Difference between revisions of "Sadiq Thesis Latex"
| Line 707: | Line 707: | ||
\section{Quadrupole Scanning Experiment} | \section{Quadrupole Scanning Experiment} | ||
| − | Quadrupole scanning method | + | Quadrupole scanning method was used to measure the accelerator's emittance. The quadrupole current is changed to alter the strength and direction of the quadrupole magnetic field such that a measurable change in the beam shape is seen by the OTR system. Initially, the beam was steered by the quadrupole indicating that the beam was not entering along the quadrupole's central axis. Several magnetic elements upstream of this quadrupole were adjusted to align the incident electron beam with the quadrupole's central axis. First, the beam current observed by a Faraday cup located at the end of beam line was maximized using upstream steering coils within the linac nearest the gun. Second, the first solenoid nearest the linac gun was used to focus the electron beam on the OTR screen. Steering coils were adjusted to maximize the beam current to the Faraday cup and minimize the deflection of the beam by the quadrupole. A second solenoid and the last steering magnet shown in Figure~\ref{fig:app-hrrl-cavity}, both near the exit of the linac, were used in the final step to optimize the beam spot size on the OTR target and maximize the Faraday cup current. A configuration was found that minimized the electron beam deflection when the quadrupole current was altered during the emittance measurements. |
| − | The emittance measurement was performed using an electron beam energy of 15~MeV and a 200~ns long | + | The emittance measurement was performed using an electron beam energy of 15~MeV and a 200~ns long macro pulse of 40~mA current. The current in the first quadrupole after the exit of the linac was changed from $-$~5~A to $+$~5~A with an increment of 0.2~A. Seven measurements were taken at each current step in order to determine the average beam width and the variance. Background measurements were taken by turning the linac's electron gun off while keep the RF on. Background image and beam images before and after background subtraction are shown in Figure~\ref{bg}. A small dark current is visible in Figure~\ref{bg} (b) that is known to be generated when electrons are pulled off the cavity wall and accelerated. |
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\begin{tabular}{ccc} | \begin{tabular}{ccc} | ||
\centerline{\scalebox{0.42} [0.42]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f4.eps}}} \\ | \centerline{\scalebox{0.42} [0.42]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f4.eps}}} \\ | ||
| Line 720: | Line 720: | ||
(c) | (c) | ||
\end{tabular} | \end{tabular} | ||
| − | \caption{Digital image from the OTR screen; (a) a beam with the dark current and background noise, (b) a background image taken | + | \caption{Digital image from the OTR screen; (a) a beam with the dark current and background noise, (b) a background image taken after the RF was on but the gun is off, (c) a beam image when dark background was subtracted.} |
\label{bg} | \label{bg} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| Line 728: | Line 728: | ||
%\subsection{Data Analysis and Results} | %\subsection{Data Analysis and Results} | ||
Images from the JAI camera were calibrated using the OTR target frame. An LED was used to illuminate the OTR aluminum frame that has a known inner diameter of 31.75~mm. Image processing software was used to inscribe a circle on the image to measure the circular OTR inner frame in units of pixels. The scaling factor can be obtained by dividing this length with the number of pixels observed. The result is a horizontal scaling factor of 0.04327~$\pm$~0.00016~mm/pixel and vertical scaling factor of 0.04204~$\pm$~0.00018~mm/pixel. | Images from the JAI camera were calibrated using the OTR target frame. An LED was used to illuminate the OTR aluminum frame that has a known inner diameter of 31.75~mm. Image processing software was used to inscribe a circle on the image to measure the circular OTR inner frame in units of pixels. The scaling factor can be obtained by dividing this length with the number of pixels observed. The result is a horizontal scaling factor of 0.04327~$\pm$~0.00016~mm/pixel and vertical scaling factor of 0.04204~$\pm$~0.00018~mm/pixel. | ||
| − | Digital images from the JAI camera were extracted in a matrix format in order to take projections on both axes and perform a Gaussian fit. The observed image profiles were not well described by a single Gaussian distribution. | + | Digital images from the JAI camera were extracted in a matrix format in order to take projections on both axes and perform a Gaussian fit. The observed image profiles were not well described by a single Gaussian distribution. |
| − | |||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | The profiles may be described using a Lorentzian distribution, however, the rms of the Lorentzian function is not defined. A super Gaussian distribution was used~\cite{sup-Gau}, because it has a sharper distribution than Gaussian and unlike Lorentzian the rms values may be directly extracted. The Chi-square for x and y profiles are $2.4 \times 10^7$ and $1.9 \times 10^7$ for super Gaussian fit and $2.6 \times 10^8$ and $9.1 \times 10^7$ Gaussian fit. The beam spot, beam projections and fits are shown in Figure~\ref{Gau-SupGaus-fits}. |
| + | In Gaussian distribution, $\phi(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}x^2}$, the variable $x$ on exponent is raised to the 2nd power while in the super Gaussian it is raised to a power smaller than 2. For example, the beam projections shown in Figure~\ref{Gau-SupGaus-fits} were fitted with the super Gaussian distributions. The variable $x$ on exponents were raised to $0.9053$ ($x$-projection) and $1.0427$ ($y$-projection). | ||
| + | |||
| + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | ||
\begin{tabular}{cc} | \begin{tabular}{cc} | ||
{\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/Gau_SupGau/Gau_ChiSqaure.eps}}} | {\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/Gau_SupGau/Gau_ChiSqaure.eps}}} | ||
| Line 740: | Line 742: | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | + | Figure~\ref{fig:par-fit} shows the square of the rms ($\sigma^2_{\textnormal{s}}$) $vs$ $k_1L$ for $x$ (horizontal) and $y$ (vertical) beam projections along with the parabolic fits using Eq.~\ref{fig:par-fit}. The emittance and Twiss parameters from these fits are summarized in Table~\ref{tab:results}. MATLAB scripts used to calculate emittance and Twiss parameters are given in appendix B. | |
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\begin{tabular}{cc} | \begin{tabular}{cc} | ||
{\scalebox{0.295} [0.295]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/par_fit_x.eps}}} | {\scalebox{0.295} [0.295]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/par_fit_x.eps}}} | ||
| Line 775: | Line 777: | ||
\section{Energy Scan} | \section{Energy Scan} | ||
| − | The energy profile | + | |
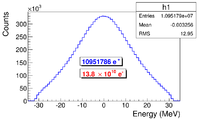
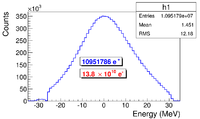
| + | The HRRL energy profile was measured when it was tuned to accelerate electrons to 12~MeV peak energy. A Faraday cup was placed at the end of the 45 degree beamline to measure the electron beam current when D1 was on and D2 was off. Dipole coil current for D1 was changed in 1~A increments. As the dipole coil current was changed, the energy of the electrons transported to the Faraday cup would change as described in Appendix A. Figure~\ref{fig:En-Scan} illustrates a measurement of the 12~MeV peak with a long low energy tail observed. The HRRL energy profile can be described by overlapping two skewed Gaussian fits~\cite{sup-Gau}. The fit function is given by | ||
\begin{equation} | \begin{equation} | ||
| − | G(En) = A_{1}e^{\frac{-(En-\mu_{1})^2}{2 | + | G(En)=A_{1}e^{\frac{-\left(En-\mu_{1}\right)^{2}}{2\left\{ \sigma_{1}\left[1+sgn\left(En-\mu_{1}\right)\right]\right\} ^{2}}}+A_{2}e^{\frac{-\left(En-\mu_{2}\right)^{2}}{2\left\{ \sigma_{2}\left[1+sgn\left(En-\mu_{2}\right)\right]\right\} ^{2}}}, |
\label{eq:skew-Gau} | \label{eq:skew-Gau} | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
| − | where $ | + | where $sgn$ is the sign function, that is defined as |
| + | $$ | ||
| + | sgn=\left\{ \begin{array}{ll} | ||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \mbox -1\ & {(x<0)} \\ |
| + | \mbox 0 \ & {(x=0)} \\ | ||
| + | \mbox 1 \ & {(x>0)}.\\ | ||
| + | \end{array}\right. | ||
| + | $$ | ||
| + | Where other variables defined as $\sigma_{1}=\frac{\sigma_{r,1}+\sigma_{l,1}}{2}$, $\sigma_{2}=\frac{\sigma_{r,2}+\sigma_{l,2}}{2}$, $E_{1}=\frac{\sigma_{r,1}-\sigma_{l,1}}{\sigma_{r,1}+\sigma_{l,1}}$, and $E_{2}=\frac{\sigma_{r,2}-\sigma_{l,2}}{\sigma_{r,2}+\sigma_{l,2}}$. The measurement results and fits are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:En-Scan} and in Table~\ref{tab:En-Scan_resluts}. | ||
| + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | ||
\centering | \centering | ||
\includegraphics[scale=0.50]{3-Apparatus/En_Fit_Assym_Gau.eps} | \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{3-Apparatus/En_Fit_Assym_Gau.eps} | ||
| − | \caption{HRRL energy scan ( | + | \caption{HRRL energy scan (dots) and fit (line) with two skewed Gaussian distribution.} |
