Difference between revisions of "EG1 Teleconferences DeltaDoverD"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| − | Our theoretical expectation | + | Our theoretical expectation, based on the description of the CLAS cherenkov detector suggests, that pions can generate up to about 10 photoelectrons compared with the 13 photoelectrons that can be generated by electrons. While the cherenkov detector can distinguish a 3 photoelectron signal generated by pions of momentum 3 GeV or less from the 10 photoelectrons generated by the typical detected electron, high momentum pions would generate photoelectron signals which are comparable to the photoelectrons generated by an electron. |
Revision as of 02:59, 29 January 2009
15-1-09
Electron-Pion Contamination Estimate
As shown in the wiki section, Particle_Identification#Cherenkov,
the expected number of photoelectrons produced by electrons traversing CLAS cherenkov detector would be
if you assume a of 1 for the detected electrons in our data sample.
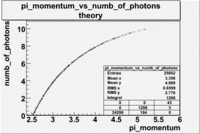
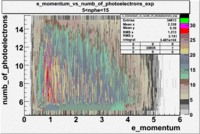
The expected number of photoelectrons in the CLAS cherenkov detector for the pion energy range in the EG1 data set is shown in the graph below.
Our theoretical expectation, based on the description of the CLAS cherenkov detector suggests, that pions can generate up to about 10 photoelectrons compared with the 13 photoelectrons that can be generated by electrons. While the cherenkov detector can distinguish a 3 photoelectron signal generated by pions of momentum 3 GeV or less from the 10 photoelectrons generated by the typical detected electron, high momentum pions would generate photoelectron signals which are comparable to the photoelectrons generated by an electron.
CLAS Cherenkov signal
Electrons
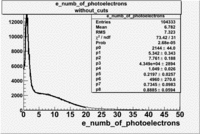
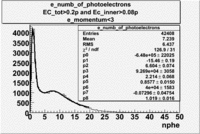
The cherenkov signal measured in CLAS for particles identified as electrons by the tracking algorithm is shown below. There are two distributions present. One distribution is centered around 1.5 PEs and the second distribution is at 8 PEs when two gaussians and a Landau distribution are combined and fit to the spectrum. As we will show below, the first peak is due to the misidentification of a negative pion as an electron.
- PE Fit equation (Osipenko's CLAS Note 2004-20 File:CLAS Note-2004-020.pdf)
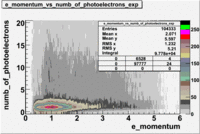
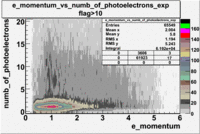
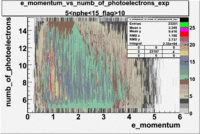
- e_Momentum_vs_Number_of_Photoelectrons
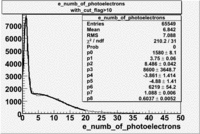
The flag cut applied on the number of photoelectrons means that in CLAS detector instead of 5 superlayers were used 6 of them in track fit. As one can see from the histograms of the Number of photoelectrons, the cut on flag does not have effect on the peak around 1.5phe and decreases the number of entries by 37.17 %. The peak is due to a high energy pions(>2.5GeV), which have enough momentum to emit Cherenkov light and also because of the bad collection of light, there are a particular polar and azimuthal combination of angles where The Cherencov Detector cannot receive emitted light. .
- Number of photoelectrons
Table: Cherenkov fit values
| Distributions | amplitude | mean | width | amplitude | mean | width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without cuts | with cut(flag>10) | |||||
| gauss(0) | p0=2144+/-44.0 | p1=5.342+/-0.343 | p2=7.761+/-0.188 | p0=1580+/-8.1 | p1=3.75+/-0.06 | p2=8.486+/-0.042 |
| landau(3) | p3=4.349e+04+/-2894 | p4=1.049+/-0.026 | p5=0.2197+/-0.0257 | p3=8600+/-3648.7 | p4=-3.861+/-1.414 | p5=-4.88+/-1.41 |
| gauss(6) | p6=4960+/-270.6 | p7=0.7345+/-0.0983 | p8=0.8885+/-0.0594 | p6=6219+/-54.2 | p7=1.088+/-0.006 | p8=0.6037+/-0.0052 |
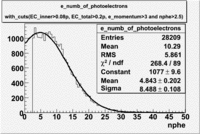
When flag cut(flag>10 cut means that 6 superlayers were used in track fit) was applied the number of entries decreased by 37.17 % and the mean value for the number of photoelectrons is about 7-8. After 5<nphe<15 cut, the number of entries decreased by 66.63 %.The mean value of the nphe is ~9 which agrees with theory(mean value ~13).
