Difference between revisions of "Uniform distribution in Energy and Theta LUND files"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[[File:Screen_Shot_2016-05-12_at_6.42.46_PM.png]] | [[File:Screen_Shot_2016-05-12_at_6.42.46_PM.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Screen_Shot_2016-05-12_at_6.44.44_PM.png]] | ||
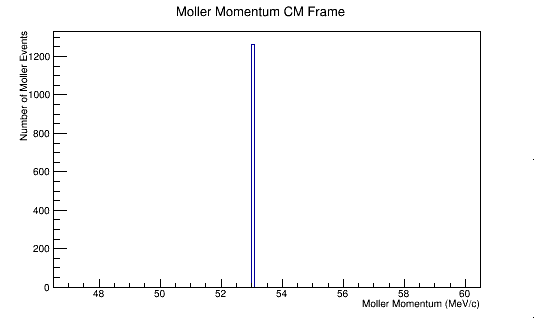
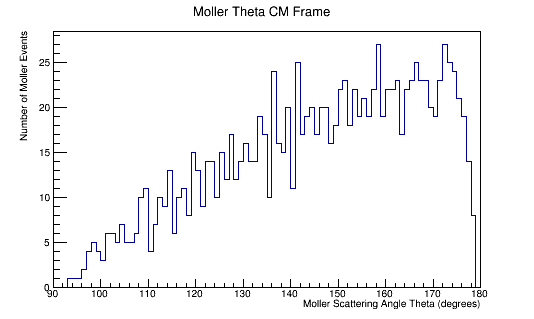
<center>[[File:Init_e_Mom_CM.png|600 px]][[File:Init_Mol_Mom_CM.png|600 px]]</center> | <center>[[File:Init_e_Mom_CM.png|600 px]][[File:Init_Mol_Mom_CM.png|600 px]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 00:46, 13 May 2016
File:LUND Spread.C
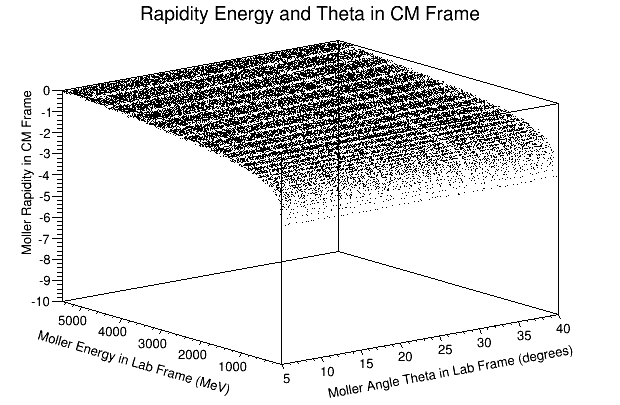
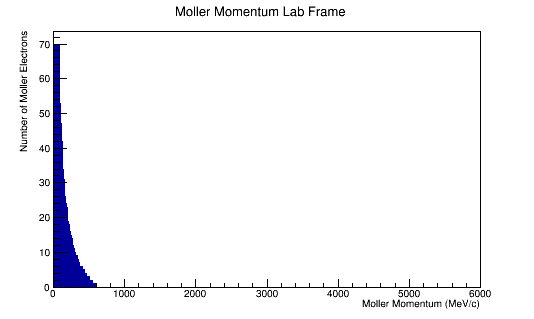
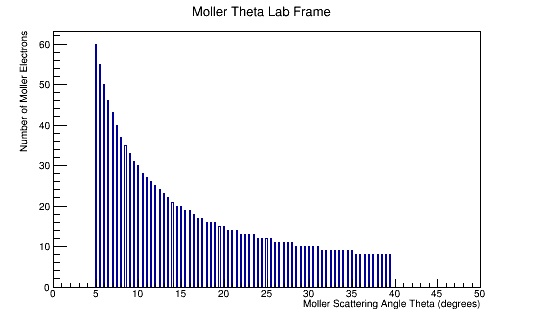
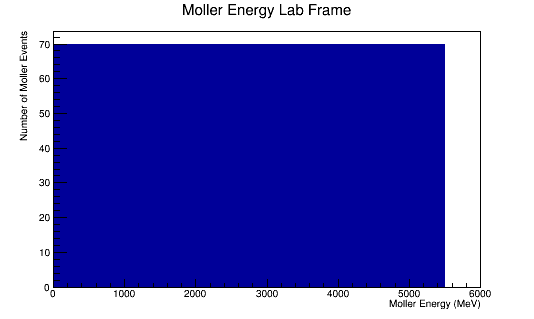
The LUND file is created by creating an isotropic distribution of particles within the energy range of 2MeV-5.5GeV as is found through GEANT simulation. These particles are also uniformly distributed through the angle theta with respect to the beam line in the range 5-40 degrees. This is done at a set angle phi (10 degrees) with respect to the perpendicular components with respect to the beam line.
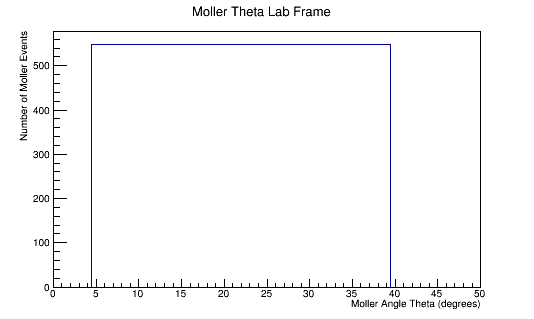
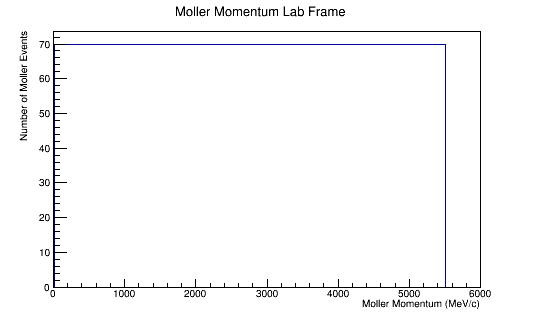
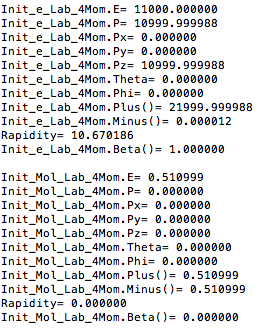
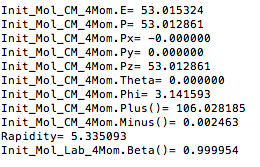
For an incoming electron of 11GeV striking a stationary electron we would expect:
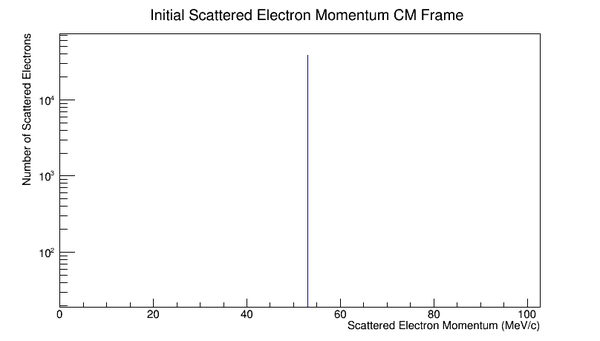
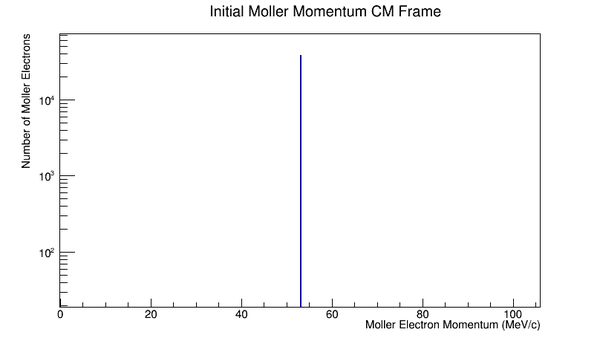
Since the angle phi has been constrained to remain constant, the x and y components of the momentum will increase in the positive first quadrant. This implies that the z component of the momentum must decrease by the relation:
In the Center of Mass frame, this becomes:
Since the momentum in the CM frame is a constant, this implies that pz must decrease. For phi=10 degrees:
This is repeated for rotations of 60 degrees in phi in the Lab frame.
We can use the variable rapidity:
where
this implies that as
For forward travel in the light cone:
For backward travel in the light cone:
For a particle that transforms from the lab frame to a CM frame with the particle inside the light cone:
Mol_Lab_4Mom.E= 92.000000 Mol_Lab_4Mom.P= 91.998581 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Px= 51.943569 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Py= 9.159060 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Pz= 75.377159 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Theta= 0.610556 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Phi= 0.174533 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Plus()= 167.377159 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Minus()= 16.622841 Beta= 0.999985 Gamma= 180.041258 Rapidity= 1.154736 Mol_CM_4Mom.E= 53.015377 Mol_CM_4Mom.P= 53.012917 Mol_CM_4Mom.Px= 51.943569 Mol_CM_4Mom.Py= 9.159060 Mol_CM_4Mom.Pz= -5.324148 Mol_CM_4Mom.Theta= 1.671397 Mol_CM_4Mom.Phi= 0.174533 Mol_CM_4Mom.Plus()= 47.691229 Mol_CM_4Mom.Minus()= 58.339525 Rapidity= -0.100766
For a particle that transforms from the Lab frame to the CM frame where the particle is not within the light cone:
Mol_Lab_4Mom.E= 92.000000 Mol_Lab_4Mom.P= 91.998581 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Px= 52.589054 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Py= 9.272868 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Pz= 74.914246 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Theta= 0.619278 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Phi= 0.174533 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Plus()= 166.914246 Mol_Lab_4Mom.Minus()= 17.085754 Beta= 0.999985 Gamma= 180.043077 Rapidity= 1.139618 Mol_CM_4Mom.E= 53.015377 Mol_CM_4Mom.P= nan Mol_CM_4Mom.Px= 52.589054 Mol_CM_4Mom.Py= 9.272868 Mol_CM_4Mom.Pz= nan Mol_CM_4Mom.Theta= nan Mol_CM_4Mom.Phi= 0.174533 Mol_CM_4Mom.Plus()= nan Mol_CM_4Mom.Minus()= nan Rapidity= nan
These particles are outside the light cone and are more timelike, thus not visible in normal space. This will reduce the number of particles that will be detected.