\label{fig:En-Scan} | \label{fig:En-Scan} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | |||
\begin{table} | \begin{table} | ||
\centering | \centering | ||
\caption{Fit Parameters for Two Skewed Gaussian.} | \caption{Fit Parameters for Two Skewed Gaussian.} | ||
| − | \begin{tabular}{ | + | \begin{tabular}{lclcc} |
\toprule | \toprule | ||
| − | {Parameter} | + | {Parameter} & Notation & Unit & {First Gaussian} & {Second Gaussian} \\ |
\midrule | \midrule | ||
| − | amplitude | + | amplitude & A & mA & ~2.14 & 10.88 \\ |
| − | mean | + | mean & $\mu$ & MeV & 12.07 & 12.32 \\ |
| − | sigma left $\sigma_L$ & MeV & ~4.47 & ~0.70 \\ | + | sigma left & $\sigma_L$ & MeV & ~4.47 & ~0.70 \\ |
| − | sigma right $\sigma_R$ & MeV & ~1.20 & ~0.45 \\ | + | sigma right & $\sigma_R$ & MeV & ~1.20 & ~0.45 \\ |
\bottomrule | \bottomrule | ||
\end{tabular} | \end{tabular} | ||
| Line 806: | Line 816: | ||
\section{The Positron Production Runs} | \section{The Positron Production Runs} | ||
| + | The annihilation target T2 is insertable into the beamline and it was placed inside a 6-way cross that has horizontal sides sealed with 1~mil stainless steel windows. Positrons intercepting T2 thermalize, annihilate, and produce 511~keV photon pairs back-to-back. These photons are detected by two NaI detectors facing T2 and shielded with Pb bricks as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:HRRL-En-Scan}. The background was measured by retracting T2 thereby allowing positrons to exit the beamline and be absorbed by the beam dump. | ||
| − | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | |
| − | |||
| − | \begin{figure} | ||
\centering | \centering | ||
| − | \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{ | + | \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{5-Experiment/Figures/PositronDetection/NaI_Setup4.png} |
\caption{Positron detection using T2 and NaI detectors.} | \caption{Positron detection using T2 and NaI detectors.} | ||
\label{fig:HRRL-En-Scan} | \label{fig:HRRL-En-Scan} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | T2 | + | As shown in Figure~\ref{fig:Dipole-in}, a 511~keV peak was observed (solid line) when T2 was in. A permanent dipole magnet was placed on the beamline after Q10 to deflect charged particles on the accelerator side preventing them from entering the shielded cell. The peak was not observed (dashed line) when T2 was in and the permanent magnet was used. The peak was also not observed (doted dashed line) when T2 and the permanent magnet were removed. Thus, one may argue that the observed peak is due to positrons annihilating in T2. |
| + | |||
| + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | ||
| + | \centering | ||
| + | \begin{tabular}{cc} | ||
| + | {\scalebox{0.35} [0.35]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/SweepingDipole/LNaI3.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.35} [0.35]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/SweepingDipole/RNaI3.png}}} \\ | ||
| + | (a) Original spectrum on left NaI. & (b) Original spectrum on right NaI.\\ | ||
| + | \end{tabular} | ||
| + | \caption{Photon spectrum when a permanent dipole magnet is inserted along with T2 (dashed line), dipole out and T2 in (solid line), and dipole removed and T2 out (dotted dashed line). The positron energy incident on the T2 was $2.15\pm0.06$~MeV.} | ||
| + | \label{fig:Dipole-in} | ||
| + | \end{figure} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The normalized photon energy spectra observed by two NaI detectors are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} when T2 was both in (signal) and out (background) of the beamline. Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (c) and (d) illustrate the events observed when 511~keV photons were required in both detectors. The signal is indicated by the solid line and background by dashed line. | ||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\centering | \centering | ||
\begin{tabular}{cc} | \begin{tabular}{cc} | ||
| − | + | {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_L1/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_R1/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} \\ | |
| − | {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/ | ||
(a) Original spectrum on left NaI. & (b) Original spectrum on right NaI.\\ | (a) Original spectrum on left NaI. & (b) Original spectrum on right NaI.\\ | ||
& \\ | & \\ | ||
& \\ | & \\ | ||
| − | {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/ | + | {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_L2/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_R2/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} \\ |
(c) Spectrum with cut on left NaI. & (d) Spectrum with cut on right NaI.\\ | (c) Spectrum with cut on left NaI. & (d) Spectrum with cut on right NaI.\\ | ||
& \\ | & \\ | ||
\end{tabular} | \end{tabular} | ||
| − | \caption{The time normalized | + | \caption{The time normalized spectra of photons. In the top row are original spectrum and in the bottom row are spectrum of incidents happened in the 511~keV peak coincidently in both detectors. The positron energy incident on the T2 was $3.00\pm0.06$~MeV.} |
\label{fig:in-out-runs} | \label{fig:in-out-runs} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | + | %\begin{table} | |
| − | + | %\centering | |
| − | \begin{table} | + | %\caption{Run Parameters of The Run No. 3735.} |
| − | \centering | + | %\begin{tabular}{lll} |
| − | \caption{Run Parameters of The Run No. 3735.} | + | %\toprule |
| − | \begin{tabular}{lll} | + | %{Parameter} & {Unit} & {Value} \\ |
| − | \toprule | + | %\midrule |
| − | {Parameter} & {Unit} & {Value} \\ | + | %run number & & 3735 \\ |
| − | \midrule | + | %repetition rate & Hz & 300 \\ |
| − | run number & & 3735 \\ | + | %run time & s & 1002 \\ |
| − | repetition rate & Hz & 300 \\ | + | %pulses & & 301462 \\ |
| − | run time & s & 1002 \\ | + | %events & & 9045 \\ |
| − | pulses & & 301462 \\ | + | %e$^+$ Counts on NaI Detectors & & 256 $\pm$ 16\\ |
| − | events & & 9045 \\ | + | %\bottomrule |
| − | e$^+$ Counts on NaI Detectors & & 256 $\pm$ 16\\ | + | %\end{tabular} |
| − | \bottomrule | + | %\label{tab:run3735} |
| − | \end{tabular} | + | %\end{table} |
| − | \label{tab:run3735} | ||
| − | \end{table} | ||
| − | |||
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % | % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % | ||
\section{The Electron Beam Current Measurement} | \section{The Electron Beam Current Measurement} | ||
| − | + | A scintillator was placed between Q9 and Q10, as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:Scint_e-}, to monitor the electron beam current. The electron beam current was changed incrementally to measure the correlation between the scintillator and the accelerated electron beam. The beam current was measured using FC1 and the output was integrated using an oscilloscope. The scintillator output was measured by integrating the output of FC1 on an oscilloscope. As the electron beam current was decreased, the signal observed on the oscilloscope decreased and ADC measured less charge from the scintillator as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:ADC-CH9}. A linear fit to data resulted a linear relation | |
| + | \begin{equation} | ||
| + | Q_{\text{e}^-}(i) = (0.0186 \pm 0.0028)i + 2.79 \pm 0.08~\text{C}, | ||
| + | \end{equation} | ||
| + | where $i$ is ADC channel number and Q is the accelerated electron beam charge. The fit is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:calb-fit}. | ||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\centering | \centering | ||
| − | \includegraphics[scale=0. | + | \includegraphics[scale=0.35]{5-Experiment/Figures/HRRL_line.eps} |
\caption{The electron beam monitor.} | \caption{The electron beam monitor.} | ||
\label{fig:Scint_e-} | \label{fig:Scint_e-} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\centering | \centering | ||
| − | \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{5-Experiment/Figures/ScintilatorCalibration/ | + | \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{5-Experiment/Figures/ScintilatorCalibration/ADC_CHAN3.eps} |
\caption{The photon flux detected using scintillator. The mean of the ADC channel decreased linearly as the electron beam current was decreased.} | \caption{The photon flux detected using scintillator. The mean of the ADC channel decreased linearly as the electron beam current was decreased.} | ||
\label{fig:ADC-CH9} | \label{fig:ADC-CH9} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| + | |||
| + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | ||
| + | \centering | ||
| + | \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{5-Experiment/Figures/ScintilatorCalibration/calb.eps} | ||
| + | \caption{Fit for accelerator beam current $v.s.$ the ADC channel.} | ||
| + | \label{fig:calb-fit} | ||
| + | \end{figure} | ||
\begin{table} | \begin{table} | ||
| Line 890: | Line 918: | ||
\label{tab:scint_calb} | \label{tab:scint_calb} | ||
\end{table} | \end{table} | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | When running in coincidence mode, the electron beam current is sampled by the scintillator only when a coincidence event occurs causing a trigger that gates the ADC and measures the scintillator output for that positron coincidence event. The charge measured by the ADC is the total charge of the electron pulses that created the positron events. The beam pulses are counted using a scaler. The total charge on T1 for the entire run is estimated using | ||
\begin{equation} | \begin{equation} | ||
| − | Q_{\text{ | + | Q_{\text{C}} = \left ( \overset{N}{\underset{i}{\sum}} 0.0186i\times(\text{bin~content}[i]) + 2.79 \right ) \times \frac{\text{(\# of beam pulses)}}{\text{(\# of events)}}. |
\label{eq:q_calc1} | \label{eq:q_calc1} | ||
\end{equation} | \end{equation} | ||
\noindent | \noindent | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
\section{Positron Rate Estimation} | \section{Positron Rate Estimation} | ||
| − | The | + | The background subtracted and normalized photon energy spectra were observed using two NaI detectors for $3.00 \pm 0.07$~MeV are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs}. |
| − | \begin{figure} | + | Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (a) and (b) are the background subtracted spectrum with no coincidence or energy cut. Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (c) and (d) illustrate events observed in coincidence and within a energy window of $511\pm75$~keV for both detectors. The measured positron rate using NaI detectors in coincidence mode was 0.25~Hz. |
| + | %The uncertainty of the power supplies used for dipoles is 0.1~A which creates 0.06~MeV uncertainty in energy of the beam bent by dipoles. | ||
| + | \begin{figure}[htbp] | ||
\centering | \centering | ||
\begin{tabular}{cc} | \begin{tabular}{cc} | ||
| Line 933: | Line 942: | ||
& \\ | & \\ | ||
\end{tabular} | \end{tabular} | ||
| − | \caption{Photon spectrum after background subtraction. (a) and (b) are spectrum | + | \caption{Photon spectrum of NaI detectors after background subtraction. (a) and (b) are spectrum after background subtractions. (c) and (d) are the spectrum of events coincident in both detectors in 511~keV peaks.} |
\label{fig:pos_NaILR} | \label{fig:pos_NaILR} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
| − | + | %The electron beam was transported to a phosphorous screen at the end of the 90 degree beamline to find the errors on the positron beam energy. The positron beam current was too low to be observed on phosphorous screen. | |
| + | %The beam centered on the phosphorous screen and then steered to the edge by changing current of D2 by 0.1~A. | ||
| + | %The phosphorous screen is twice as large as T2 in horizantal direction. | ||
\section{Positron to Electron Ratio} | \section{Positron to Electron Ratio} | ||
| − | The | + | The ratios of positrons detected using NaI detectors in coincidence mode to the electrons impinging T1 at different energies are given in Table~\ref{tab:e+2e-} and Figure~\ref{fig:e+2e-}. |
| − | + | A simulation was used to estimate the systematic error of the electron energy. | |
| + | The ratios errors are calculated by propagating the statistical errors of positron and electron rates. | ||
%error on total counts = sqt(total counts). Rate = Counts/time. Error on rates = sqrt(d(rate)/d(counts)^2*(error on the counts)^2)=sqrt((error on the counts)^2/time^2)=sqrt(counts/time^2)=sqrt(rate/time). | %error on total counts = sqt(total counts). Rate = Counts/time. Error on rates = sqrt(d(rate)/d(counts)^2*(error on the counts)^2)=sqrt((error on the counts)^2/time^2)=sqrt(counts/time^2)=sqrt(rate/time). | ||
\begin{table} | \begin{table} | ||
| Line 950: | Line 962: | ||
{Energy} & {Positron to Electron Ratio} \\ | {Energy} & {Positron to Electron Ratio} \\ | ||
\midrule | \midrule | ||
| − | $1.02 \pm 0. | + | $1.02 \pm 0.03$ & $(0.19 \pm 0.19)\times10^{-16}$ \\ |
$2.15 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.69 \pm 0.24)\times10^{-16}$ \\ | $2.15 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.69 \pm 0.24)\times10^{-16}$ \\ | ||
| − | $3.00 \pm 0. | + | $3.00 \pm 0.07$ & $(8.25 \pm 0.96)\times10^{-15}$ \\ |
| − | $4.02 \pm 0. | + | $4.02 \pm 0.07$ & $(4.20 \pm 0.80)\times10^{-15}$ \\ |
$5.00 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.62 \pm 0.16)\times10^{-16}$ \\ | $5.00 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.62 \pm 0.16)\times10^{-16}$ \\ | ||
| Line 960: | Line 972: | ||
\label{tab:e+2e-} | \label{tab:e+2e-} | ||
\end{table} | \end{table} | ||
| − | \begin{figure} | + | \begin{figure}[htbp] |
\centering | \centering | ||
\includegraphics[scale=0.72]{5-Experiment/Figures/Ratio/R.eps} | \includegraphics[scale=0.72]{5-Experiment/Figures/Ratio/R.eps} | ||
| − | \caption{The | + | \caption{The ratios of positrons detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode to the electrons impinging T1.} |
\label{fig:e+2e-} | \label{fig:e+2e-} | ||
\end{figure} | \end{figure} | ||
Revision as of 08:51, 3 October 2013
overlay positron energy distribution at T1 with what is seen at T2 for several values of Q7 Put the e+ simulated results results with experimentally detected results. Flux weighted cross section for positron production. Put the scintilator calibration in the thesis: Mean of ADC9 vs charge on the scope. Separate simulated and experimental systematic errors, then put them together in conclusions.
Text
Anstract
\addcontentsline{toc}{chapter}{Abstract} \chapter*{Abstract}
Positrons were produced using a tungsten target when impinged by an electron beam from the High Repetition Rate Linac (HRRL) at the Beam Lab of the Physics Department at Idaho State University (ISU). % To measure the intensity of positrons at five (1-5~MeV) different energies, two dipoles were used to bend positrons to the second tungsten target where they annihilate and create 511~keV photons. 511~keV photons were measured using two NaI detectors placed horizontally and operated in coincidence. % The positron beam creation and loss are explained with simulation studies using G4beamline. The simulation results are compared with the experiment. Although positron distribution in both simulation and experiment peaked at 3~MeV, the simulation predicted higher counts than the experiment.
Introduction
\chapter{Introduction}
\section{Positron Beam}
Positrons are used in several disciplines of sciences, like chemistry, physics, material science, surface science, biology and nanoscience~\cite{Chemerisov:2009zz}. Different approaches are used to generate positrons. The main challenge is increasing the intensity (or current) of the positron beam. One of the most common methods used to generate a positron beam is using an electron linac. The electron beam produces a positron beam by bremsstrahlung and pair production. One of the advantages of the linac based positron beam is its variable energy and intensity. %Other applications of positron
\subsection{Positron Beam for Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy} Positron annihilation spectroscopy is a non-damaging technique to detect defects in materials. It is based on the fact that positrons tend to annihilate near defects in the material~\cite{Pos-app1}. Different depths of the materials can be probed by using variable energy positron source and a linac based variable energy positron source may be used for this purpose. %Being the anti-matter of electron, it can be used to as high density energy source via annihilation in long term perspective [citation]. %Positrons can be transported to the cancer tumor and the radiation they emit in the annihilation can be used to kill the cancer cell [citation].
%\subsection{Positron Production Using Low Energy Electron Linac} \subsection{Positron Beam for Measuring The Impact of Two Photon Exchange } %Low energy positron beam The nucleon electromagnetic form factors are fundamental quantities that are related to the charge and magnetization distribution in the nucleon. Conventionally, the nucleon form factors are measured using the Rosenbluth Technique (RT)~\cite{Rosenbluth1950}. The form factor scaling ratio, \begin{math}R=\mu _p G_{Ep} / G_{Mp}\end{math}, is measured using this technique is around unity as shown in the Fig.~\ref{rosen-com-RPT}~\cite{PhysRevD.49.5671}. Since the 1990's, a technique using elastic electron-proton polarization transfer to measure this ratio has been developed~\cite{PhysRevD.49.5671, PhysRevC.68.034325, WalkerThesis1989}. In this technique, form factor scaling ratio linearly decreases as the \begin{math}Q^2\end{math} increases, as shown in the Fig.~\ref{rosen-com-RPT}.
\begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.70]{1-Introduction/Figures/Sadiq_thesis_mot_RT_RPT_1.png} \caption{Form factor ratio, obtained by Rosenbluth Technique (hollow square) and results from Recoil Polarization Technique~\cite{PhysRevC.68.034325}.} \label{rosen-com-RPT} \end{figure}
The disagreement could arise from the fact that the Rosenbluth Techqniue assumes that only One Photon Exchange (OPE) occurs during the scattering while the Two Photon Exchange (TPE), which depends weakly on \begin{math}Q^2\end{math}, could also become considerable with increasing \begin{math}Q^2\end{math}~\cite{PhysRevC.68.034325}. The contribution of TPE can be obtained by comparing the ratio of \begin{math}e^+~p\end{math} to \begin{math}e^-~p\end{math} scattering. The interference of OPE and TPE can also be studied in the scattering process \begin{math}e^+e^- \rightarrow p\bar p\end{math}.
