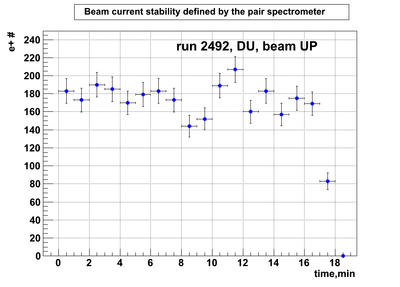
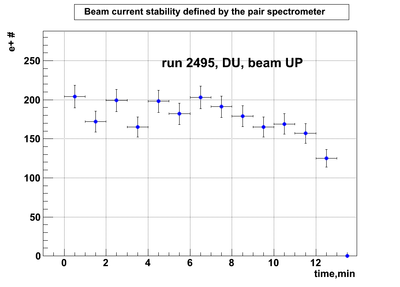
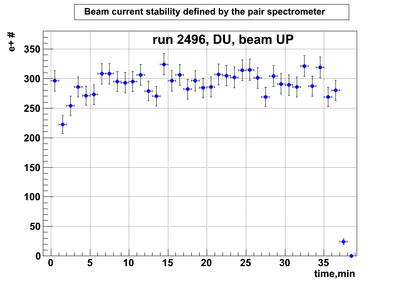
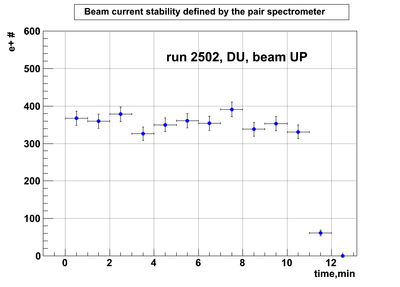
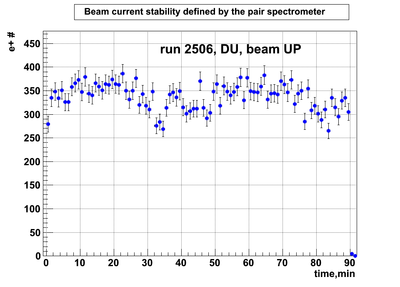
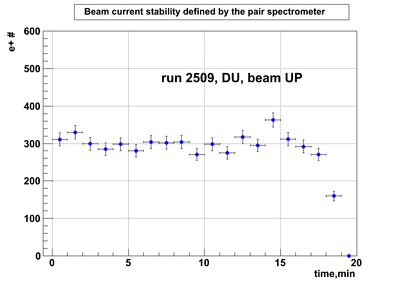
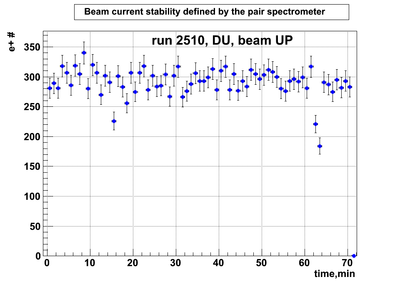
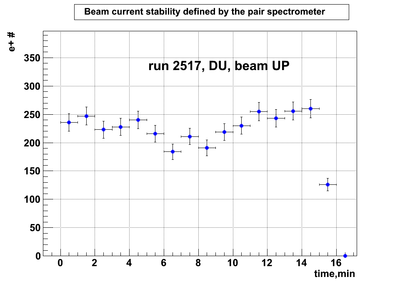
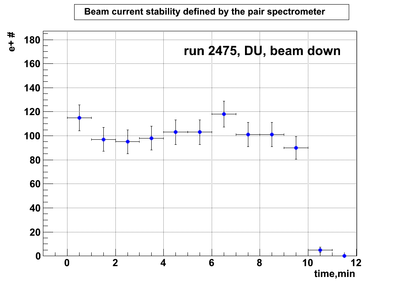
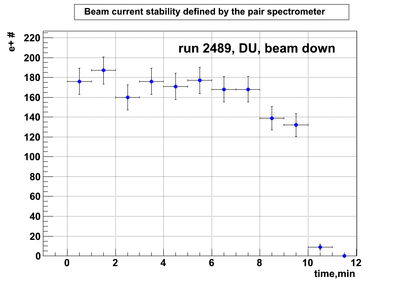
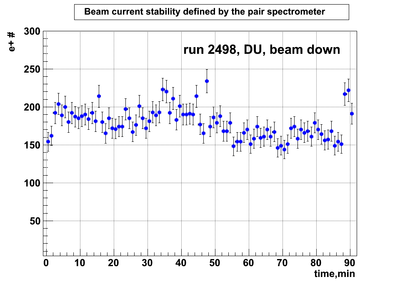
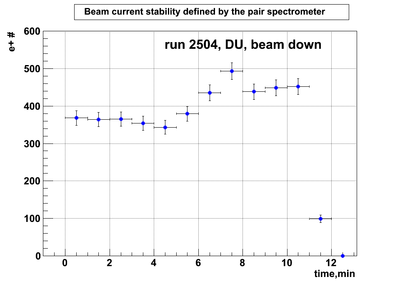
DU data
Current ~ 160 mA
Pulse width ~ 2 ns
