Difference between revisions of "Rotating Tungsten Target System"
(→Test) |
|||
| (60 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Parts = | = Parts = | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pS0cBeT_trE&context=C41942f6ADvjVQa1PpcFPVZGpWjIhpT6B3B7hDLZHuaQKYXRQ0xVc= Motor test vedio] | ||
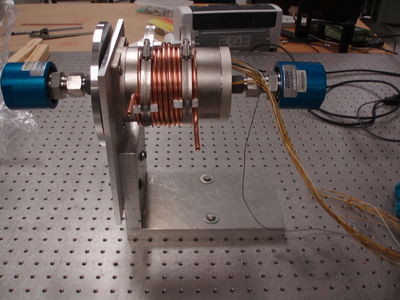
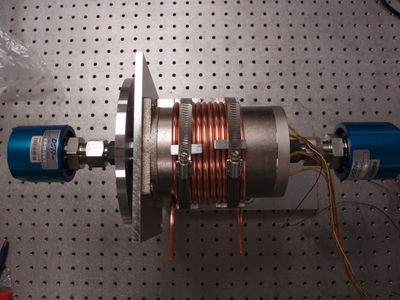
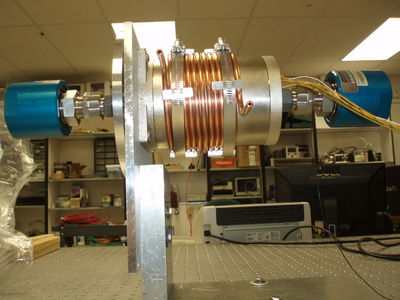
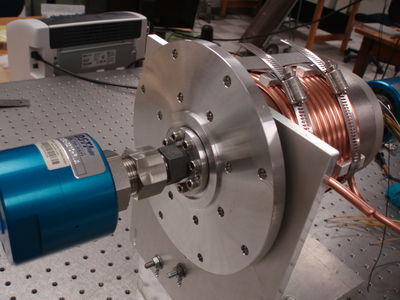
[[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot1.png | 400 px]] [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot11.png | 400 px]] | [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot1.png | 400 px]] [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot11.png | 400 px]] | ||
| Line 7: | Line 9: | ||
| − | == | + | == Rotary Union == |
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.dsti.com/products/rotary-unions/sps/ SPS-5510] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:hrrl-pos-tar-rotary.pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
[[File:HRRL_Pos_Rotating_W_Target_Sys_Parts_Roter_1.jpg | 400 px]] | [[File:HRRL_Pos_Rotating_W_Target_Sys_Parts_Roter_1.jpg | 400 px]] | ||
[[File:HRRL_Pos_Rotating_W_Target_Sys_Parts_Roter_2.jpg | 400 px]] | [[File:HRRL_Pos_Rotating_W_Target_Sys_Parts_Roter_2.jpg | 400 px]] | ||
| Line 24: | Line 31: | ||
= STR8 - Step Motor Drives= | = STR8 - Step Motor Drives= | ||
| + | |||
| + | Applied Motion Products motor control. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file:STR8.png | 300 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Power Supply == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.lamonde.com/acatalog/Products_Power_Supplies_992.html#aSTP_2dPWR_2d4810 Power Supply] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Rotating_Tar_PS.pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | STP-PWR-4810 Power supply for stepping systems, dual output with 48 VDC @ 10A (at full load) unregulated and 5 VDC at 0.5A regulated. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 120/240 VAC, 50/60 Hz supply voltage, overcurrent protection. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot_PS1.png | 400 px]] [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot_PS2.png | 400 px]] | ||
| + | [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot_PS6.png | 400 px]] [[File:HRRL_Beam_Rot_Tar_Sys_Mot_PS9.png | 400 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[https://wiki.iac.isu.edu/index.php/Images#Rotating_Target More PS Images]] | ||
== Document == | == Document == | ||
| Line 51: | Line 77: | ||
== Features == | == Features == | ||
| − | + | Operates from a 24 to 75 volt DC power supply | |
| + | |||
| + | Running current up to 7.8 amps per phase | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Block_Diagram.png | 600 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Other Parts needed == | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1) a 24 to 75 volt DC power supply | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2) a source of step signals, such as a PLC or motion controller. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Wire Connection == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:STR8-Connection.png | 500 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:STR8-Connection_2.png | 600 px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Wiring the Motor === | ||
| − | + | Connect the drive to the motor. Four lead motors can be connected in only one way, as shown in Figure 1. | |
| + | We recommend that eight lead motors be connected in parallel, as shown in Figure 2. | ||
