Difference between revisions of "TF EIM Chapt6"
(→JFET) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
Consider the following circuit | Consider the following circuit | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_{DD} =</math> the drain driving voltage | ||
| + | |||
| + | R_D = resistor between the drain and V_{DD} | ||
| + | |||
| + | if | ||
| + | <math>\pho</math> = resistivity of the n-type semiconductor | ||
| + | |||
| + | then | ||
| + | |||
| + | :r = <math>\pho \frac{\ell}{A}</math> = resistance of the JFET | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>I_D = \frac{V_{DD}}{r+R_D}</math> | ||
=MOSFET= | =MOSFET= | ||
Revision as of 04:50, 5 April 2011
Field Effect Transistors (FET, JFET, MOSFET)
Properties
FETs differ from the bipolar transistors in the las chapter in that the current from a FET is only due to the majority charge carriers in the semiconductor while bi-polar transistors current is produced from both carrier types; electron and hole.
- higher input impedance than bi-polar
- less gain than bi-polar
JFET
JFET Junction Field Effect Transistor
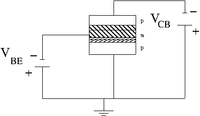
In a bi-polar transistor you have a depletion region with mixed charge carriers
 |
 |
|
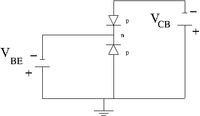
| pnp bi-polar transistor | Equivalence circuit | Circuit diagram |
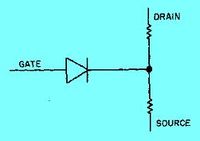
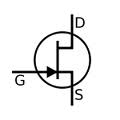
In the Junction Field Effect Transistor you have a single charge carrier with the minority charge carriers forming a choke point for the majority carrier current flow. It is similar to "pinching" a garden hose when water is flowing through it.
 |
 |
|
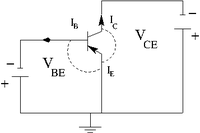
| JFET | Equivalence circuit | Circuit diagram |
The semiconductor material of the gate is the opposite of the channel. Here the n-p (or p-n) junction is between the gate and the channel.
The JFET operates by reverse biasing the gate-channel junction (diode) so the gate current doesn't flow in the direction indicated by the circuit diagram symbol. This means that the current through the gate is small (nAmps). As a result the input impedance looking into the gate is high (M) for the equivalent circuit.
The current junction rule is
for the Bi-Polar transistor
FET resistor
The FET acts like a resistor.
Consider the following circuit
Let
the drain driving voltage
R_D = resistor between the drain and V_{DD}
if = resistivity of the n-type semiconductor
then
- r = = resistance of the JFET
MOSFET
MOSFET Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor