Difference between revisions of "ProposalDeepBlueMarine 2013"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Project Summary= | =Project Summary= | ||
| − | We propose | + | We propose to measure the concentrations of several nuclei using photon activation analysis (PAA) and determine if there is a correlation between several coin samples and candidate mines that may have been the source for the silver in the coin. Based on previous work (insert NAA reference) and our preliminary results, we intend to focus on Gold, Irridum, and Strontium nuclei. PAA has been able to measure the content of nuclei in a sample to the level of parts-per-million (PPM). Elemental and matching analyses were successfully performed for a wide variety of samples including museum artifacts [1], fossils [2], forensic samples [3], agricultural samples [4], and various environmental samples [5-6]. PAA is an ideal tool for performing the above measurements due to its ability to measure PPM level concentration accuracies without destroying the sample as compared to other methods of detecting base elements [7 - 9]. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
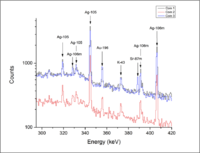
[[File:DBM_2013_Sr87mFig.png| 200 px]] | [[File:DBM_2013_Sr87mFig.png| 200 px]] | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 17 May 2013
Project Summary
We propose to measure the concentrations of several nuclei using photon activation analysis (PAA) and determine if there is a correlation between several coin samples and candidate mines that may have been the source for the silver in the coin. Based on previous work (insert NAA reference) and our preliminary results, we intend to focus on Gold, Irridum, and Strontium nuclei. PAA has been able to measure the content of nuclei in a sample to the level of parts-per-million (PPM). Elemental and matching analyses were successfully performed for a wide variety of samples including museum artifacts [1], fossils [2], forensic samples [3], agricultural samples [4], and various environmental samples [5-6]. PAA is an ideal tool for performing the above measurements due to its ability to measure PPM level concentration accuracies without destroying the sample as compared to other methods of detecting base elements [7 - 9].