\section{Positron Beam Generation from Bremsstrahlung}
When a moving charged particle interacts with the electric field of another charged particle, it can be deflected and lose energy in the form of photons, as shown in the Fig.~\ref{fig:Theo-Brem}. This interaction is known as the bremsstrahlung process. The probability of this interaction increases with the atomic number of the material traversed by the incident charged particle. The Fig.~\ref{fig:Brems_photon_Ene} shows the photon energy distribution produced when the 12~MeV electron energy distribution from the Fig.~\ref{fig:Theo-Brems_ele_Ene} interacts with a 1~mm thick tungsten target. As shown in the Fig.~\ref{fig:Brems_photon_Ene}, the distribution peaks at 0.3~MeV. As the photon energy increases the number of photons produced decreases.
\begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.40]{2-Theory/Figures/bremsstrahlung/brems.eps} \caption{Photon generation from bremsstrahlung processes.} \label{fig:Theo-Brem} \end{figure}
The bremsstrahlung cross section given is by~\cite{brms-cors} \begin{equation} d \sigma = 4 Z^2r_e^2 \alpha \frac{d \nu}{\nu} \left \{ \left (1 + \left( \frac{E}{E_0} \right )^2 \right ) \left [ \frac{\phi_1(\gamma)}{4} - \frac{1}{3} \ln Z -f(Z)\right ] - \frac{2E}{3E_0} \left [ \frac{\phi_2(\gamma)}{4} - \frac{1}{3} \ln Z -f(Z)\right ] \right \}, \label{eq:Brem-cross} \end{equation} \noindent where $E_0$ is initial total energy of the electron, $E$ is final total energy of the electron, $\nu = \frac{E_0-E}{h}$ is frequency of the emitted photon, and $Z$ is atomic number of the target. $\gamma = \frac{100 m_ec^2 h \nu}{E_0 E Z^{1/3}}$ is charge screening parameter and $f(Z)$ is given by \begin{equation} f(Z) = (Z \alpha)^2 \sum_1^{\infty} \frac{1}{ n [ n^2 + (Z \alpha)^2]}, \end{equation} \noindent where $\alpha = \frac{1}{137}$ is fine-structure constant, $\phi_1$ and $\phi_2$ are screening functions that depend on Z. \begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.70]{2-Theory/Figures/En_photon_dnT1_logY.eps} \caption{Bremsstrahlung photon energy right after a tungsten foil in simulation.} \label{fig:Brems_photon_Ene} \end{figure} \begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.70]{2-Theory/Figures/En_e_upT1.eps} \caption{The electron energy distribution incident on a tungsten foil in simulation.} \label{fig:Theo-Brems_ele_Ene} \end{figure}
There are three competing processes that a photon can undergo when interacting with matter. The Fig.~\ref{fig:Theo-3pro-in-W} are the cross-sections for different types of photon interactions with tungsten as a function of photon energy. At electron volt (eV) energies which is comparable to the electron atomic binding energy, the dominant photon interaction is via the photoelectric effect. As the photon energy increases up to kilo electron volt (keV) range, the Compton scattering process starts to be more dominant. Although the photon is totally absorbed during the photoelectric effect, photons merely lose energy when undergoing the Compton scattering. As the photon energy reaches twice the rest mass energy of the electron, $i.e.$ 2 \begin{math} \times \end{math} 511~keV, the pair production begins to occur. The pair production becomes the dominant interaction process when photon energies are beyond 5~MeV~\cite{Krane}. In this process, a photon interacts with the electric field of the nucleus or the bound electrons and is converted into an electron and positron pair.
\begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.36]{2-Theory/Figures/xcom/Xcom9.eps} \caption{The cross-sections for different types of photon interactions with tungsten as a function of photon energy~\cite{nistxcom}.} \label{fig:Theo-3pro-in-W} \end{figure}
Using natural unit, where \begin{math}c \equiv 1\end{math}, the differential cross-section for pair production can be expressed as \begin{equation} \begin{array}{l} \frac{d \sigma}{d \epsilon_1 d \theta_1 d \theta_2} = 8 \left ( \frac{\pi a}{\sinh (\pi a)} \right )^2 \frac{a^2}{2 \pi} \frac{e^2}{\hbar c} \left ( \frac{\hbar}{m_e c }\right )^2 \frac{\epsilon_1 \epsilon_2}{k^3} \theta_1 \theta_2 \\ \\ \times \left \{ \frac{V^2(x)}{q^4} \left [ k^2 (u^2 + v^2) \xi \eta - 2 \epsilon_1 \epsilon_2 (u^2 \xi^2 + v^2 \eta^2 ) + 2 (\epsilon_1^2 + \epsilon_2^2)uv \xi \eta cos(\phi) \right ] \right . \\ \\ \left . + a^2W^2(x) \xi^2 \eta^2 \left [ k^2(1 - (u^2+v^2)\xi \eta - 2 \epsilon_1 \epsilon_2 (u^2 \xi^2 + v^2 \eta^2) -2 (\epsilon_1^2 + \epsilon_2^2) u v \xi \eta \cos(\phi)\right ]\right \}, \\ \end{array} \end{equation}
\noindent where $k$ is photon energy, $\theta_{1}$ and $\theta_2$ are the scattering angle of $e^+$ and $e^-$ respectively, $ \phi = \phi_1 - \phi_2$ is the angle between the $e^+$ and $e^-$ pair, $\epsilon_1$ and $\epsilon_2$ are the energy of the positron and electron respectively. Other constants are $u = \epsilon_1 \theta_1$, $v=\epsilon_2 \theta_2$, $\xi = \frac{1}{1+u^2}$, $\eta= \frac{1}{1+v^2}$, $q^2 = u^2 + v^2 + 2 u v \cos(\phi)$, $x= 1-q^2 \xi \eta$, $a = \frac{Ze^2}{\hbar c}$, $V(x) = 1 + \frac{a^2}{(1!)^2} + \frac{a^2 (1+a^2) x^2}{(2!)^2} + \frac{a^2 (1+a^2)(2^2+a^2)x^4 x^2}{(3!)^2} + \cdots$, and $W(x) = \frac{1}{a^2} \frac{d V(x)}{d x}$.
In pair production, positron and electron pairs are created back to back in the center of mass frame. In the lab frame, electrons and positrons tend to move in the direction of the photon, as shown in the Fig.~\ref{fig:Theo-pair-pro}. The positron and electron carry away the energy from the photon that is in excess of 1.022~MeV. In the center of mass frame, the kinetic energy is equally shared. Photons with an energy above 1.022~MeV in the bremsstrahlung spectrum of the Fig.\ref{fig:Brems_photon_Ene} have the potential to create electron and positron pairs. The Fig.~\ref{fig:Theo-brem} is the simulation of 10 million 12~MeV mono energy electrons impinging on a tungsten target with 1.016~mm thickness. Turning on the annihilation process resulted in a 511~keV peak on top of the bremsstrahlung spectrum. This 511~keV peak represents photons produced when the created positrons from the pair production annihilate with atomic electrons inside the tungsten target.
\begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.650]{2-Theory/Figures/Pair_Production/Pair_Production.png} \caption{Pair production.} \label{fig:Theo-pair-pro} \end{figure}
\begin{figure} \centering {\scalebox{0.75} [0.7]{\includegraphics{2-Theory/Figures/pair/on/Eng2.eps}}} \\ \caption{Photon spectrum of created by million 12~MeV mono energy electrons impinging on a 1.016~mm thick tungsten target.} \label{fig:Theo-brem} \end{figure}
\section{Emittance Measurement} Emittance is an important parameter in accelerator physics. When the emittance and Twiss parameters are given at the exit of the gun, one will be able to calculate the beam size and the divergence at any given point along the beamline. To study the process of positron creation, one need to know the beam size and divergence on the target. Emittance and Twiss parameters are input parameters for any accelerator simulation tools that can be used to study the experimental processes and to make predictions.
\subsection{Emittance} In accelerator physics, Cartesian coordinate system is used to describe the motion of the accelerated particles. The $z$-axis of Cartesian coordinate system is defined as the natural coordinate that is going along the electron beam line. The $x$-axis and $y$-axis are horizontal and vertical coordinates which constitute the transverse beam profile. For the convenience of representation, one may use $z$ to represent transverse coordinates and express longitudinal profile with natural coordinates $s$ along the beamline. The transverse beam profiles are described as a function of the longitudinal coordinate, $i.e.$ $x(s)$ and $y(s)$. The angle of an accelerated charge regarding the designed orbit can be defined as $z'=\frac{dz}{ds}$.
