Difference between revisions of "Comparison of GEANT Simulation to Whitney Data"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (25 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
| − | {| | + | {| align=center border=1 |
|+ '''Rates''' | |+ '''Rates''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | + | ! Simulation || GEANT4(1cm target) ||GEANT4(1cm target)|| GEANT4(5cm target) || GEANT4(5cm target) || Whitney | |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Length of Target (cm) || 1 || 1 || 5 ||5 ||5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <math>N_{incident}(Total)</math> || 4E7 ||4E8 || 6E6 ||6E7 || 6E7 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <math>N_{events}(Total)</math> || 1026940 || 10270829|| 771161 ||4826141 || 1001700 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <math>N_{events}(5^{\circ}-40^{\circ})</math> || 305570 || 3054080|| 229266|| || |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <math>N_{Moller}(Total)</math> || 975593 || 9757288|| 732603||4584834 || 951138 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | N_{ | + | | <math>N_{Moller}(5^{\circ}-40^{\circ})</math> ||290291 || 2901376|| 217803|| 1362098|| |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | <math>t_{simulated}(Total)</math> (s) || 1.3E-5 ||1.3E-4 || 9.57E-6||9.62E-5 ||9.54E-5 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | Total Event Cross-Section (b) || 0.61 || 0.61|| 0.61 ||0.38 || 0.079 |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Total Moller Cross-Section (b) || 0.58||0.58 || 0.58 ||0.361 || 0.075 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Detector Event Cross-Section (b) || 0.18 || 0.18|| 0.18 || || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Detector Moller Cross-Section (b) ||0.17 ||0.17 ||0.17 || || | ||
|} | |} | ||
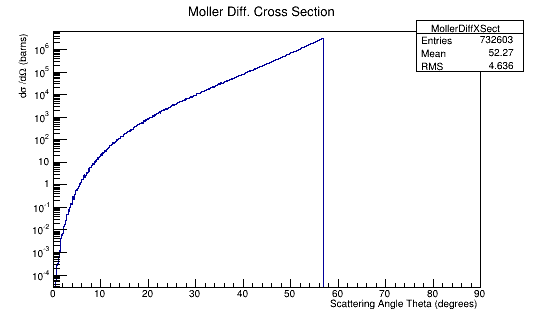
Total dectector events occur for about 2.5% of the incident electrons on a LH2 target. We can assume that the Moller rate is 95% of the total event rate. We can assume the number of Moller events that occur within the DC range to be around 30% of the total Moller events occuring for the number of incident electrons for LH2 as well. Since the differential cross-section over the angel theta is proportional to the differtial cross-section over wire number we can dividing the Moller differential cross-section by the product of the density and length of the target material | Total dectector events occur for about 2.5% of the incident electrons on a LH2 target. We can assume that the Moller rate is 95% of the total event rate. We can assume the number of Moller events that occur within the DC range to be around 30% of the total Moller events occuring for the number of incident electrons for LH2 as well. Since the differential cross-section over the angel theta is proportional to the differtial cross-section over wire number we can dividing the Moller differential cross-section by the product of the density and length of the target material | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Cross_Section.png]] | ||
| + | |||
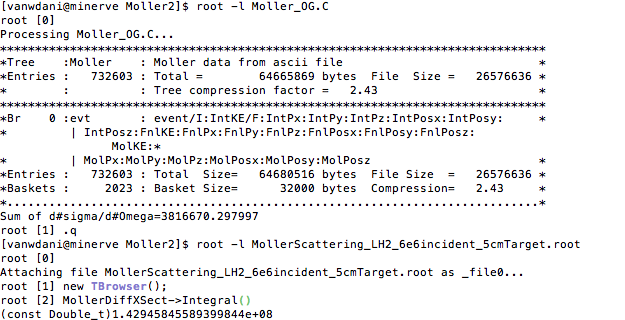
| + | If we were to integrate the Moller Differential Cross Section | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:6e7incLH2_MolDiffXSect.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Screen_Shot_2018-03-29_at_8.57.34_AM.png]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:21, 30 March 2018
| Simulation | GEANT4(1cm target) | GEANT4(1cm target) | GEANT4(5cm target) | GEANT4(5cm target) | Whitney |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length of Target (cm) | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| 4E7 | 4E8 | 6E6 | 6E7 | 6E7 | |
| 1026940 | 10270829 | 771161 | 4826141 | 1001700 | |
| 305570 | 3054080 | 229266 | |||
| 975593 | 9757288 | 732603 | 4584834 | 951138 | |
| 290291 | 2901376 | 217803 | 1362098 | ||
| (s) | 1.3E-5 | 1.3E-4 | 9.57E-6 | 9.62E-5 | 9.54E-5 |
| Total Event Cross-Section (b) | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.38 | 0.079 |
| Total Moller Cross-Section (b) | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.361 | 0.075 |
| Detector Event Cross-Section (b) | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.18 | ||
| Detector Moller Cross-Section (b) | 0.17 | 0.17 | 0.17 |
Total dectector events occur for about 2.5% of the incident electrons on a LH2 target. We can assume that the Moller rate is 95% of the total event rate. We can assume the number of Moller events that occur within the DC range to be around 30% of the total Moller events occuring for the number of incident electrons for LH2 as well. Since the differential cross-section over the angel theta is proportional to the differtial cross-section over wire number we can dividing the Moller differential cross-section by the product of the density and length of the target material
If we were to integrate the Moller Differential Cross Section