Difference between revisions of "Forest ModernPhysics"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Davisson and Germer== | ==Davisson and Germer== | ||
| − | We know that X-rays having a wavelength of <math>\lambda_{X-rays} = 7.1 \times 10^{-11} \mbox{m}</math> make | + | We know that X-rays having a wavelength of <math>\lambda_{X-rays} = 7.1 \times 10^{-11} \mbox{m}</math> make a diffraction pattern on an aluminum foil. |
[[File:X-rayInterferencePattern.gif | 100px]] | [[File:X-rayInterferencePattern.gif | 100px]] | ||
Revision as of 02:53, 30 September 2009
Matter Waves (Wave Particle Duality)
Special relativity said that
if m=0
Plank said he could fit the Black Body radiation data assuming that that
where = Plank's constant
Combining the two we have
photons have momentum like a particle (mv)
Do particles reciprocate and behave like photons?
De Broglie's Hypothesis
If photons can behave like particles by having momentum
Then can a particle behave like a wave by having wavelength
or
de Broglie Hypothesis
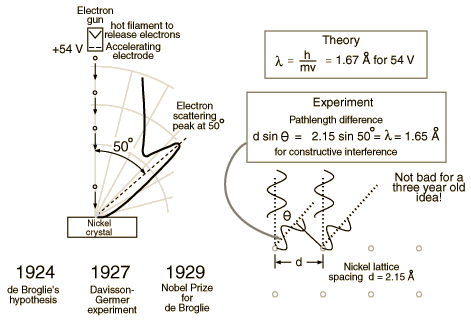
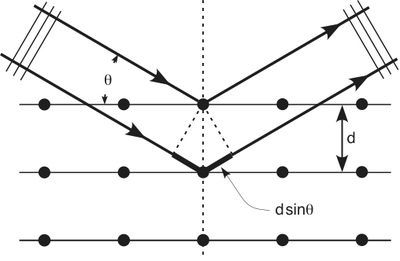
Davisson and Germer
We know that X-rays having a wavelength of make a diffraction pattern on an aluminum foil.
Another way to calculate
- What would be the energy of an electron with the same wavelength as the above X-ray?
relativistic total energy relation
- = 511.3 keV
relativistic kinetic energy
- Note classical physics may be used for electrons below 50 keV
- Clinton Davisson and Lest Germer in 1927 published conclusive evidence for the diffraction of electron waves using 54 eV electrons impinging a crystal made of nickel.
One problem to overcome for the experiment was that such a low energy electron scatters in air. The had to do the experiment in a vacuum.
From hyperphysics: