Difference between revisions of "DeltaDoverD Progress"
| Line 197: | Line 197: | ||
Rebin asymmetry hisograms and combine the two into a total asymmetry histogram | Rebin asymmetry hisograms and combine the two into a total asymmetry histogram | ||
| + | |||
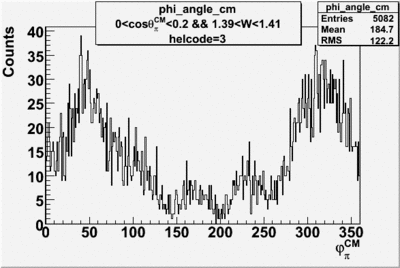
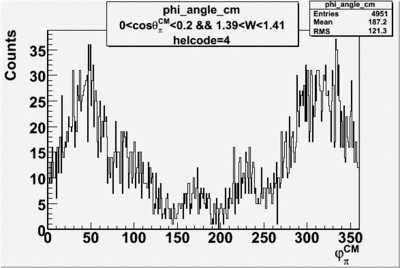
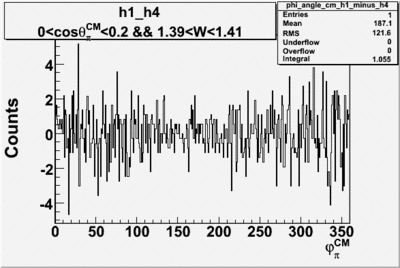
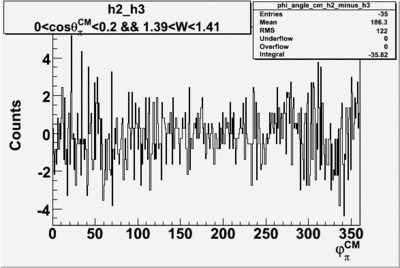
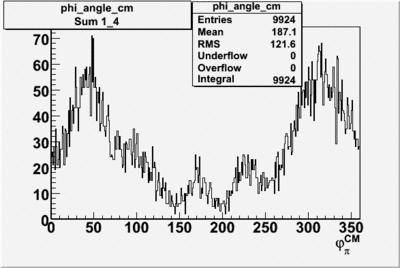
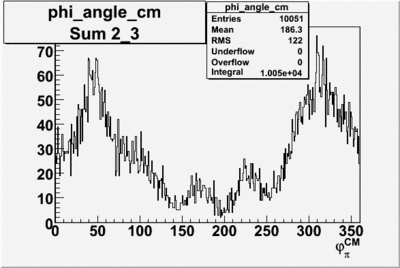
| + | ==Phi_Angle_CM_Frame for Positive and Negative Target Polarization== | ||
[http://www.iac.isu.edu/mediawiki/index.php/Delta_D_over_D Go Back] | [http://www.iac.isu.edu/mediawiki/index.php/Delta_D_over_D Go Back] | ||
Revision as of 01:06, 24 November 2008
9/5/08
SIDIS Analysis
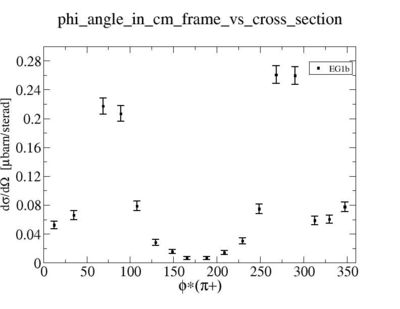
a.) Cross-Section comparison
i.) Calculate absolute cross section for = 0.5, 1 < Q^2 < 4 GeV^2 , W = 1.45 +/- 0.2 GeV
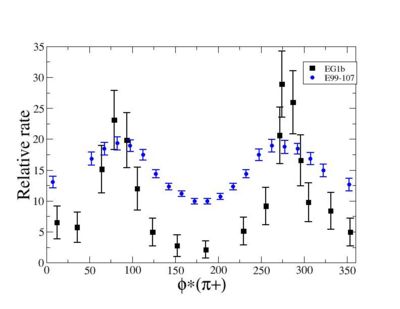
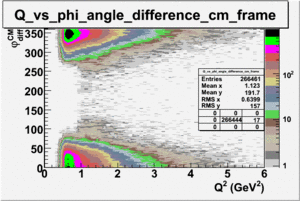
ii.) Plot -vs- when = -0.3 also plot -vs-
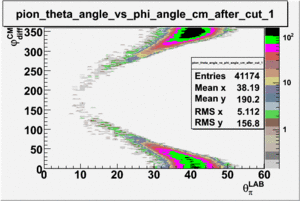
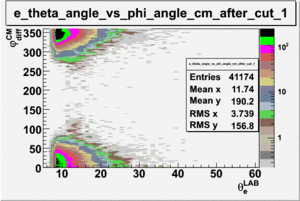
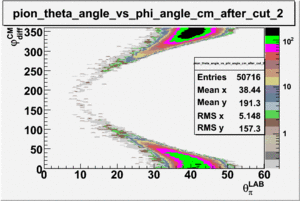
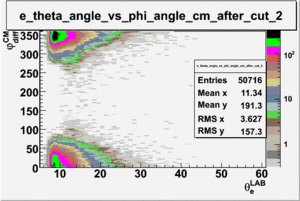
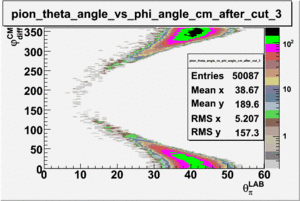
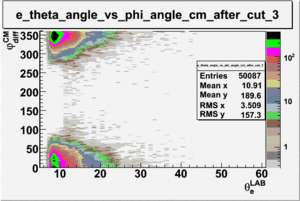
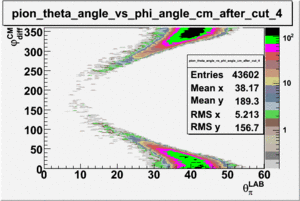
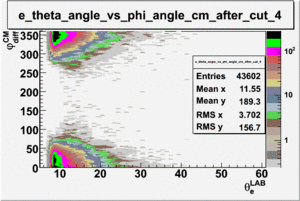
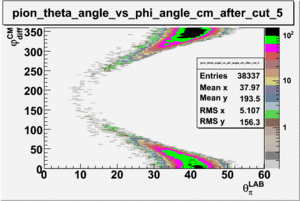
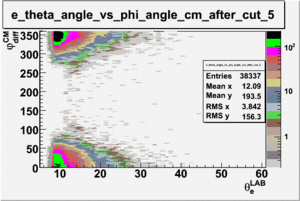
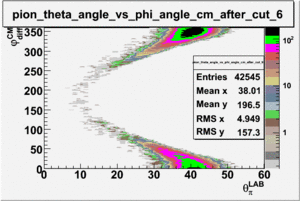
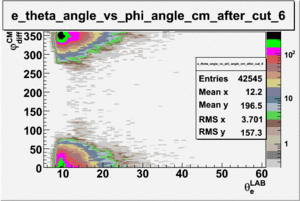