The phase space $z'$ vs. $z$ of the beam is an ellipse with invariant area (along the beamline). This invariant is called the Courant-Snyder invariant~\cite{Conte}. The transverse emittance $\epsilon$ of the beam is defined to be the area of the ellipse that contains 90\% of the particles. Beam divergence and Twiss parameters are related to the beam size and divergence by \begin{equation} \sigma_{x}(s)=\sqrt{\epsilon _x (s) \beta _x (s)},~ \sigma_{x'}(s)=\sqrt{\epsilon _x (s) \gamma _x (s)}, \label{eq:twiss-emit} \end{equation}
\noindent where $\epsilon_{x}$ is beam horizontal emittance, $\sigma_{x}$ is rms beam size, $\sigma_{x'}$ is rms beam divergence, and $\beta _x $ and $\gamma _x$ are two of the Twiss parameters.
\subsection{Emittance Measurement} The HRRL beam emittance was measured using an Optical Transition Radiation (OTR). Transition radiation was theoretically predicted by Ginzburg and Frank~\cite{Ginzburg-Frank} in 1946 to occur when a charged particle passes the boundary of two medium and emits radiation. %The particle carries certain field when it passes through certain medium with certain motion~\cite{ENM-Jackson}. When it passes into the second medium, it has to reorganize its field characteristics at the boundary, and emit pieces of the field in the form electromagnetic radiation. The fields are emitted in the forward and backward directions~\cite{OTR-Gitter}. The backward radiated photons An OTR based viewer was installed to observe electron beam size at the high electron currents, available using the HRRL at 15~MeV with 200~ns macro pulse width and 37.2~mA peak current. The visible light is produced when a relativistic electron beam crosses the boundary of two mediums with different dielectric constants. Visible radiation is emitted at an angle of 90${^\circ}$ with respect to the incident beam direction when the electron beam intersects the target at a 45${^\circ}$ angle. These backward-emitted photons are observed using a digital camera and can be used to measure the shape and the intensity of the electron beam based on the OTR distribution. Although an emittance measurement can be performed in a several ways~\cite{emit-ways, sole-scan-Kim}, the quadrupole scanning method~\cite{quad-scan} was used to measure the emittance, Twiss parameters, and beam energy in this work.
\subsection{Quadrupole Scanning Method} Fig.~\ref{q-scan-layout} illustrates the beamline components used to measure the emittance for the quadrupole scanning method. A quadrupole is positioned at the exit of the linac to focus or de-focus the beam as observed on the OTR view screen. The 3.1~m distance between the quadrupole and the screen was chosen in order to minimize chromatic effects and to satisfy the thin lens approximation. %The quadrupole and the screen are located far away to minimize chromatic effects and to increase the veracity of the thin lens approximation used to calculate beam optics. \begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.55]{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f1.eps} \caption{Apparatus used to measure the beam emittance.} \label{q-scan-layout} \end{figure} Assuming the thin lens approximation, $\sqrt{k_1}L << 1$, is satisfied, the transfer matrix of a quadrupole magnet may be expressed as % thin lens approximation (sqrt{k1}*L << 1). In our case sqrt{k1}*L =0.07 \begin{equation} \label{quad-trans-matrix} \mathrm{\mathbf{Q}}=\Bigl(\begin{array}{cc} 1 & 0\\ -k_{1}L & 1 \end{array}\Bigr)=\Bigl(\begin{array}{cc} 1 & 0\\ -\frac{1}{f} & 1 \end{array}\Bigr), \end{equation} where $k_{1}$ is the quadrupole strength, $L$ is the length of quadrupole, and $f$ is the focal length. A matrix representing the drift space between the quadrupole and screen is given by \begin{equation} \label{drift-trans-matrix} \mathbf{\mathbf{S}}=\Bigl(\begin{array}{cc} 1 & l\\ 0 & 1 \end{array}\Bigr), \end{equation} where $l$ is the distance between the scanning quadrupole and the screen. The transfer matrix $\mathbf{M}$ of the scanning region is given by the matrix product $\mathbf{SQ}$. In the horizontal plane, the beam matrix at the screen ($\mathbf{\sigma_{s}}$) is related to the beam matrix of the quadrupole ($\mathbf{\sigma_{q}}$) using the similarity transformation \begin{equation} \mathbf{\mathbf{\sigma_{s}=M\mathrm{\mathbf{\mathbf{\sigma_{q}}}}}M}^{\mathrm{T}}. \end{equation} where the $\mathbf{\sigma_{s}}$ and $\mathbf{\sigma_{q}}$ are defined as~\cite{SYLee} \begin{equation} \mathbf{\mathbf{\sigma_{s,\mathnormal{x}}=}}\Bigl(\begin{array}{cc} \sigma_{\textnormal{s},x}^{2} & \sigma_{\textnormal{s},xx'} \\ \sigma_{\textnormal{s},xx'} & \sigma_{\textnormal{s},x'}^{2} \end{array}\Bigr) ,\; \mathbf{\mathbf{\sigma_{q,\mathnormal{x}}}}=\Bigl(\begin{array}{cc} \sigma_{\textnormal{q},x}^{2} & \sigma_{\textnormal{q},xx'}\\ \sigma_{\textnormal{q},xx'} & \sigma_{\textnormal{q},x'}^{2} \end{array}\Bigr). \end{equation} \noindent %By defining the new parameters~\cite{quad-scan}, $A \equiv \sigma_{11},~B \equiv \frac{\sigma_{12}}{\sigma_{11}},~C \equiv\frac{\epsilon_{x}^{2}}{\sigma_{11}}$ By defining the new parameters~\cite{quad-scan} \begin{equation} A \equiv l^2\sigma_{\textnormal{q},x}^{2},~B \equiv \frac{1}{l} + \frac{\sigma_{\textnormal{q},xx'}}{\sigma_{\textnormal{q},x}^{2}},~\text{and}~C \equiv l^2\frac{\epsilon_{x}^{2}}{\sigma_{\textnormal{q},x}^{2}}. \end{equation} The matrix element $\sigma_{\textnormal{s},x}^{2}$, the square of the rms beam size at the screen, may be expressed as a parabolic function of the product of $k_1$ and $L$ \begin{equation} \sigma_{\textnormal{s},x}^{2}=A(k_{1}L)^{2}-2AB(k_{1}L)+(C+AB^{2}). \label{par_fit} \end{equation}
The emittance measurement was performed by changing the quadrupole current, which changes $k_{1}L$, and measuring the corresponding beam image on the view screen. The measured two-dimensional beam image was projected along the image's abscissa and ordinate axes. A Gaussian fitting function is used on each projection to determine the rms value, $\sigma_{\textnormal{s}}$ in Eq.~(\ref{par_fit}). Measurements of $\sigma_{\textnormal{s}}$ for several quadrupole currents ($k_{1}L$) is then fit using the parabolic function in Eq.~(\ref{par_fit}) to determine the constants $A$, $B$, and $C$. The emittance ($\epsilon$) and the Twiss parameters ($\alpha$ and $\beta$) can be found using Eq.~(\ref{emit-relation}). \begin{equation} \epsilon=\frac{\sqrt{AC}}{l^2},~\beta=\sqrt{\frac{A}{C}},~\alpha=\sqrt{\frac{A}{C}}(B+\frac{1}{l}). \label{emit-relation} \end{equation}
Apparatus
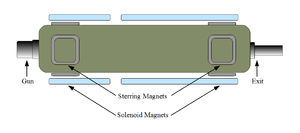
\chapter{Apparatus} \section{HRRL Beamline} A 16~MeV S-band High Repetition Rate Linac (HRRL) located at the Beam Lab of the Department of Physics, Idaho State University is used to generate incident 12~MeV electron beam on a tungsten foil. The energy of the HRRL is tunable between 3 to 16~MeV and its repetition rate variable from 1 to 300~Hz. Basic parameters of the HRRL are given in Table~\ref{tab:hrrl-par}. As shown in Figure~\ref{fig:app-hrrl-cavity}, the HRRL has a thermionic gun, vertical and horizontal steering magnet sets on two ends and two solenoid magnets.
\begin{table} \centering \caption{The Basic Parameters of the HRRL.} \begin{tabular}{lcc} \toprule {Parameter} & {Unit} & {Value} \\ \midrule maximum energy & MeV & 16 \\ peak current & mA & 100 \\ repetition rate & Hz & 300 \\ absolute energy spread & MeV & 2-4 \\ macro pulse length & ns & $>$50 \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:hrrl-par} \end{table}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering %\includegraphics[scale=0.6]{3-Apparatus/Figures/HRRL_Cavity.eps} \includegraphics[scale=0.6]{3-Apparatus/Figures/HRRL_Cavity4.png} \caption{The configuration of the HRRL cavity.} \label{fig:app-hrrl-cavity} \end{figure}
The accelerator's cavity was relocated to the position shown in Figure~\ref{fig:app-hrrl-line} to provide enough space for a beam line that can transport either positrons or electrons. The beam elements are described in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-coordinates}. Quadrupole and dipole magnets were added to the new beam line as well as diagnostic tools like OTR and YAG screens, Faraday cups and toroids were installed to measure the electron beam size and the current. Energy slits were installed to control energy/momentum spread of the beam after the first dipole. A retractable tungsten foil target (T1) was placed between the 1st and 2nd triplets and used to produce positrons when the electron beam interacts with it. The room where the HRRL is located is divided by a wall into two parts; the accelerator side and the experimental cell. A beam pipe at the end of the 90 degree beamline goes through a hole on the wall and delivers the beam from the accelerator side to the experimental cell. The positron detection system consisting of two NaI detectors was placed at the end of the beamline in the experimental cell side as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:app-hrrl-line}.