Rep rate ~ 180 Hz
Electron energy ~ 25 MeV
Two thicknesses of Al brem radiator were used (A) 10 um for 10% of the beam time, (B) 25 um for 90% of the beam time.
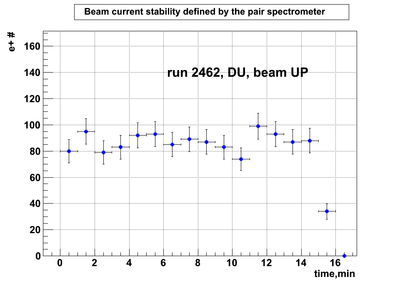
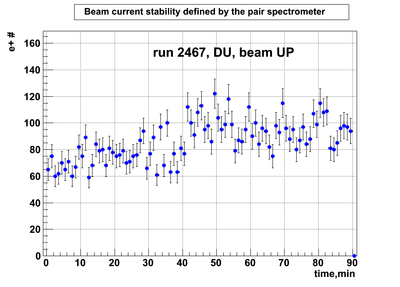
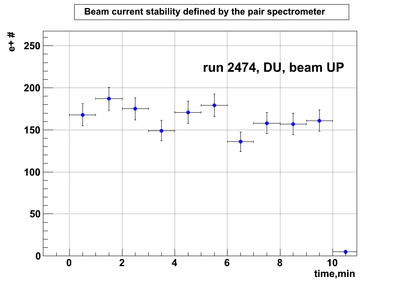
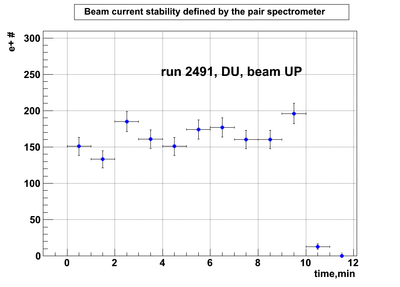
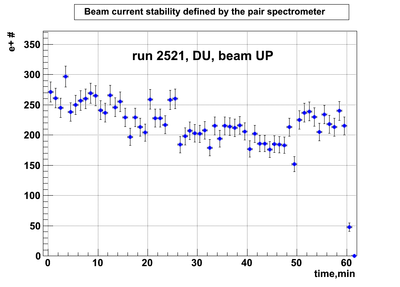
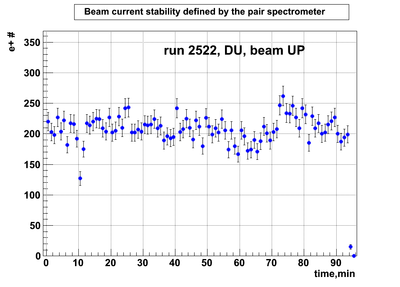
Relative photon flux monitoring. Beam up. DU target
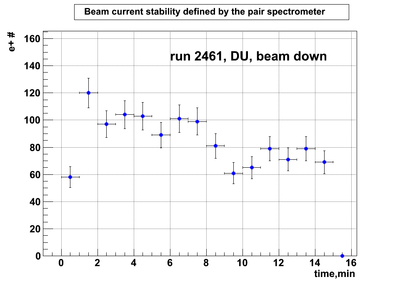
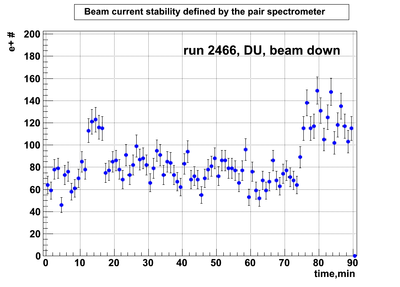
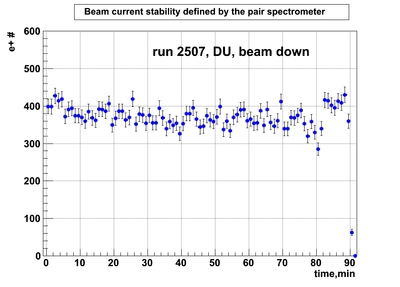
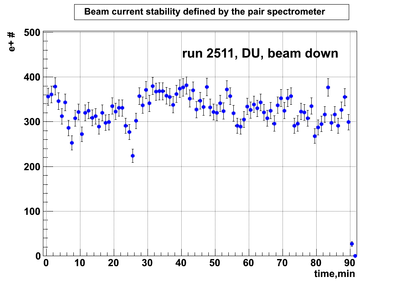
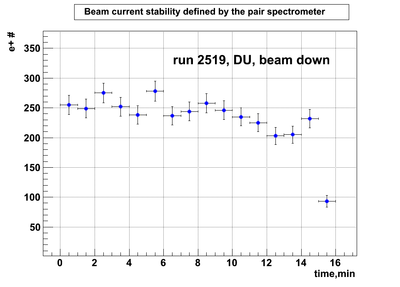
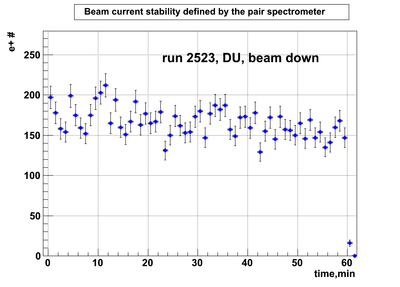
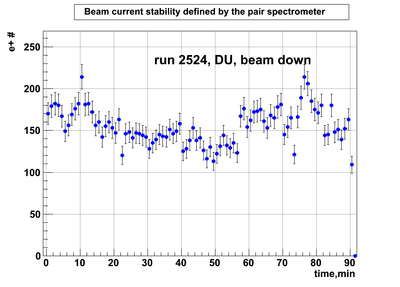
Relative photon flux monitoring. Beam down. DU target
Beam UP configuration
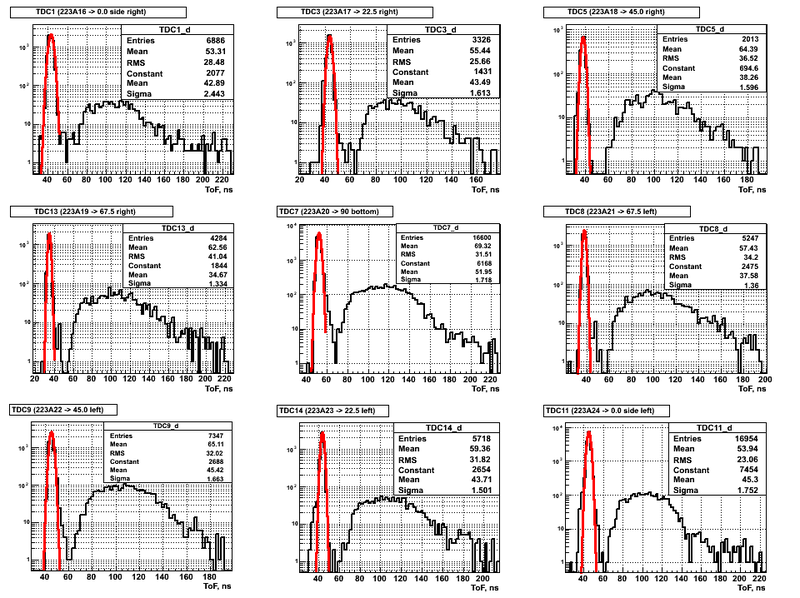
Cumulative raw ToF spectra obteined for the case of DU target and beam UP position are presented below:
The width of the photon peak (sigma) shows the IAC linac pulse width at it was mentioned above it was around 2 ns.