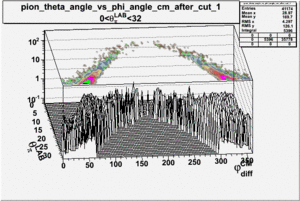
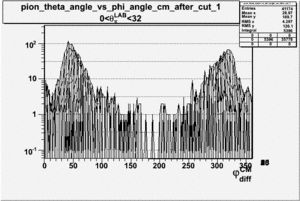
As one can see from histograms of the pion_theta_angle_vs_phi_angle_in_CM_Frame and the electron_theta_angle_vs_phi_angle_in_CM_Frame, the pion and electron acceptance in the region of is nearly zero(significantly low).
_vs_ plot shows that the cut should not make much difference on plot. The cut around should reduce the number of pions around 0 and 360 of phi angle.
9/19/08
SIDIS Analysis
a.) Cross-Section comparison
i.) Calculate absolute cross section for = 0.5, 1 < Q^2 < 4 GeV^2 , W = 1.45 +/- 0.2 GeV
?
- Documentation
The five-fold differential cross section for single pion production is equal to the following:
The Jacobian term can be given as:
where is the virtual photon flux and can be written as
The reason of having low cross section might be binning
In paper they use the following number of bins:
| Variable | Num. Bin | Range | Bin Size |
| W | 27 | 1.15 - 1.7 GeV | 20 MeV |
| 7 | 1.1 - 5.0 | variable | |
| 10 | -1.0 - 1.0 | 0.2 | |
| 24 | -180. - 180 | 15 |
Number of bins in my case were 360.
Number of bins equal is ~24
When i applied cut, the number of entries were reduced to 152.
In paper they use liquid-hydrogen unpolarized target(we have NH3 and ND3 polarized). The polarized electron beam current is 8 nA(in our case it is about 6 nA). and luminosity is different too. It also depends on statistics.
ii.) What is smallest angular coverage of EC (8 degrees?) Determine phi region where there is no acceptance ( where should we stop plotting data)?
