Difference between revisions of "Neutron Polarimeter"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
| − | + | By conservation of four-momentum: | |
<math> p^{\mu}_{\gamma} + p^{\mu}_D = p^{\mu}_p + p^{\mu}_n\ \ \Rightarrow \ \ p^{\mu}_p = p^{\mu}_{\gamma} + p^{\mu}_D - p^{\mu}_n</math> | <math> p^{\mu}_{\gamma} + p^{\mu}_D = p^{\mu}_p + p^{\mu}_n\ \ \Rightarrow \ \ p^{\mu}_p = p^{\mu}_{\gamma} + p^{\mu}_D - p^{\mu}_n</math> | ||
| − | + | and squaring both side of equation above: | |
<math> (p^{\mu}_p)^2 = (p^{\mu}_{\gamma})^2 + (p^{\mu}_D)^2 + (p^{\mu}_n)^2 + | <math> (p^{\mu}_p)^2 = (p^{\mu}_{\gamma})^2 + (p^{\mu}_D)^2 + (p^{\mu}_n)^2 + | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
2\ p^{\mu}_{\gamma}\ p^{\mu}_D - 2\ p^{\mu}_{\gamma}\ p^{\mu}_n - 2\ p^{\mu}_D\ p^{\mu}_n </math> | 2\ p^{\mu}_{\gamma}\ p^{\mu}_D - 2\ p^{\mu}_{\gamma}\ p^{\mu}_n - 2\ p^{\mu}_D\ p^{\mu}_n </math> | ||
| + | and using the four-momentum invariants: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>(p^{\mu}_p)^2 = m_p^2</math> | ||
| + | <math>(p^{\mu}_p)^2 = m_p^2</math> | ||
| + | <math>(p^{\mu}_p)^2 = m_p^2</math> | ||
| + | <math>(p^{\mu}_p)^2 = m_p^2</math> | ||
<math> m_p^2 - m_{\gamma}^2(=0) - m_D^2 - m_n^2 = </math><br> | <math> m_p^2 - m_{\gamma}^2(=0) - m_D^2 - m_n^2 = </math><br> | ||
Revision as of 16:07, 5 April 2011
Analysis of energy dependence
four-vectors algebra
Let's do the four-vector algebra:
By conservation of four-momentum:
and squaring both side of equation above:
and using the four-momentum invariants:
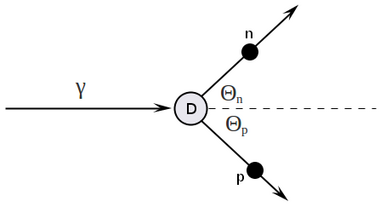
Detector is located at , so
and visa versa
how it looks
low energy approximation
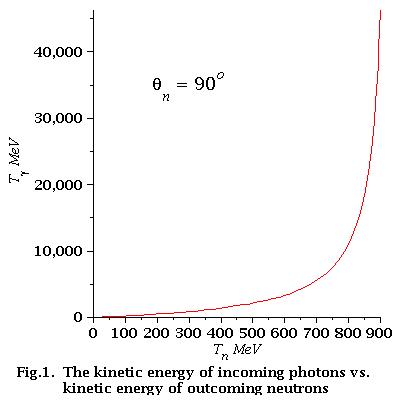
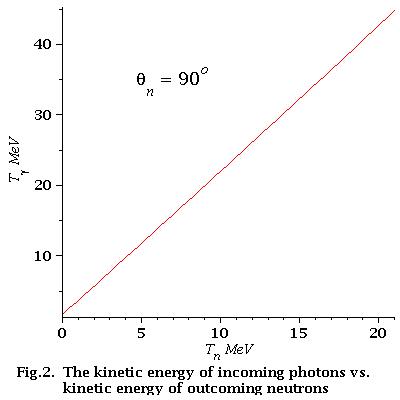
As we can see from Fig.2 for low energy neutrons (0-21 MeV)
energy dependence of incident photons is linear
Find that dependence. We have:
So, the equation of the line is:
Finally for low energy neutrons (0-21 MeV):
example of error calculation
example 1
Say, we have, 10 MeV neutron with uncertainty 1 MeV, the corresponding uncertainly for photons energy is:
example 2
Say, the neutron's time of flight uncertainly is 1 ns
The neutron's kinetic energy is:
And:
Also we need the neutron's time of flight as function of neutron's kinetic energy:
Say, we have 10 MeV neutron, 1 m away detector, and neutron's time of flight uncertainty is 1 ns. Then the neutron time of flight is:
Neutron kinetic energy errors are:
And photon energy errors are:
Below are some examples for different detector distance and neutron kinetic energy:
| 1 ns | 1 m | 5 MeV | 0.103 | 32 ns | 0.31 MeV | 6.2 % | 0.64 MeV | 5.3 % |
| 1 ns | 1 m | 10 MeV | 0.145 | 23 ns | 0.88 MeV | 8.8 % | 1.81 MeV | 8.1 % |
| 1 ns | 1 m | 20 MeV | 0.203 | 16 ns | 2.51 MeV | 12.6 % | 5.16 MeV | 12.1 % |
| 1 ns | 1 m | 0.5 MeV | 0.033 | 102 ns | 0.010 MeV | 1.9 % | ||
| 1 ns | 1 m | 1 MeV | 0.046 | 72 ns | 0.028 MeV | 2.8 % | ||
| 1 ns | 1 m | 2 MeV | 0.065 | 51 ns | 0.078 MeV | 3.9 % | ||
| 1 ns | 1 m | 4 MeV | 0.092 | 36 ns | 0.22 MeV | 5.5 % |