Difference between revisions of "TF IsotopeTracers"
| Line 133: | Line 133: | ||
===Medical isotopes=== | ===Medical isotopes=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2013 DOE Medical Isotope program budget and info | ||
| + | |||
| + | http://science.energy.gov/~/media/budget/pdf/sc-budget-request-to-congress/fy-2013/Cong_Budget_2013_IsoptopeProductionandDistributionProgramFunding.pdf | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
2010 Talk on Future Isotope needs in medicine and industry | 2010 Talk on Future Isotope needs in medicine and industry | ||
Revision as of 06:12, 3 December 2012
MRI RFP
http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2013/nsf13517/nsf13517.htm
Highlights.
"MRI is not used to buy a suite of insturments to outfit research laboratories/facilities or be used to conduct independent research activities simultaneously".
"MRI is used for a single insturment or when combined serves as an integrated instrument."
The photon flux monitor when combined with the rabbit will be an instrument for both isotope production and PAA analysis research. The tool will have inter-disciplinary uses ranging from engineering to archeology.
- Track1
- Acquisition of a single instrument
- Track2
- development of a single instrument or for equipment that when combined serves as an integrated instrument.
We will be track 2. The combined equipment will be an integrated instrument for the production of Isotopes to be used in research and industry. The devise will also be an instrument for PAA analysis.
Proposal
Purpose
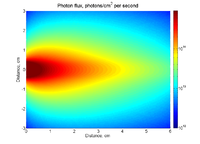
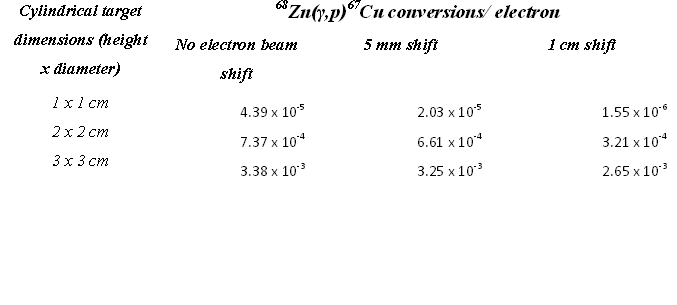
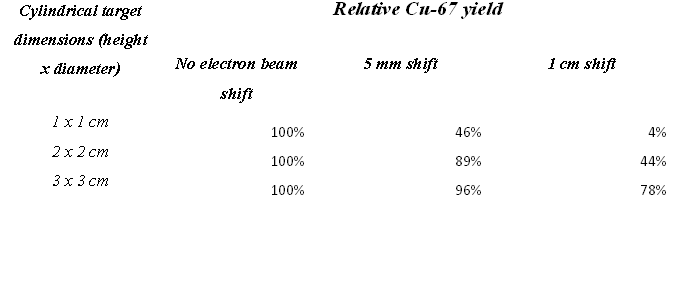
In June of 2012, the Idaho Accelerator Center received a grant from the state of Idaho as part of the Idaho Global Entrepreneurial Mission (IGEM) program. One of the proposed objectives was to research the use of an electron accelerator to the produce Copper isotopes to be used in medical diagnostic procedures. Preliminary results of the work sponsored by this research have indicated that the production of Copper isotopes strongly depends on the alignment of incident radiation to the sample. While a sample size of 2 cm may produce the highest number of isotopes per volume, a missalignment of more than a centimeter may reduce the amount of isotopes produced by a factor of at least two. A strong need now exists for a system to monitor the spatial distribution of the photons used to irradiate the samples. Based on these results, we propose the development of an irradiation instrument, that qualifies for the MRI category "Track 2", to be used for isotope production and PAA analysis.
The proposed instrument will be composed of a photon beam monitoring system and a sample conveyor. Support from this MRI will be used to construct the photon monitoring system. Matching support from the IGEM project will be used for the sample conveyor system. The conveyor, commonly referred to as a rabbit, will transport samples into the irradiation region and then to a shielded container (lead pig) after irradiation. The transportation system is a necessity due to the high activity isotopes that may be produced. When used as an instrument for PAA, the transportation system will eliminate the step of shutting the accelerator off in order to change to the control sample thereby risking a change in the experimental conditions whose uniformity is essential for meaningful measurements. Once calibrated, the photon monitoring system would allow users to irradiate sample with a known amount of radiation.
The proposed instruments ability to enhance the production of copper isotopes for medical diagnostic tests is only one potential use. Isotope production in the US is a $$$ busines..