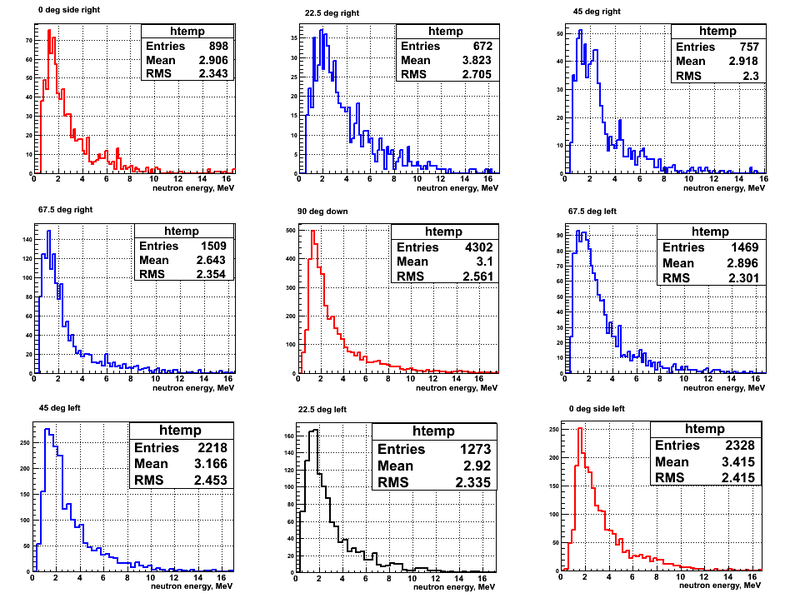
Neutron energy spectra reonstructed from the ToF spectra for the beam UP and DU are shown below:
The neutron detectors was placed azimuthally symmetric around the target so the distance was 135.5 cm from the center of the target to the face of each of the detector.
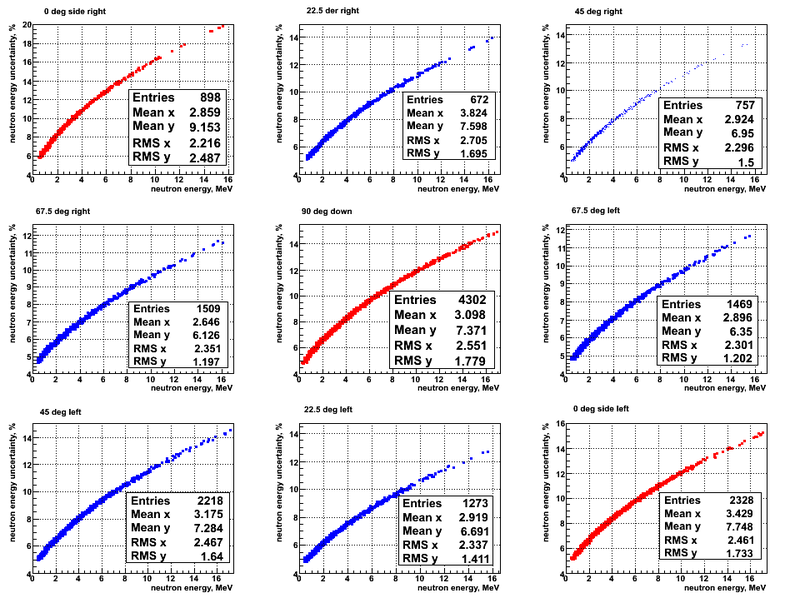
The uncertainty on the neutron energy depends mostly on the knowledge of the photon peak center position. The width of the photon peak gives an uncertainty in the neutron energy.
