Difference between revisions of "Lab 6 TF EIM"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
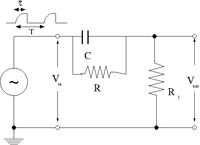
2.)Construct the circuit below selecting an RC combination such that RC <math>\approx</math> 1/10 | 2.)Construct the circuit below selecting an RC combination such that RC <math>\approx</math> 1/10 | ||
| + | [[File:TF_EIM_Lab6a.png| 200 px]] | ||
3.)Measure<math> V_{in}</math> and <math>V_{out}</math>. Sketch a picture comparing<math> V_{out}</math> and <math>V_{in}</math>. | 3.)Measure<math> V_{in}</math> and <math>V_{out}</math>. Sketch a picture comparing<math> V_{out}</math> and <math>V_{in}</math>. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
2.) What happens if R is doubled and C is halved? | 2.) What happens if R is doubled and C is halved? | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Integrator= | =Integrator= | ||
Revision as of 05:35, 8 February 2011
Lab 6 Pulses and RC Filters
Differentiator
1.) Adjust the pulse generator to output square pulses which at sec in time. 2.)Construct the circuit below selecting an RC combination such that RC 1/10
3.)Measure and . Sketch a picture comparing and .
4.) Change the pulse width such that
5.)Measure and .Sketch a picture comparing and .
6.) Change the pulse width such that
7.)Measure .Sketch a picture comparing and .
Questions
1.) What happens if than amplitude of is doubled.
2.) What happens if R is doubled and C is halved?
Integrator
To illustrate the integrator circuit we need to have an input pulse which looks like the output of the above differentiator circuit. In other words, input a pulse whose output is obviously the integral of the input pulse.