\begin{sidewaysfigure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.3]{3-Apparatus/Figures/HRRL_line.eps} \caption{The HRRL beamline layout and parts.} \label{fig:app-hrrl-line} \end{sidewaysfigure}
\begin{table} \centering \caption{The HRRL Beamline Parts and Coordinates.} \begin{tabular}{lll} \toprule {Label} & {Beamline Element} & {Distance from} \\ {} & {} & {Linac Exit (mm)} \\ \midrule Q1 & quadrupole & 335 \\ Q2 & quadrupole & 575 \\ Q3 & quadrupole & 813 \\ T1 & e$^+$ production target & 1204 \\ Q4 & quadrupole & 1763 \\ Q5 & quadrupole & 2013 \\ Q6 & quadrupole & 2250 \\ D1 & dipole & 2680 \\ S1 & OTR screen & 3570 \\ FC1 & Faraday cup & 3740 \\ EnS & energy slit & 3050 \\ S2 & YAG screen & 3410 \\ Q7 & quadrupole & 3275 \\ D2 & dipole & 3842 \\ FC2 & Faraday cup & 4142 \\ Q8 & quadrupole & 4044 \\ Q9 & quadrupole & 4281 \\ Q10 & quadrupole & 4571 \\ T2 & annihilation target & 7381 \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:app-hrrl-coordinates} \end{table}
\section{The OTR Imaging System} The OTR target is 10~$\mu$m thick aluminum foil with a 1.25 inch diameter. The OTR is emitted in a cone shape with the maximum intensity at an angle of $1/\gamma$ with respect to the reflecting angle of the electron beam~\cite{OTR-Gitter}. Three lenses with 2 inches of diameter are used for the imaging system to avoid optical distortion at lower electron energies. The focal lengths and position of the lenses are shown in Figure~\ref{image_sys}. The camera used is a JAI CV-A10GE digital camera with a 767 by 576 pixel area. The images were taken by triggering the camera synchronously with the electron gun. \begin{figure}[htbp] \centering {\scalebox{0.35} [0.35]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/image_sys2.eps}}} {\scalebox{0.40} [0.40]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f3}}} \caption{The OTR imaging system.} \label{image_sys} \end{figure}
\section{Positron Detection} When the electron beam is incident on T1, photon and secondary electrons are created along with positrons. These particles are the main source of noises in the experiment. The positrons were transported to the second tungsten target (T2) which was shielded from noise by the concrete wall and Pb bricks. The setup is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:HRRL-pos-det-setup}. A 6-way cross was placed at the end of the beamline to hold T2. The 6-way cross has three 1~mil (0.0254 millimeters) thick stainless steel windows. The two horizontal windows perpendicular to the beamline were for the exiting of the 511~keV photons created during the positron annihilation. The one at the end of the 90 degree beamline was used as the beam exit. Two NaI detectors were placed facing two exit windows to detect the photons produced in T2. A lead brick collimator with 2 inch diameter hole placed between the exit window and NaI detector. A scintillator and a Faraday cup were placed at the end of the beamline and were used to tune the electron and positron beam. When positrons reach T2, they are thermalized and annihilated inside T2. During the thermalization, a positron loses its kinetic energy. When it annihilates with an electron, two 511~keV photons are emitted back to back. Two NaI detectors and accelerator RF pulse are in coincidence mode to detect these back to back scattered 511~keV photons and to eliminate noises.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{3-Apparatus/HRRL_Pos_detection2.eps} \caption{The positron detection system: T2 (pink) was placed with 45$^\circ$ angle to the horizontal plane first, then rotated 45$^\circ$ along the vertical axis.} \label{fig:HRRL-pos-det-setup} \end{figure}
\subsection{NaI Detectors}
NaI crystals, shown as in Figure~\ref{fig:PMT}, were used to detect 511~keV photons from positron annihilation. Originally, the detectors had pulse lengths around 400~$\mu$s. Resistors and capacitors were added to the PMT bases and pulse length is shorten to less than 1~$\mu$s. The NaI detector has one dynode and one anode outputs. The PMT base configuration of the NaI detector is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:PMT_base} and bases made shown in Figure~\ref{fig:new_base_made}. The crystal is SAINT-GOBAIN CRYSTAL \& DETECTORS (MOD. 3M3/3) NaI crystal with a dimension of $3"\times3"$. The PMT base takes HV around -1150~V. It takes ADC 5.7~$\mu$s to convert the analog signal to a digital signal. The signal from anode was delayed 6~$\mu$s by a long cable and sent to the ADC. \begin{table} \centering \caption{The Radioactive Sources and Corresponding Photon Peaks.} \begin{tabular}{lccc} \toprule {Radioactive Sources} & Unit & First Peak & Second Peak \\ \midrule Co-60 & keV & 1173 & 1332 \\ Na-22 & keV & 511 & 1275 \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:Na22_Co60} \end{table}
\begin{figure}[htbp]
\centering
\includegraphics[scale=0.4]{3-Apparatus/SAINT-GOBAIN_3M33.png}
\caption{The NaI crystal dimension.}
\label{fig:PMT}
\end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.75]{3-Apparatus/Modified_PMT.png} \caption{The modified PMT base design.} \label{fig:PMT_base} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.13]{3-Apparatus/IAC_NaI.png} \caption{The NaI crystals and new bases.} \label{fig:new_base_made} \end{figure}
The NaI detectors were calibrated using a Na-22 and a Co-60 sources with photon peaks indicated in Table~\ref{tab:Na22_Co60}. Figure~\ref{fig:NaI_Co60_Scope} is the oscilloscope image of Co-60 photon pulses incident on the detector with new PMT. The calibrated NaI detector spectrum of Na-22 and Co-60 sources are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:NaI-Calb}. The rms values of the fits on the four peaks shown in Figure~\ref{fig:NaI-Calb} are $\sigma_{Na, 511}=18.28\pm0.04$~keV, $\sigma_{Na, 1275}=44.51\pm0.27$~keV, $\sigma_{Co, 1173}=42.49\pm0.24$~keV, and $\sigma_{Co, 1332}=50.30\pm0.39$~keV.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.4]{3-Apparatus/NaI_Co60_Scope.png} \caption{Pulses of the Co-60 source obtained using new PMT. The amplitude of of the pulse is about 60~mV. The rise time of the pulse is larger than 50 ns, and the fall time is larger than 700~ns.} \label{fig:NaI_Co60_Scope} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.75]{3-Apparatus/Figures/NaI_Calbration/NaI_Calb1.eps} \caption{The calibrated NaI spectrum of Na-22 and Co-60 sources.} \label{fig:NaI-Calb} \end{figure}
The Na-22 source was placed between two NaI detectors to photon spectrum for both when RF was on (no electrons were fired from accelerator gun) and off. The 511 keV peak in the right NaI detector was shifted to the right side of spectrum by 17 channels when RF was on as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:NaI-peak-shift} (a) while in the left NaI the peak shifted to the left by 28 channels. When 3~MeV positrons were transported to T2, the observed 511~keV peak was at the right side comparing to the peak observed in Na-22 source run with RF on. The reason of creating the shift is unclear and needs further investigation. One must keep in mind that the NaI detectors' calibration factor do change in the experiment.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{ccc} \centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/Figures/RunDec2012/PeakShiftNaIR4.eps}}} \\ (a) Right NaI detector.\\ \\ \\ \centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/Figures/RunDec2012/PeakShiftNaIL4.eps}}}\\ (b) Left NaI detector. \\ \end{tabular} \caption{The 511 keV peak in NaI detectors shifted when RF is on.} \label{fig:NaI-peak-shift} \end{figure}
\subsection{Trigger for The DAQ}
The trigger for the DAQ requires a coincidence between two NaI detectors and the electron accelerator gun pulse. The last dynode signals from left and right NaI detectors were inverted using a ORTEC 474 amplifier and sent to a CAEN Mod. N842 Constant Fraction Discriminator (CFD). The RF noise from the accelerator was as large as the signal from the NaI detector. Since it was correlated in time with the gun pulse, the gun pulse was used to generate a VETO pulse that prevent the CFD from triggering on this RF noise. After this discrimination and RF noise rejection, the discriminated dynode signals were sent to an GG 8000-01 octalgate generator that increased the width of the logic signals and created one larger pulse from multiple smaller pulses. This can prevent multiple pulsing. Then the signals were sent to a LeCroy model 622 quad coincidence to generate coincident signals with the electron gun. These coincident signals sent to the third channel of the GG800-01 octalgete generator to generate coincidence between the two signals from detector and gun trigger as given by \begin{equation} \text{(NaI~Left~\&\&~Gun~Trigger)~\&\&~(NaI~Rgiht~\&\&~Gun~Trigger)}. \end{equation} This is to make sure that there is a trigger only when there are trigger signals from both detectors and the electron gun is firing.