| + | If using a non-Applied Motion Products motor, please refer to your motor specs for wiring information. | ||
| − | + | [[File:STR8-Connection_3.png | 1000 px]] | |
| − | + | === Step Control === | |
| − | + | Step Pulse Type | |
| + | Most indexers and motion controllers provide motion commands in the “Step and Direction” format. The Step signal pulses once for each motor step and the direction signal commands direction. However, a few PLCs use a different type of command signal: one signal pulses once for each desired step in the clockwise direction (called STEP CW), while a second signal pulses for counterclockwise motion (STEP CCW). '''The STR drives can accept this type of signal if you remove the drive cover and move jumper S3 from the “1-2” position to the “1-3” position.''' In STEP CW/STEP CCW mode, the CW signal should be connected to the STEP input and the CCW signal to the DIR input. | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:hrrl-pos-tar-motor-puls-cont-step-dir.png | 500 px]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | === Test === | |
| − | + | Two Al slabs are place to the disk. | |
| − | + | Weight of the Al slab is 235 and 240 grams. Their center of mass are 13 +- 1 cm from the center of disk. | |
| − | + | Inertia Solid cuboid of height h, width w, and depth d, and mass m: <math>I_h~=~\frac{1}{12}m(w^2+d^2)</math> | |
| − | + | <math>I_h~=~\frac{1}{12}0.2375(0.126^2+0.72^2) =\frac{1}{12} 0.2375 \times 0.534276 =\frac{1}{12} 0.12689055 = 0.0106</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | <math>I_d = I_h + md^2 = 0.0106 + 0.2375 \times 0.13^2 = 0.0106 + 0.00401375 = 0.01461375 </math> | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>2I_d = 0.03 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | I was able to rotate these two slabs with with maximum frequencies from the pulser | ||
| + | |||
| + | steps/rev TTL from pulser Disk rotation | ||
| + | 200 1.4 kHz 7 Hz | ||
| + | 200 smooth 1.6 kHz 8 Hz | ||
| + | 400 3.2 kHz 8 Hz | ||
| + | 400 smooth 3.2 kHz 8 Hz | ||
| + | 2000 16.5 kHz 8.25 Hz (TTL frequency increase with small increment.) | ||
| + | 5000 40 kHz 8 Hz | ||
| + | 20000 164 kHz 8.2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | If I go above these these speed, motor stops. To reach highest speed, the TTL pulse should be increased with small increment. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== W disk inertia calculation ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thickness of the disk is 0.04 inch = 1.016 mm. Disk inner diameter is 5.75 inches (0.14605 m) and outer diameter is 14.5 inches (0.3683 m). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Density of tungsten: <math>19.25 ~ g·cm^{−3}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_z~=~\frac{1}{2} \pi \rho h (r_2^4 - r_1^4) = 0.5~\times~3.14~\times~19.25~\times~10^3~kg·m^{-1}~1.016~\times10^{-3}~\times~((0.3683/2~m)^4 - (0.14605/2~m)^4) </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I_z = 0.5*3.14*19.25*10^3*1.016*10^{-3}*((0.3683/2)^4 - (0.14605/2)^4)</math> | ||
| − | + | <math>I_z = 30.70606* (0.00112153384) = 0.0344 </math> | |
Latest revision as of 00:03, 29 September 2012
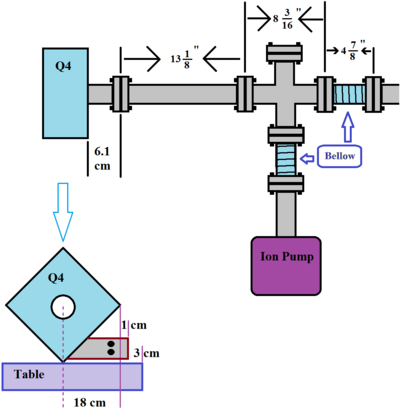
Parts
[More Images ]
Rotary Union
Positron Target Box
The pipe that go through quads has inner diameter: 47.38 * mm
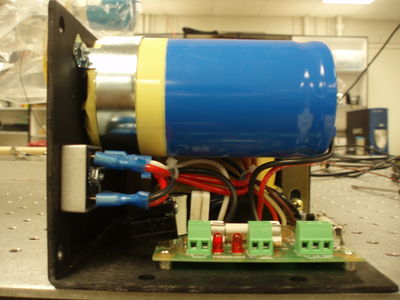
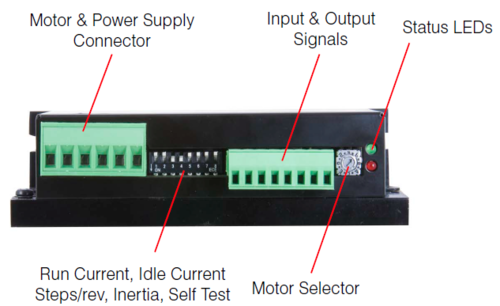
STR8 - Step Motor Drives
Applied Motion Products motor control.
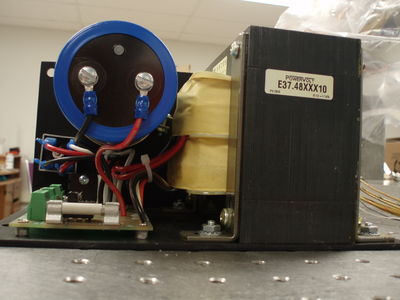
Power Supply
STP-PWR-4810 Power supply for stepping systems, dual output with 48 VDC @ 10A (at full load) unregulated and 5 VDC at 0.5A regulated.
120/240 VAC, 50/60 Hz supply voltage, overcurrent protection.
