradians
- Differential cross section
- =
- Units
- Cross-sections have the units of Area
- 1 barn =
- [units of ] =
- Fixed target scattering
- = # of particles in =
- is the area of the ring of incident particles
- = # particles in a ring of radius and thickness
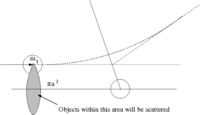
Scattering Length (a)
- Definition
While scattering length has the dimension of length it really represents the strength of the scattering (probability of scattering). It effectively give the amplitude of the scattered wave.
- Note
- the above definition is essentially an expression of how the low energy cross section corresponds to the classical value of
- = scattering cross-section
- classically: the number of particles scattered = number of incident particles (the collision probability is unity)
- Area = = The area profile in which a collision occurs
To derive an expression for the scattering length lets start with a general expression for a scattered wave.
- A general scattered wave function has the form
The first term represents a plane wave and the second term represent a modification of the plane wave due to the scattering in terms of the scattering probability .
From our previous phase shift calculation, Schrodinger solutions tend to have the general form
- (our previous solution was for )
where
the angular part is given as
and the radial part is
By comparing our general solution from the phase shift and our schrodinger solution we can cast f(q) in terms of the phase shift and then define the cross section as
in order to get a gereral expression for a scattering cross section which we then take the limit of the momentum going to zero in order to get a general expression for the scattering length.
- Math trick to recast plane waves
where
- and are the and directions of and respectively.
To determine the scattering length we will be looking at so let use the approximation
- using the above to recast to look more like
- which we want to compare to \Psi_S
Using the identities:
- By equating the two solutions
For S-wave scattering
To keep "a" finite the phase shift must approach zero at low energy
Singlet and Triplet States
Our previous calculation of the total cross section for nucleon nucleon scattering using a phase shift analysis gave
assuming =0.
When solving Schrodinger's equation for a neutron scattering from a proton we were left with the transcendental equation from boundary conditions
In the case of a Deuteron bound state
- and
- R = 2 fm
- = 0.2 /fm
when
then
Experimentally the cross section is quite a bit larger
- = 20.3 b
Apparently our assumption that the dominant part of the cross section is S=1 is wrong. There also exists a spin singlet (S=0) contribution to the cross section.
When the neutron and proton interact (create a bound state or an intermediate state) their spins can couple to either a net value of S=0 or S=1. There is only one component along the quantization axis in the event that they couple to an S=0 state. There are 3 possible components ( = -1/2, 0 . + 1/2) in the event that they couple to an S=1 state.
If you sum up the two possible cross-section, and , then you must weight them according to the possible psin compinations such that
- Solving for
- barns
Because the cross sections depend on the spin date we can conclude that
- The Nuclear Force is SPIN DEPENDENT
- Also
- Using the spatial wave functions for the singlet and triplet state one can deduce that
- = + 6.1 fm there is a triplet np bound state
- = - 23.2 fm there is NO singlet np bound state
Doing similar but more complicated calculations for p-p and n-n scattering results in
- = -7.82 fm there is NO pp bound state
- = -16.6 fm there is NO nn bound state
The Nuclear Potential
From the above we have found information on the range of the nuclear force, it's spin dependence, and it's ability to create non-spherically disrtibuted systems (quadrupole moments).
The Central Potential
No matter what potential Well geometry we choose for the nucleon, we consistently find a term which is purely radial in nature (a Central term).
where
- = a parameterization of which is constrained by scattering phase shift information.
The Spin Potential
We know from the lack of a p-p or n-n bound system that the nuclear force is strongly spin dependent. This is reenforced even more based on our observations of the S=1 n-p bound state (the Deuteron).
Experiments also indicate that parity is conserved to the level. experiments with an relative precision of have yet to find a parity violation.
- The spin potential would have terms involving spin scalar quantities because a spin potential with terms that are linear combinations of spin would violate parity.
Consider a spin potential function such that the total spin is given by
The scalar spin quantity would be given by
or
Spin Singlet
if
- S=0
then
Spin Triplet
if
- S=1
then
Construct the Spin Potential
Let
- V_1(r) = spin singlet parameterized potential
- V_3(r) = spin triplet parameterized potential
Then
- V_s(r) = - (
Yukawa Potential
Nuclear Models
Given the basic elements of the nuclear potential from the last chapter, one may be tempted to construct the hamiltonian for a group of interacting nucleons in the form
where
- represent the kinetic energy of the ith nucleon
- represents the potential energy between two nucleons.
If you assume that the nuclear force is a two body force such that the force between any two nucleons doesn't change with the addition of more nucleons, Then you can solve the Schrodinger equation corresponding to the above Hamiltonian for A<5.
For A< 8 there is a technique called Green's function monte carlo which reportedly finds solution that are nearly exact. J. Carlson, Phys. Rev. C 36, 2026 - 2033 (1987), B. Pudliner, et. al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4396 - 4399 (1995)
Shell Model
Independent particle model
This part of the Shell model suggests that the properties of a nucleus with only one unpaired nucleon are determined by that one unpaired nucleon. The unpaired nucleon usually, though no necessarily, occupies the outer most shell as a valence nucleon.
SN-130 Example
The low lying excited energy states for Sn-130 taken from the LBL website are given below.
File:Sn-130 LowLyingE Levels.tiff
The listing indicates that the ground state of Sn-130 is a spin 0 positive parity state. The first excited state of this nucleus is 1.22 MeV above the ground state and has . The next excited state is 1.95 MeV above the ground state and has .
Let's see how well the shell model does at predicting these states
Liquid Drop Model
Bohr and Mottelson considered the nucleon in terms of its collective motion with vibrations and rotations that resembled a suspended drop of liquid.
Electric Quadrupole Moment
Electric_QuadrupoleMoment_Forest_NuclPhys_I
Nuclear Decay
Nuclear_Decay_Forest_NucPhys_I
Nuclear Reactions
Forest_NucPhys_I_Nuclear_Reactions
Electro Magnetic Interactions
Weak Interactions
Strong Interaction
Applications
Homework problems
Midterm Exam Topics list
Basically everything before section 5.3 (The Nuclear Force). Section 5.3 and below is not included on the midterm.
Topics of emphasis:
- 1-D Schrodinger Equation based problems involving discrete potentials ( wells, steps) and continuous potentials (simple Harmonic, coulomb).
- Calculating form factors given the density of a nucleus
- Determining binding and nucleon mass separation energies
- , , and angular momentum operations
- Calculating scattering rates given the cross-section and a description of the experimental apparatus
Formulas given on test
Schrodinger Time independent 1-D equation
Particle Current Density
Form Factor
If the density has no or dependence
Coulomb energy difference between point nucleus and one with uniform charge distribution
Nucleus Binding Energy
Neutron Separation energy
Proton Separation energy
Semiempirical Mass Formula
where
| Parameter | Krane |
| 15.5 | |
| 16.8 | |
| 0.72 | |
| 23 | |
| 34 |
Final
1.) Calculate the magnetic moment of a proton assuming that it may be described as a neutron with a positive pion in an state.
2.) Show that the phase shift () for the scattering of a neutron by a proton can be given by the equation
where
V = 36.7 MeV R = 2.1 fm
3.)
a.) Write the reaction equations for the following processes. Show all reaction products.
i.)
ii.)
iii.)
iv.)
b.) Determine the Q-values for the first two reactions above.
4.) Find the Quadrupole moment of using the shell model and compare to the experimental value of -0.37 barns.
5.) Find , using the shell model, for the following nuclei
a.)
b.)
c.)
d.)
6.) Use the shell model to predict the ground state spin and parity of the following nuclei:
a.)
b.)
c.)
d.)
7.) Tabulate the possible states for a nucleus three quadrupole phonon state ( ). Show that the permitted resultant states are , , , , and .