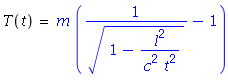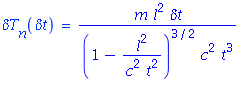Difference between revisions of "Neutron Polarimeter"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
Say, we have, 1 meter away detector with 1 ns time of flight neutron uncertainly | Say, we have, 1 meter away detector with 1 ns time of flight neutron uncertainly | ||
| − | After some works, the neutron kinetic energy is: | + | After some works, the neutron's kinetic energy as function of the neutron's time of flight is: |
[[File:formula0.png]] | [[File:formula0.png]] | ||
| − | And it follows, that | + | And it follows, that neutron's kinetic energy error as function of the neutron's time of flight error is: |
[[File:formula1.png]] | [[File:formula1.png]] | ||
Revision as of 22:42, 16 June 2010
Analysis of energy dependence
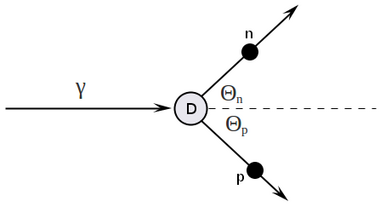
four-vectors algebra
writing four-vectors:
Doing four-vector algebra:
Detector is located at , so
and visa versa
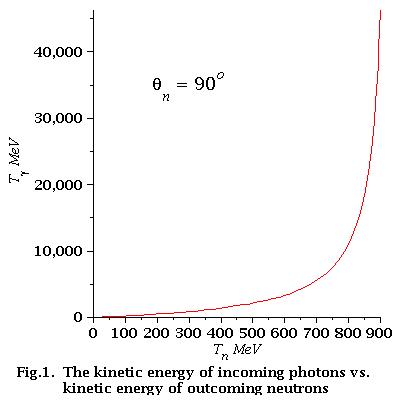
how it looks
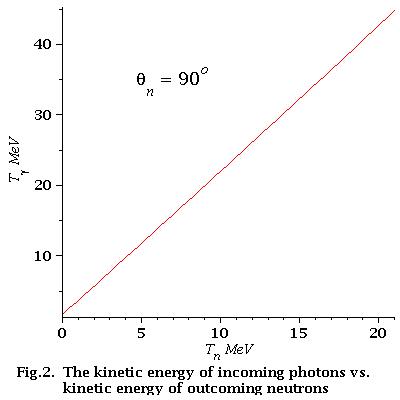
low energy approximation
As we can see from Fig.2 for low energy neutrons (0-21 MeV)
energy dependence of incident photons is linear
Find that dependence. We have:
So, the equation of the line is:
Finally for low energy neutrons (0-21 MeV):
example of error analysis
example 1
Say, we have, 10 MeV neutron with uncertainty 1 MeV, the corresponding uncertainly for photons energy is:
example 2
Say, we have, 1 meter away detector with 1 ns time of flight neutron uncertainly
After some works, the neutron's kinetic energy as function of the neutron's time of flight is:
And it follows, that neutron's kinetic energy error as function of the neutron's time of flight error is:
Take the worth case 10 MeV neutron. The corresponding time of flight is:
So neutron uncertainty is:
absolute:
relative:
Corresponding photon uncertainty is:
absolute:
relative: