G4Beamline PbBi
Development of a Positron source using a PbBi converter and a Solenoid
Converter target properties
Definition of Lead Bismuth
1cm diameter target
2 mm thick PbBi
0.5 Tesla solenoid
Desire to know
Emmittance (mrad * mm)
dispersion (Delta P/P) (mradian/1000th mm/1000th)
of electrons after the PbBi target.
pole face rotation in vertical plane.
G4BeamLine and MCNPX
Target thickness optimization
PbBi_THickness_GaussBeam
PbBi_THickness_CylinderBeam
PbBi_THickness_PntSource
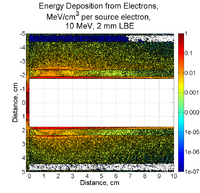
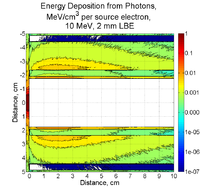
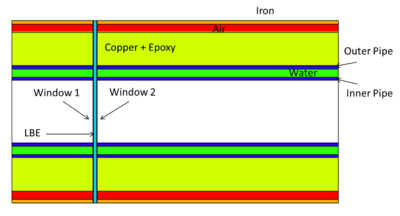
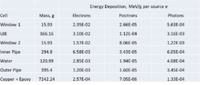
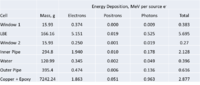
Energy Deposition in Target system (Heat)
MCNPX simulations of energy deposition into different cells are below. There is a slight overestimate (they add up to about 120%). Positrons contribute less than 1% of electrons' contribution. No magnetic filed is assumed.
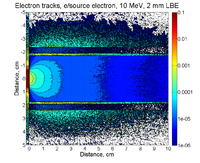
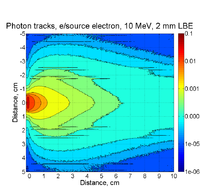
2mm thick PbBi, 10 MeV, point source
G4beamline pencil beam 10 cm radius
beam ellipse particle=e- nEvents=1000000 beamZ=0.0 beamX=0. beamY=0. \
sigmaX=10.0 sigmaY=10.0 sigmaXp=0.000 sigmaYp=0.000 \
meanMomentum=10. sigmaE=0. maxR=10.
| PbBi Thickness (mm) | #positrons/million electrons (G4Beamline) | #positrons/million electrons (MCNPX) |
| 1 | 1091 | |
| 1.5 | 1728 | |
| 2 | 1902 43 | 1984 |
| 2.5 | 2062 | |
| 3 | 13 | 1986 |
| 3.5 | 1938 | |
| 4 | 39 | 1858 |
| 5 | 1646 | |
| 6 | 37 | 1541 |
| 10 | 1216 |
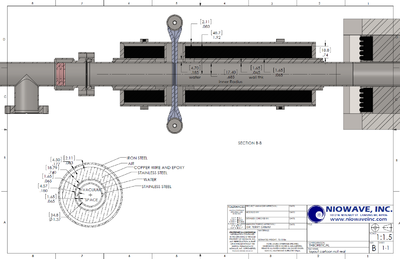
Solenoid
Inner Radiusu=
Outer Radius =
Length =
Current=
Magnetic Field Map in cylindrical coordinates (Z & R) from Niowave