Paragraph of the instruments impact on the production of isotopes.
Using the instrument for PAA and the large potential user base.
The University of Missouri's Research Reactor is a current producer of medical isotopes with a total operating budget o
Talking points
1.) The accelerator "Jack" is an instrument for PAA and isotope production
2.) Isotope production impact on other areas of research (medical, fracking, underground pipelines, spikants for homeland security)
3.) Inter organizational use of PAA ( Geology, Archeology, certification for coffee origins....)
4.) Impact of Photon Flux monitoring for PAA analysis
5.) Device will train accelerator physicists, nuclear chemists, ...
Budget
Equipment list
two steps
1.) purchase 16, single crystal detectors from http://www.npl.co.uk/upload/pdf/091104_nuc_galbiati.pdf. These will serve as monitors distributed symmetrically around the beam line and used to steer the electron beam until equal photon rates are observed => centered photon beam.
2.) A wire tungsten wire coated with diamond will sweep through the photon beam in the location of the target to measure the photon flux.
get http://www.npl.co.uk/upload/pdf/091104_nuc_galbiati.pdf to build a pixelated 3 x 3 cm detector with .5 x .5 cm size pixels (36 pixels)
OR if the photon flux is too high construct a wire array.
| Cost | Device | Purpose |
| 50,000 | BPMs | 4 electron beam position monitors |
| 20,000 | 16, CVD Diamond detector | Off the shelf single crystal single pixel detector pg 49 in[ http://www.npl.co.uk/upload/pdf/091104_nuc_galbiati.pdf] |
| 10,000 | 20 , 5 x 5 mm^2 CVD films | films for pixel detector array or wire (tungsten coated with diamond) scanner |
| 10,000 | Circuitry | PCB board, connectors, and single crystal mounting by external vendor |
| 30,000 | beam time | 3 weeks of beam time to test device and measure performance |
| $28,000 | DAQ | VME based DAQ system with EPICs monitoring, 32 channel ADC ($6k), ROC($3k), MiniCrate($4k), Server ($2k), Tigger supervisor ($3k), NIM Discriminator /Trigger/ECL output module ($10k) |
| $10k Cost Share | Beam Line components | Steering coils ($1k), power supplies ($4k), and Beam line components($5k) to install BPMs |
| $160k Cost Share | Rabbit | sample conveyor system from IGEM grant |
- Proposed Budget
- $148k + $160k (Cost share) = $308k
References
Nitrogen tracers: N-15 is rare. If you dope nitrogen sources with it you can see where the leak into environment. This is a stable tracer so it would be able to monitor long time plume expansions.
Catchment hydrology
Review of Diamond detectors
http://www.ifh.de/~akg/phys/tapper.pdf
Simulations
http://www.osti.gov/energycitations/product.biblio.jsp?query_id=1&page=0&osti_id=20658046
High Flux MeV photon profiler
http://accelconf.web.cern.ch/accelconf/p99/PAPERS/WEA90.PDF
http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/ielx5/5379507/5398121/05398374.pdf?tp=&arnumber=5398374&isnumber=5398121
CVD Diamond film
Film Vendor only
http://www.e6cvd.com/cvd/page.jsp?pageid=415
Alemeda Applied Sciences Corporation
http://www.aasc.net/drds http://www.aasc.net/media/DRD-AppNote.pdf
Diamond x-ray view screen http://www.diamond-materials.com/EN/products/cvd_for_xray/fluorescence_beam_monitors.htm
http://www.npl.co.uk/upload/pdf/091104_nuc_galbiati.pdf
NIM paper from 2002
http://144.206.159.178/ft/787/47160/14168748.pdf
Diamond Detectors LtD (Vendor for single crystal Chip on Board Package)
http://www.npl.co.uk/upload/pdf/091104_nuc_galbiati.pdf
Medical isotopes
2013 DOE Medical Isotope program budget and info
2010 Talk on Future Isotope needs in medicine and industry
http://www.nscl.msu.edu/~mantica/radio-frib/runde-acsboston.pdf
Need Mo-99, Tc-99m, I-131, I-125, Cu-67, At-211, Ac-225, Bi-213, Am-241, Gd-148, Sr-90, Pm-147
A big isotope supplier is Eckert & Ziegler
http://www.ezag.com/fileadmin/ezag/user-uploads/pdf/analyses-englisch/concord_e_01.pdf
2009 Medical Isotope industry & trade study
http://www.usitc.gov/publications/332/ITS-1.pdf