Document
STR8 Manuals:
Media:STR_Quick_Setup_Guide.pdf
Datasheet:
Media:STR_Brochure_925-0002_RevC.pdf
2D Drawing:
Speed-Torque Curves:
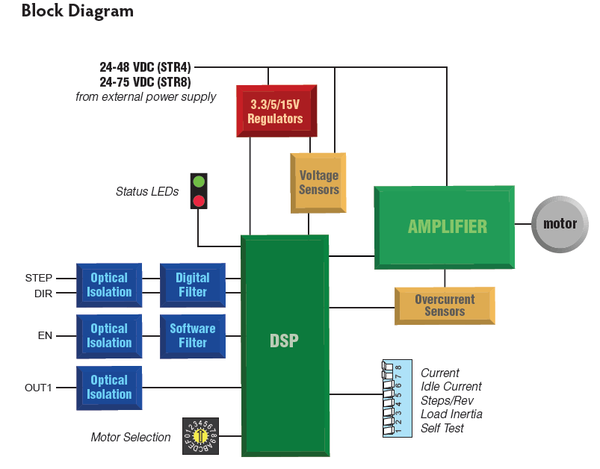
Features
Operates from a 24 to 75 volt DC power supply
Running current up to 7.8 amps per phase
Other Parts needed
1) a 24 to 75 volt DC power supply
2) a source of step signals, such as a PLC or motion controller.
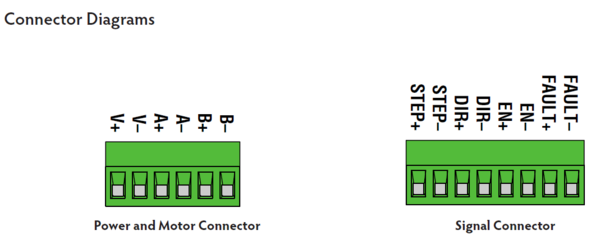
Wire Connection
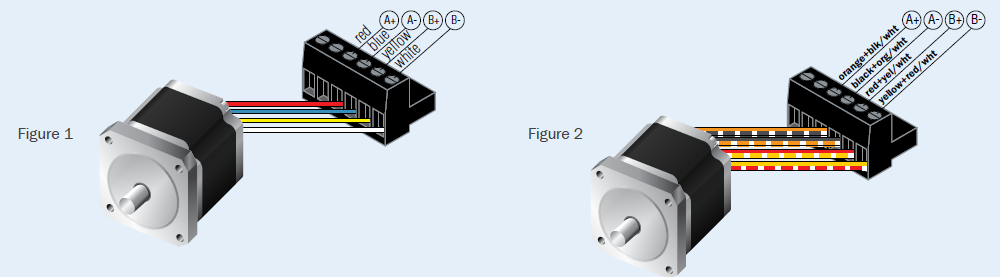
Wiring the Motor
Connect the drive to the motor. Four lead motors can be connected in only one way, as shown in Figure 1. We recommend that eight lead motors be connected in parallel, as shown in Figure 2. If using a non-Applied Motion Products motor, please refer to your motor specs for wiring information.
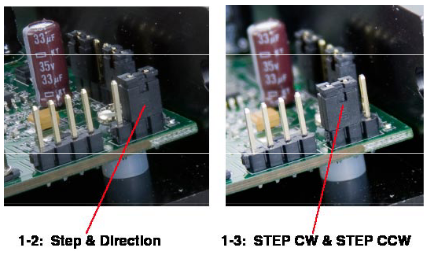
Step Control
Step Pulse Type Most indexers and motion controllers provide motion commands in the “Step and Direction” format. The Step signal pulses once for each motor step and the direction signal commands direction. However, a few PLCs use a different type of command signal: one signal pulses once for each desired step in the clockwise direction (called STEP CW), while a second signal pulses for counterclockwise motion (STEP CCW). The STR drives can accept this type of signal if you remove the drive cover and move jumper S3 from the “1-2” position to the “1-3” position. In STEP CW/STEP CCW mode, the CW signal should be connected to the STEP input and the CCW signal to the DIR input.
Test
Two Al slabs are place to the disk.
Weight of the Al slab is 235 and 240 grams. Their center of mass are 13 +- 1 cm from the center of disk.
Inertia Solid cuboid of height h, width w, and depth d, and mass m:
I was able to rotate these two slabs with with maximum frequencies from the pulser
steps/rev TTL from pulser Disk rotation 200 1.4 kHz 7 Hz 200 smooth 1.6 kHz 8 Hz 400 3.2 kHz 8 Hz 400 smooth 3.2 kHz 8 Hz 2000 16.5 kHz 8.25 Hz (TTL frequency increase with small increment.) 5000 40 kHz 8 Hz 20000 164 kHz 8.2
If I go above these these speed, motor stops. To reach highest speed, the TTL pulse should be increased with small increment.
W disk inertia calculation
Thickness of the disk is 0.04 inch = 1.016 mm. Disk inner diameter is 5.75 inches (0.14605 m) and outer diameter is 14.5 inches (0.3683 m).
Density of tungsten: