Difference between revisions of "TF EIM Chapt6"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(→JFET) |
(→JFET) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| pnp bi-polar transistor || Equivalence circuit || Circuit diagram | | pnp bi-polar transistor || Equivalence circuit || Circuit diagram | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="3" cellpadding="20" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | |[[File:TF_EIM_JFETnchan.jpg| 200 px]] || [[File:TF_EIM_nchanDiodeRep.png| 200 px]] ||[[File:TF_EIM_JFETnchanCircuit.png| 200 px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | JFET || Equivalence circuit || Circuit diagram | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 04:02, 4 April 2011
Field Effect Transistors (FET, JFET, MOSFET)
Properties
FETs differ from the bipolar transistors in the las chapter in that the current from a FET is only due to the majority charge carriers in the semiconductor while bi-polar transistors current is produced from both carrier types; electron and hole.
- higher input impedance than bi-polar
- less gain than bi-polar
JFET
JFET Junction Field Effect Transistor
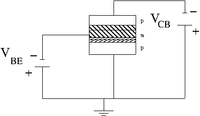 |
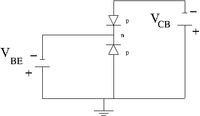 |
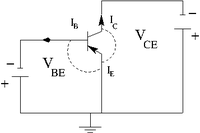
|
| pnp bi-polar transistor | Equivalence circuit | Circuit diagram |
| 200 px | 200 px | 200 px |
| JFET | Equivalence circuit | Circuit diagram |
MOSFET
MOSFET Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor