[math]\underline{\textbf{Navigation}}[/math]
[math]\vartriangleleft [/math]
[math]\triangle [/math]
[math]\vartriangleright [/math]
Scattering Amplitude
In the Møller scattering [math](\mathbf P_{1} + \mathbf P_{2} \rightarrow \mathbf P_{1}^{'} + \mathbf P_{2}^{'})[/math] we have identical particles in the initial and final states. This that the amplitude to be symmetric under interchange of particles [math](\mathbf P_{1}^{'} \leftrightarrow \mathbf P_{2}^{'} [/math] or [math] \mathbf P_{1} \leftrightarrow \mathbf P_{2})[/math]. Due to this symmetry we can determine two 1st level Feynman diagrams to describe this scattering.
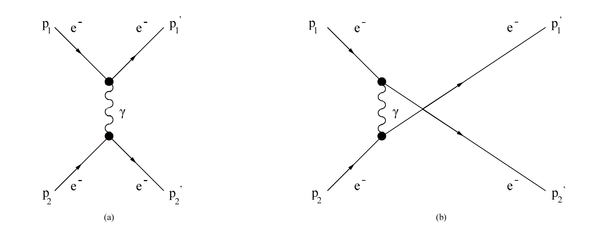
The amplitudes of the individual Feynman diagrams add linearly to form the total amplitude
[math]\mathfrak{M}=\mathfrak{M}_{1}+\mathfrak{M}_{2}[/math]
Using the Feynman rules, each vertex contribute a factor
[math]ie(\mathbf p_{initial} + \mathbf p_{final})^{\mu}[/math]
and the propagator gives
[math] \frac{−ig_{\mu \nu}}{q^2}[/math]
where q is the momentum of the photon
[math]q \equiv \mathbf p_{final}-\mathbf p_{initial}[/math]
and [math]g_{\mu \nu}[/math] is the Mandelstam metric which allows the transformation from the contravariant to covariant form needed for tensor multiplication. Examining both Feynman diagrams seperately, we find for their individual amplitudes
[math]-i \mathfrak{M}_{1}=ie\left(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'}\right)^{\mu} \left(\frac{-ig_{\mu \nu}}{q^{2}} \right) ie \left( \mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'}\right)^{\nu} \qquad \qquad -i \mathfrak{M}_{2}=ie\left(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'}\right)^{\mu} \left(\frac{-ig_{\mu \nu}}{q^2} \right) ie \left( \mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'}\right)^{\nu}[/math]
[math]-i \mathfrak{M}_1=ie(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'})^{\mu} \left (\frac{-ig_{\mu \nu}}{(\mathbf p_{2}^{'}-\mathbf p_{2})^{2}} \right ) ie( \mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'})^{\nu} \qquad \qquad -i \mathfrak{M}_{2}=ie(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'})^{\mu} \left (\frac{-ig_{\mu \nu}}{(\mathbf p_{1}^{'}-\mathbf p_{2})^{2}} \right ) ie( \mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'})^{\nu}[/math]
[math]-i \mathfrak{M}_{1}=ie^{2}\left (\frac{\left(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'}\right)_{\mu} \left(\mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'}\right)^{\mu}}{\left(\mathbf p_{2}^{'}-\mathbf p_{2}\right)^{2}} \right ) \qquad \qquad -i \mathfrak{M}_{2}=ie^{2}\left (\frac{\left(\mathbf p_{1}+\mathbf p_{2}^{'}\right)_{\mu} \left(\mathbf p_{2}+\mathbf p_{1}^{'}\right)^{\mu}}{\left(\mathbf p_{1}^{'}-\mathbf p_{2}\right)^{2}} \right ) [/math]
Without loss of generality, we can extend this to the center of mass frame
[math]-i \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}=-ie^2 \left ( \frac{(\mathbf p_1^*+\mathbf p_{1}^{'*})_{\mu}(\mathbf p_2^*+\mathbf p_{2}^{'*})^{\mu}}{(\mathbf p_{2}^{'*}-\mathbf p_2^*)^2}- \frac{(\mathbf p_1^*+\mathbf p_{2}^{'*})_{\mu}(\mathbf p_2^*+\mathbf p_{1}^{'*})^{\mu}}{(\mathbf p_{1}^{'*}-\mathbf p_2^*)^2} \right )[/math]
[math] \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}= e^2\left ( \frac{\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+\mathbf P_{1}^{'*} \mathbf P_{2}^{'*}+\mathbf P_{1}^{'*} \mathbf P_2^*+\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_{2}^{'*}}{(\mathbf P_{2}^{'*}-\mathbf P_2^*)^2}- \frac{\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+\mathbf P_{2}^{'*} \mathbf P_{1}^{'*}+\mathbf P_{2}^{'*} \mathbf P_2^*+\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_{1}^*}{(\mathbf P_{1}^{'*}-\mathbf P_2^*)^2} \right )[/math]
Using the fact that [math]\mathbf P_1^{'*} \mathbf P_2^{'*}=\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^* \quad \quad \mathbf P_1^{'*} \mathbf P_1^{*}=\mathbf P_2^{'*} \mathbf P_2^* \quad \quad \mathbf P_1^{*}
\mathbf P_2^{'*}=\mathbf P_2^* \mathbf P_1^{'*}[/math]
[math] \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}= e^2\left ( \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_{1}^{'*} \mathbf P_2^*}{(\mathbf P_{2}^{'*2}-2\mathbf P_{2}^{'*}\mathbf P_2^{*}+\mathbf P_2^{*2})}- \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_{1}^{'*}}{(\mathbf P_{1}^{'*2}-2\mathbf P_{1}^{'*}\mathbf P_2^{'*}+\mathbf P_2^{'*2})} \right )[/math]
[math] \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}= e^2\left ( \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_{1}^{'*} \mathbf P_2^*}{(\mathbf P_2^{*2}-2\mathbf P_2^{*}\mathbf P_{2}^{'*}+\mathbf P_{2}^{'*2})}- \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_{1}^{'*}}{(\mathbf P_2^{'*2}-2\mathbf P_2^{'*}\mathbf P_{1}^{'*}+\mathbf P_{1}^{'*2})} \right )[/math]
[math] \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}= e^2\left ( \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_{1}^{'*} \mathbf P_2^*}{(\mathbf P_2^*-\mathbf P_{2}^{'*})^2}- \frac{2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+2\mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_{1}^{'*}}{(\mathbf P_2^{'*}-\mathbf P_{1}^{'*})^2} \right )[/math]
[math] \mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}= e^2\left ( \frac{ (\mathbf P_1^{*2}-2 \mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^{'*}+ \mathbf P_2^{'*2})-(\mathbf P_1^{*2}+2 \mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+ \mathbf P_2^{*2})}{t}- \frac{(\mathbf P_1^{*2}-2 \mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_1^{'*}+ \mathbf P_1^{'*2})-( \mathbf P_1^{*2}+2 \mathbf P_1^* \mathbf P_2^*+ \mathbf P_2^{*2})}{u} \right )[/math]
[math]\mathfrak{M}_{e^-e^-}=e^2 \left (\frac{u-s}{t}+\frac{t-s}{u} \right )[/math]
[math]\underline{\textbf{Navigation}}[/math]
[math]\vartriangleleft [/math]
[math]\triangle [/math]
[math]\vartriangleright [/math]