The energy uncertainty for the beam UP and DU target are shown below:
Beam DOWN configuration
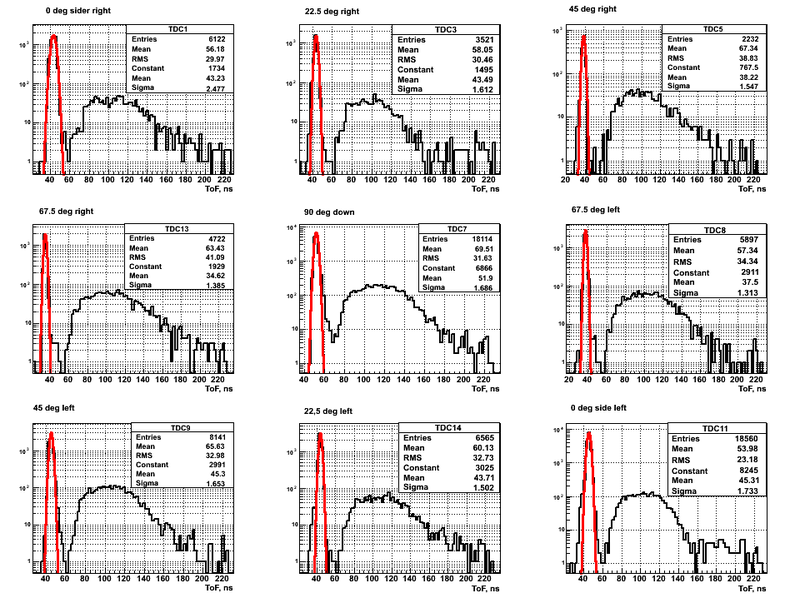
Cumulative raw ToF spectra obteined for the case of DU target and beam DOWN position are presented below:
The width of the photon peak (sigma) shows the IAC linac pulse width at it was mentioned above it was around 2 ns.
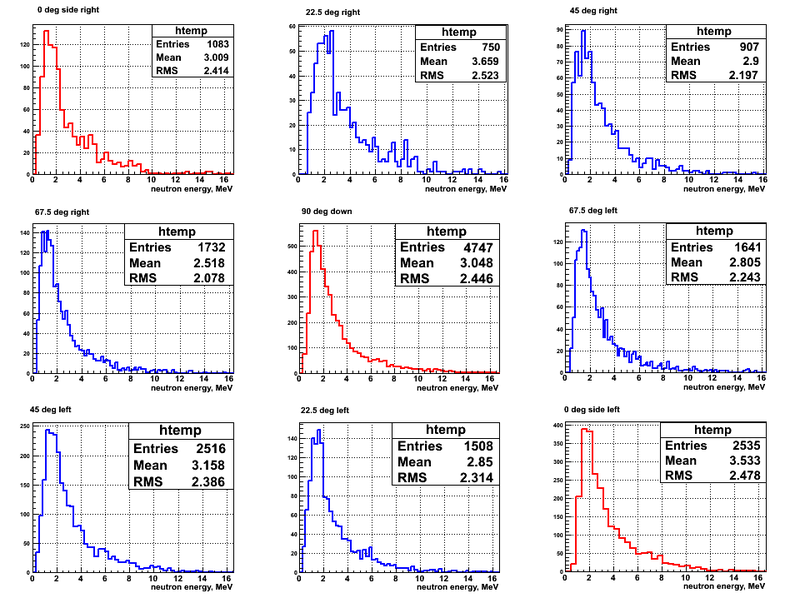
Neutron energy spectra reonstructed from the ToF spectra for the beam DOWN and DU are shown below:
The neutron detectors was placed azimuthally symmetric around the target so the distance was 135.5 cm from the center of the target to the face of each of the detector.