The ADC was set to convert the analog signals from the NaI detectors to digital signals when the electron gun is firing. But the converted date were fast cleared unless there is a veto. The first output of the GG800-01 octalgete generator was sent to the CAEN Mod. N93B dual timer to create the veto that prevent the ADC from fast clearing the converted data. The second output of the GG800-01 octalgete generator was sent to ORTEC Gate \& Delay Generator to be delayed by 6~$\mu$s, a necessary time to convert the analog signal from the anode to digital signal, and was used as the trigger for the DAQ to read data in the ADC.
%When there is a trigger in the ADC, the data in the ADC is read
Simulation
\chapter{Simulation} Simulations were performed using G4beamline~\cite{muonsinc} to study the processes of position generation and transportation. ``G4beamline is a particle tracking and simulation program based on the Geant4~\cite{geant4} toolkit that is specifically designed to easily simulate beamlines and other systems using single-particle tracking~\cite{muonsinc}." The simulation predicts that at least one positron is created per 1000 incident 10~MeV electrons. A large amount of beam loss was observed during the initial simulation. As a result,the simulation was divided into three steps based on the locations along the beamline that saw more than 90\% beam loss. A new beam event generator was created based on the results of the previous step in the simulation.
The first step generated an electron beam with the energy distribution that was observed in the experiment. The electrons were focused by three quadrupoles onto the target T1. Electrons transversing T1 produced bremsstrahlung photons of sufficient energy to produce $e^+e^-$ pairs. The second step simulated the transportation of positrons exiting T1 to the entrance of the first dipole D1. The third step transported positrons from the entrance of D1 to the annihilation target T2, the interactions of positrons with T2, and the detection of the resulting 511~keV photon pairs.
\section{Step 1 - The Electron Beam Generation and Transpiration to T1} In one of the simulation step, an electron beam was generated with an energy distribution that was observed in the experiment. The emittance, the Twiss parameters, and the energy distribution of the electron beam were measured experimentally and used to generate the electron beam. The energy distribution of the electron beam is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:En-Scan}. The distribution was fit using two skewed Gaussian distributions. The fit parameters given in Table~\ref{tab:En-Scan_resluts} were used to generated the electrons.
A series of virtual detectors were placed along the beamline to sample the beam. As an example, three detectors and T1 are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:T1_UpD_DwD2}. The electron beam was detected by DUPT1 (Detector 25.52~mm UPstream of T1). Positrons, electrons, and photons generated during the interaction of the electron beam with T1 were observed by DT1 (Detector of T1) and DDNT1 (Detector 25.52~mm DowNstream of T1). %In Figure~\ref{fig:SimS1_pos_En_DDNT1}, $13.8 \times 10^{10}$ electrons shot at T1 and generated positrons positrons shown in blue.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{4-Simulation/Figures/sim_setup_T1_UpD_DwD2.png} \caption{T1 is the positron production target. DUPT1 is a virtual detector located upstream of T1 to detect the incoming electron beam. DDNT1 is a virtual detector downstream of T1. DT1 is a virtual detector that is placed right after T1 parallel to it.} \label{fig:T1_UpD_DwD2} \end{figure}
\subsection{The Positron Beam on DDNT1}
In the first step, $1.38 \times 10^{10}$ (13799743900) electrons, as shown by the dotted dashed line in Figure~\ref{fig:SimS1_T1UPDN}, incident on T1 and created positrons represented by solid the line. The dashed line is the electrons that were detected downstream of T1. In Figure~\ref{fig:SimS1_T1UPDN}, 1000th of the total number of particles are shown due to the large size. The incident electrons were detected by the virtual detector DUPT1 and downstream positrons and electrons were detected by the DDNT1.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/overlay2.eps} \caption{Energy distribution of incident electrons (dotted dashed line), electrons after T1 (dashed line) and created positrons (solid line).} \label{fig:SimS1_T1UPDN} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/X_e+_DDNT1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/Y_e+_DDNT1.eps}}} \\ (a) $x$ projection. & (b) $y$ projection. \\ {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/XP_e+_DDNT1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/YP_e+_DDNT1.eps}}} \\ (c) $x$ projection of the divergence. & (d) $y$ projection of the divergence.\\ {\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/XY_e+_DDNT1.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/XY_e+_DDNT1_zoom.png}}} \\ (e) The transverse beam profile. & (f) The transverse beam profile zoomed in. \\ \end{tabular} \caption{The transverse beam projections and angular distributions of positrons detected.} \label{fig:DDNT1_results} \end{figure}
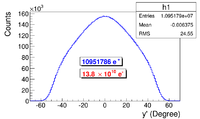
The positron beam distribution detected by DDNT1 is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_results}. The $y$ $vs.$ $x$ spatial distribution of the beam is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_results}~(e) and Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_results} (f). As can be seen from Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_results} (b) and (d), the $y$ spatial distribution and divergence of the positron beam have a sharp drop in counts in the region between $-25.8$~mm and $-27.2$~mm from the beam center. Figure~\ref{fig:sim-DDNT1-T1-geo} shows the geometry and location of T1 and DDNT1. If the size of T1 were to be increased, it would eventually intersect with DDNT1 at a distance between $25.8$~mm and $27.2$~mm from the beam center, $i.e.$ the edge of the T1 is facing this $1.4$~mm wide low count area. %This is the result of the target's thickness of 1.016 mm and the 45$^{\circ}$ angle of intersection ($1.016\sqrt{2}=1.44$). The edge of the target does not produce many positrons compared to the face of the target. \begin{figure}[htbp] \centering %\includegraphics[scale=0.18]{4-Simulation/Figures/sim-DDNT1-T1-geo.png} \includegraphics[scale=0.9]{4-Simulation/Figures/sharp_drop2.eps} \caption{The geometry of the target T1 and the virtual detector DDNT1.} \label{fig:sim-DDNT1-T1-geo} \end{figure}
As shown in Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_YpY}, the $y$ distribution counts decreases at $\theta$ = 45$^{\circ}$. Positrons were emitted from both the downstream and upstream side of T1. Positrons from the downstream side of T1 intersected the detector at angles below 45$^{\circ}$ while positrons from the upstream side of T1 begin to hit the detector at angles beyond 45$^{\circ}$. Neither positrons upstream nor downstream of T1 traveled to the 1.4~mm wide low count area. Only positrons created on the edge of T1 reached the low count area between 25.8~mm~$<x<$~27.2~mm. Thereby, the counts in this area are lower comparatively.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/STSimS1_YYP_DDNT1.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.4} [0.4]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/STSimS1_YYP_DDNT1_zoom.png}}} \\ (a) y' $vs.$ y. & (b) y' $vs.$ y zoom. \\ \end{tabular} \caption{The positron beam $y'$ $vs$. $y$ detected by DDNT1.} \label{fig:DDNT1_YpY} \end{figure}
\subsection{The Positron Beam on Virtual Detectors DQ4 and DD1}
The positron beam energy distribution on virtual detectors DQ4 (Detector placed at the entrance of Q4) and DD1UP (Detector placed at the UPstream entrance of D1) are shown in Figure~\ref{STSimS1_En_DQ4_DD1}. Nearly 90\% of positrons are lost when transported from DQ4 to DD1UP due to the large divergence of positrons. %484.4 mm from T1 to DQ4. 1476.4 mm from T1 to DD1UP. 992 mm from DQ4 to DD1UP.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{ccc} \centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/En_e+_DQ4.eps}}} \\ (a) The positron energy distribution on DQ4. \\ \centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/En_e+_DD1.eps}}}\\ (b) The positron energy distribution on DD1. \\ \end{tabular} \caption{The positron beam energy distribution detected downstream of T1.} \label{STSimS1_En_DQ4_DD1} \end{figure}
\section{Step 2 - The Transportation of The Positron Beam from DDNT1 to The Entrance of The First Dipole}
In the step 1, the beam incident on detector DDNT1 was sampled to generate positrons in the second step. At detector DDNT1, the higher energy positrons tend to have smaller polar angles and be closer to the beam center and vise versa. So, in the step 2, positrons were generated in 1~keV/c momentum bins with different weights and spatial and angular distributions. The positrons are generated at DDNT1 (where they were sampled) and transported to the entrance of D1 as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:STSimSetupS2}. The virtual detectors were placed at the entrance of Q4 (DQ4) and D1 (DD1UP) to track the positrons. The beam was detected using DD1UP to generate positrons in the third step.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.60]{4-Simulation/Figures/STSimSetupS2_2.png} \caption{The generation and transpiration of the positron beam in step 2. The virtual detectors were used to track the positrons.} \label{fig:STSimSetupS2} \end{figure}