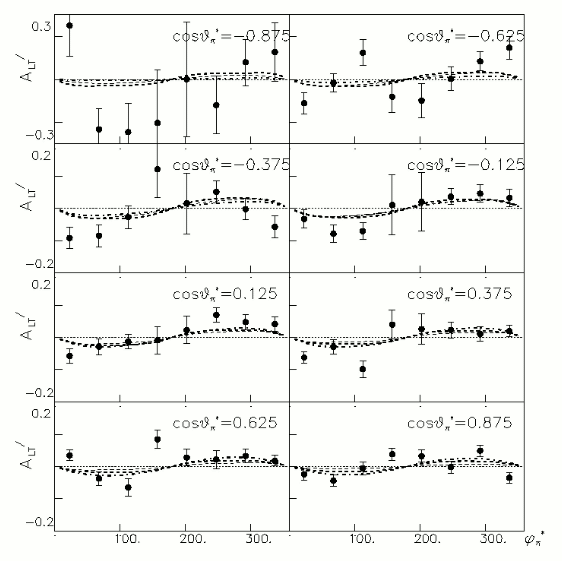
iii.) Asymmetry Calculation
a.) Beam Asymmetry Plot
In order to plot Beam Asymmetry we need to plot for the first time the histogram of the invariant_mass_vs_cross_section. Then determine the structure function fitting the cross section and calculating the beam asymmetry function which is given as :
for given cos(theta) of the pion in cm, Q^2 and W invariant mass.
Choose kinematics ( a single theta and phi point )to max our stats and comparison to paper Histogram the following
- Number of e-pi coincidence events, number of FC counts
- Number of e-pi coincidence events/FC counts
- Number of e-pi coincidence events/FC count/Pt
for groups of runs with h_e,P_t = ++, +-, -+, --
table with 4 columns of h_e, P_t and 3 rows of the above histograms
9/26/08
SIDIS Analysis
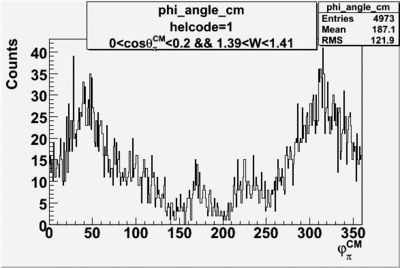
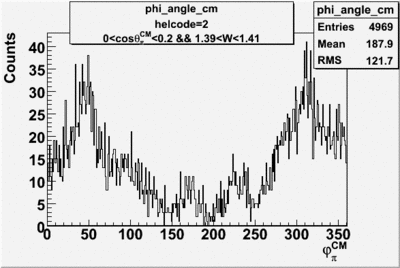
1.) make semi-inclusive spectrum:
a.) h>0 Pt>0 b.) h > 0 pt<0 c.)h<0 pt>0 d.)h<0 pt<0
2.) ad up opposite target polarization histograms
3.) subtract h> 0 and h<0
helflag = 1 =>
helflag = 2 =>
helflag = 3 =>
helflag = 4 =>
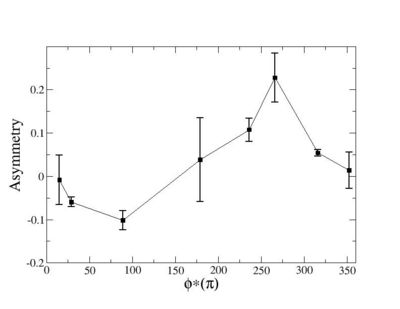
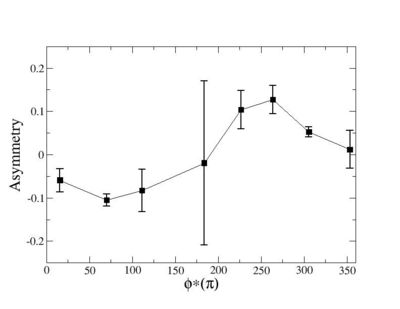
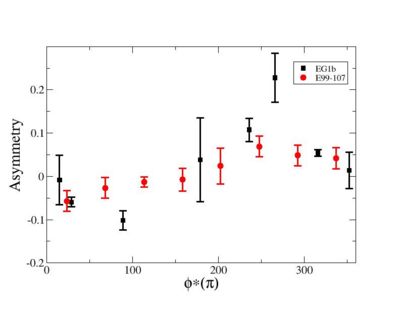
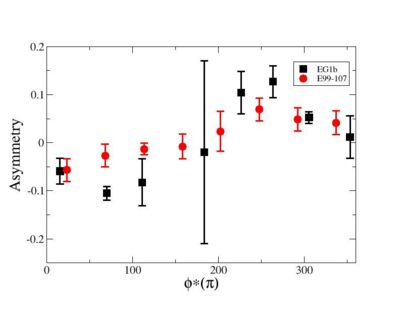
Phi_angle_CM vs Asymmetry
Compared data(there is no table for asymmetry values like cross section):
11/21/08
0.) insert run summarry table, Pb, Pt, PB*Pt, Btorus
1.) make semi-inclusive spectrum:
a.) h>0 Pt>0
b.) h > 0 pt<0
c.)h<0 pt>0
d.)h<0 pt<0
2.) helicity difference plots for Pt>0 and Pt<0
3.) Asym plots for Pt>0 and Pt< 0
4.) unpolarized target asymmetry
Rebin asymmetry hisograms and combine the two into a total asymmetry histogram