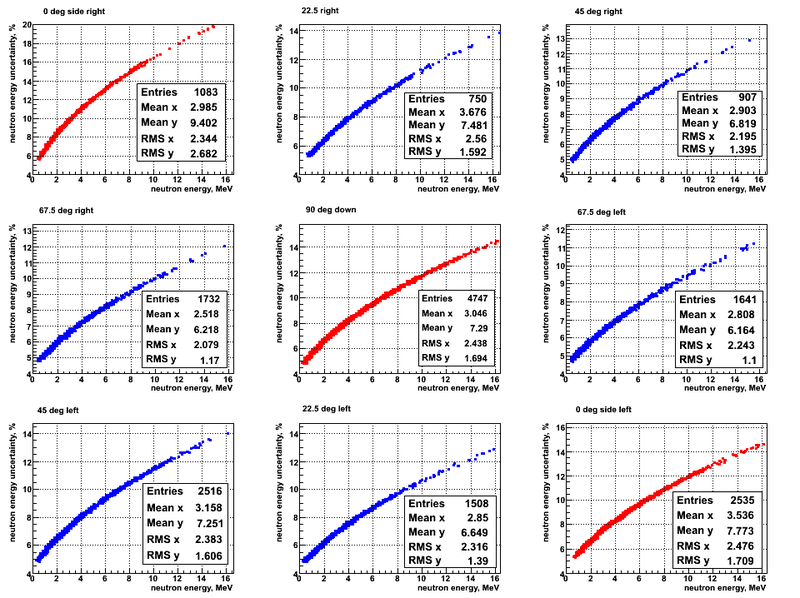
The uncertainty on the neutron energy depends mostly on the knowledge of the photon peak center position. The width of the photon peak gives an uncertainty in the neutron energy.
The energy uncertainty for the beam DOWN and DU target are shown below:
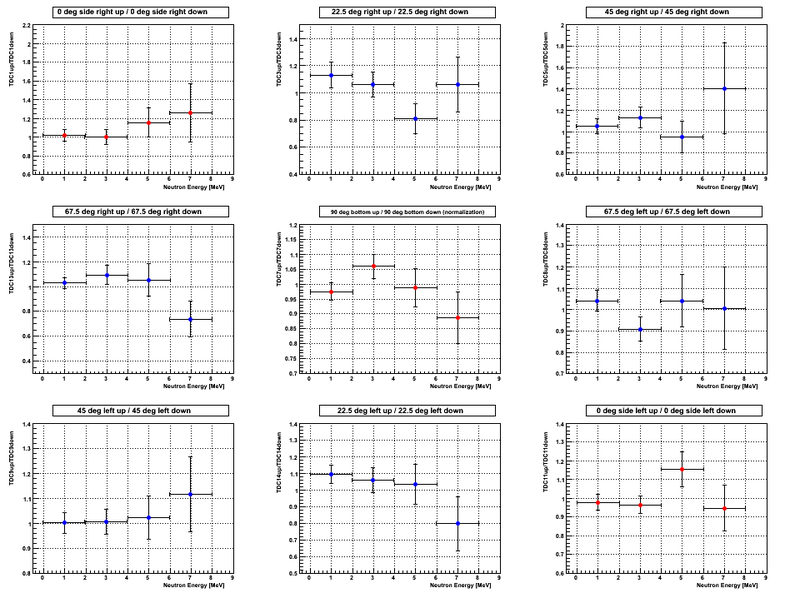
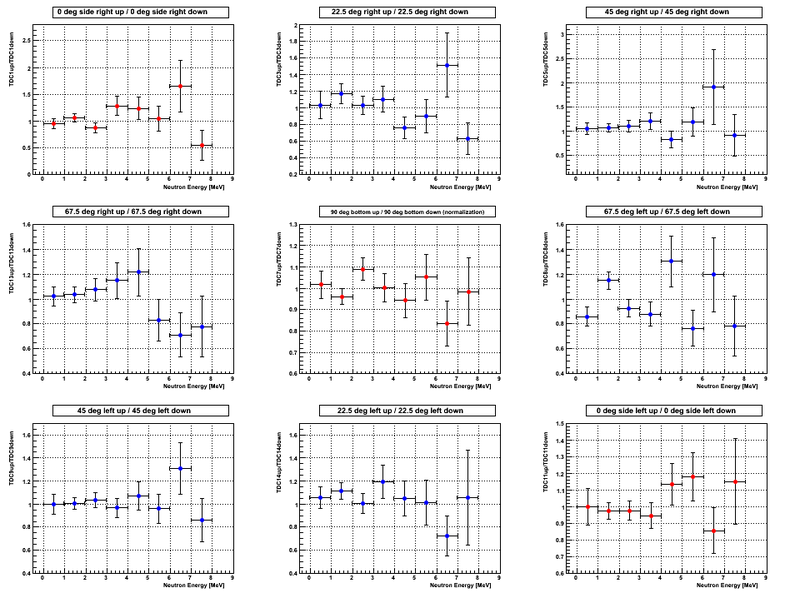
Asymmetry. 4 channel binning of the neutron energy spectrum
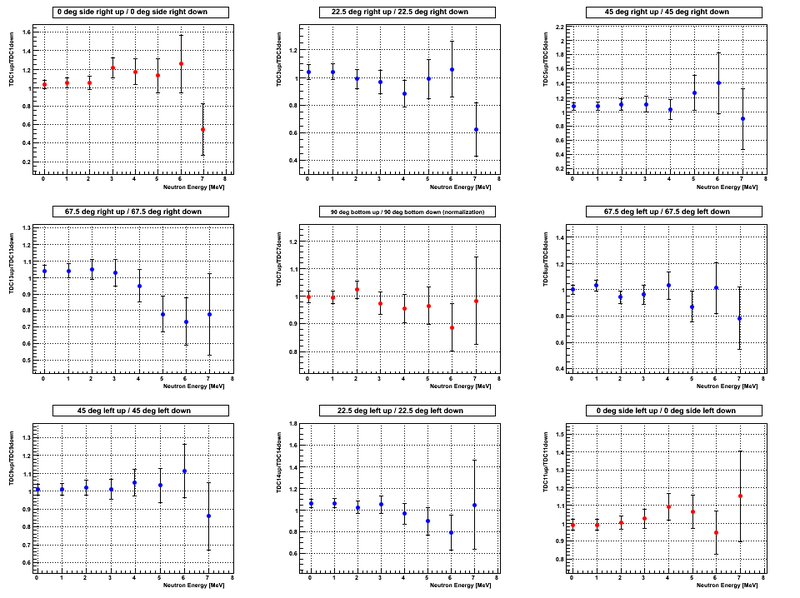
The sum of the number of neutrons in three detectors placed at 0 deg left, 90 deg bottom and 0 deg right was used to do the narmalization for both beam UP and DOWN configurations, i.e. the procedure that takes into account possible photon flux change. For the justification of the normalization procedure see [1]
Asymmetry. 8 channel binning of the neutron energy spectrum
Running asymmetry. High-to-low neutron energy binning
The asymmtry was measured starting with 8 MeV as a maximum bin number and then adding 1 MeV the asymmetry was measured for the whole neutron energy spectrum finally (point at zero MeV)