| Experiment | B>0 | without cuts | flag>10 | 5<nphe<15 | 5<nphe<15 and flag>10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Pions()
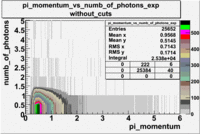
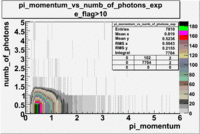
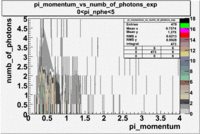
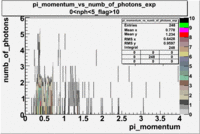
- _Momentum_vs_Number_of_Photons
After e_flag>10 cut, the number of entries decreased by 30.45 % and the mean value for the number of photons is ~9
| Experiment | B>0 | without cuts | e_flag>10 | 0<e_nphe<5 | 0<nphe<5 and e_flag>10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Electron-pion contamination
Osipenko's CLAS Note 2004-20 File:CLAS Note-2004-020.pdf
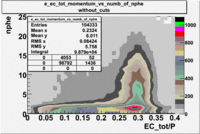
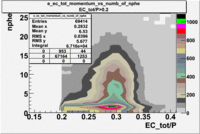
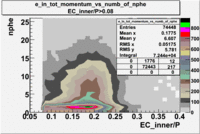
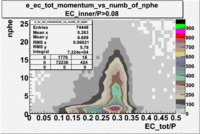
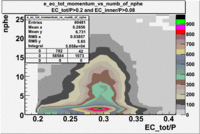
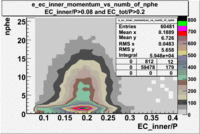
- EC_tot/P_vs_Number_of_Photoelectrons and EC_inner/P_vs_Number_of_Photoelectrons
Two types of cuts were applied on the distributions below, one on the energy deposited to the inner calorimeter and another one on the total energy absorbed by the calorimeter , to improve the electron particle identification. In this case was used dst27095_05 file, the beam energy is 5.735 GeV and target NH3.
| without cut | _vs_nphe() | _vs_nphe () | _vs_nphe() |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| _vs_nphe() | _vs_nphe( and ) | _vs_nphe ( and ) |
|---|---|---|

|
|
|
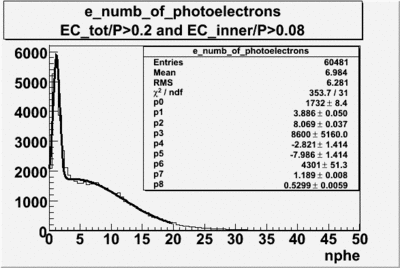
From the EC_tot/P_vs_Number_of_Photoelectrons histogram one can see that the released energy fraction() at ~1.5 nphe peak is much smaller than it should be for electrons. In conclusion, the ~1.5 nphe peak is produced by the tail of negatively charged particles(pions). To eliminate negatively charged pions cut is applied on Calorimeter. After the cut was applied the number of entries decreased by ~33.47%.
| Distributions | amplitude | mean | width |
|---|---|---|---|
| with cuts( and ) | |||
| gauss(0) | p0=1732+/-8.4 | p1=3.886+/-0.050 | p2=8.069+/-0.037 |
| landau(3) | p3=8600+/-5160.0 | p4=-2.821+/-1.414 | p5=-7.986+/-1.414 |
| gauss(6) | p6=4301+/51.3 | p7=1.189+/-0.008 | p8=0.5299+/-0.0059 |
e_numb_of_photoelectrons with the following cuts , . To eliminate the photons produced by the negatively charged pions was used the cut on the momentum e_momentum<3 GeV. Because the high energy pions are able to produce photons, which are misidentified with photoelectrons.