%\section{Comparing Positrons in Step 1 and Step 2} % %Positrons generated in step 1 and step 2 detected on the virtual detector located at the entrance of the first dipole is compared to validate the positrons generated in the step 2 is similar to the beam in step 1. Results, given in Figure~\ref{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-en},~\ref{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-xy},~\ref{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-xpyp}, show that the beam regenerated in step 2 seems is similar to the one in step 1. % %\begin{figure}[htbp] %\begin{tabular}{cc} %\centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/EnDD1.eps}}} \\ %(a) Beam Energy in step 1\\ % \\ %\centerline{\scalebox{0.6} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s2/EnDD1.eps}}}\\ %(b) Beam Energy in step 2\\ %\end{tabular} %\caption{Comparison of positron energy in first and second steps at virtual detector located at the entrance of first dipole.} %\label{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-en} %\end{figure} % %\begin{sidewaysfigure} %\begin{tabular}{cc} %{\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/xDD1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s2/xDD1.eps}}} \\ %(a) Beam X-projection in step 1 & (b) Beam X-projection in step 2 \\ %{\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/yDD1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s2/yDD1.eps}}} \\ %(c) Beam Y-projection in step 1 & (d) Beam Y-projection in step 2 \\ %\end{tabular} %\caption{Comparison of positron transverse beam profile in first and second steps at virtual detector located at the entrance of first dipole.} %\label{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-xy} %\end{sidewaysfigure} % %\begin{sidewaysfigure} %\begin{tabular}{cc} %{\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/xPDD1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s2/xPDD1.eps}}} \\ %(c) Beam divergence X-projection in step 1& (d) Beam divergence X-projection in step 2\\ %{\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s1/yPDD1.eps}}} & {\scalebox{0.5} [0.6]{\includegraphics{4-Simulation/Figures/s/s2/yPDD1.eps}}} \\ %(e) Beam divergence Y-projection in step 1 & (f) Beam divergence Y-projection in step 2 \\ %\end{tabular} %\caption{Comparison of positron transverse divergence in first and second steps at virtual detector located at the entrance of first dipole.} %\label{fg:sim-s1s2-comp-xpyp} %\end{sidewaysfigure}
\section{Step 3 - The Transportation of Positrons from the Entrance of The First Dipole to T2 and The Detection of 511~keV Photons}
In this simulation, the positron beam were started at the entrance of the first dipole (DD1UP) as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:STSimSetupS2}). The beam was bent $90^{\circ}$ by two dipoles and transported to annihilation target T2 located at the end of the beamline as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:T2}. Two virtual detectors with 48~mm diameter (48~mm is the inner diameter of the beam pipe) were placed upstream and downstream of T2 to detect positrons. Two other detectors with the same diameters as T2 were placed parallel to T2 at two ends of T2 to detect positrons. Two NaI virtual detectors were placed horizontally 170~mm away from the beamline center to detect photons. 2 inches thick Pb bricks with 2-inch diameter openings facing T2 were placed around NaI detectors. When a positron annihilates inside T2, two back-to-back scattered 511~keV photons are generated with the same event number. When both NaI detectors detect 511~keV photons with a same event number, 1 event is registered which indicates one positron is being annihilated inside T2. %The NaI detectors register 1 event when they both detect 511~keV photons with same event number which indicates one positron is being annihilated inside T2.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.4]{4-Simulation/Figures/HRRL_T2.png} \caption{T2 and virtual detectors located upstream (DT2UP) and downstream (DT2DN) of T2 are shown at the center of the figure. NaI detectors and Pb shielding are located horizontally at two sides.} \label{fig:T2} \end{figure}
\subsection{Positrons Detected by The Detection System}
The detector efficiency chart shown in Figure~\ref{fig:NaI_Ef}, obtained from SAINT-GOBIAN CRYSTALS~\cite{NaI-Eff}, indicates the NaI crystals has 68\% efficiency for 511~keV photons. If two detectors are operated in coincidence mode, the detection efficiency of the system is $68\% \times 68\%~=~46.24\%$. Figure~\ref{fig:e+_Generated_and_Detected} shows the counts of 511~keV photon pairs detected in coincidence mode (multiplied to 46.24\%) overlaid with the positrons that are detected on DDNT1.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.60]{4-Simulation/Figures/NaI_Ef_3.png} \caption{NaI detector efficiency obtained from SAINT-GOBIAN CRYSTALS~\cite{NaI-Eff}.} \label{fig:NaI_Ef} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.70]{4-Simulation/Figures/overlay/e+_Generated_and_Detected.eps} \caption{Positrons detected on virtual detector DDNT1 and 511~keV photon pairs detected by the NaI detectors in coincidence mode when Q7 is at 0~A, 3.5~A and 10~A.} \label{fig:e+_Generated_and_Detected} \end{figure}
%\begin{figure}[htbp] %\centering %\includegraphics[scale=0.70]{4-Simulation/Figures/S2E/S2E.eps} %\caption{Results of simulation of positron generation and transportation process.} %\label{fig:S2E} %\end{figure} % % %\begin{sidewaysfigure} %\centering %\includegraphics[scale=1.2]{4-Simulation/Figures/S2E/S2E_32.eps} %\caption{Results of simulation of positron generation and transportation process.} %\label{fig:S2E_32} %\end{sidewaysfigure}
\subsection{Beam Loss Study} The positron distribution observed after T1 was used to send a sample of positrons towards the dipole D1 that would be used to create a positron event generator at the entrance to dipole D1. This procedure was repeated at D1 in order to generate a large positron sample at the annihilation target (T2). This three step procedure reduced the simulation time to generate large positron samples. $7.253 \times 10^{16}$ electrons incident on the T1 created $5.756 \times 10^{13}$ positrons shown in Column 2 in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par}. Columns 2 and 3 in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par} represent the number of positrons that would need to be generated in order to observe the number of positrons in the remaining columns. 511~keV photon pairs were detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode are shown in the last column of Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par}. Positrons along the beamline and 511~keV photon pairs detected are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:TransEff}.
\begin{sidewaystable} \centering \caption{Predicted Number of Positrons Transported and Number of 511~keV Photons Detected.} \begin{tabular}{lccccccccc} %\begin{tabular}{lllllllllll} \toprule Energy & On & Enter & Enter & Exit & Enter & Enter & Exit & Reach & $\gamma$ on \\ (MeV) & DDNT1 & Q4 & D1 & D1 & Q7 & D2 & D2 & T2 & NaI \\ \midrule $1.02 \pm 0.25$ & $2.5 \times 10^{12} $ & $1.4 \times 10^{10} $ & $1.4 \times 10^{9} $ & $1.2 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.6 \times 10^{7} $ & $2.7 \times 10^{6} $ & $1.2 \times 10^{6} $ & $4.3 \times 10^{3} $ & $7$\\ $1.50 \pm 0.25$ & $4.9 \times 10^{12} $ & $2.8 \times 10^{10} $ & $2.8 \times 10^{9} $ & $1.8 \times 10^{8}$ & $9.1 \times 10^{7} $ & $2.7 \times 10^{7} $ & $1.2 \times 10^{7} $ & $5.1 \times 10^{4} $ & $97 $\\ $2.15 \pm 0.25$ & $6.5 \times 10^{12} $ & $3.8 \times 10^{10} $ & $3.8 \times 10^{9} $ & $3.8 \times 10^{8}$ & $1.7 \times 10^{8} $ & $7.8 \times 10^{7} $ & $3.6 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.4 \times 10^{5} $ & $734 $\\ $2.50 \pm 0.25$ & $6.8 \times 10^{12} $ & $4.1 \times 10^{10} $ & $4.1 \times 10^{9} $ & $4.4 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.3 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.1 \times 10^{8} $ & $5.0 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.6 \times 10^{5} $ & $794 $\\ $3.00 \pm 0.25$ & $6.6 \times 10^{12} $ & $4.1\times 10^{10} $ & $4.1 \times 10^{9} $ & $4.6 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.7 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.3 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.1 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.5 \times 10^{5} $ & $723 $\\ $3.50 \pm 0.25$ & $6.1 \times 10^{12} $ & $3.9 \times 10^{10} $ & $3.9 \times 10^{9} $ & $4.4 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.8 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.4 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.7 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.4 \times 10^{5} $ & $716 $\\ $4.02 \pm 0.25$ & $5.3 \times 10^{12} $ & $3.5 \times 10^{10} $ & $3.5 \times 10^{9} $ & $4.1 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.7 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.4 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.9 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.3 \times 10^{5} $ & $702 $\\ $4.50 \pm 0.25$ & $4.6 \times 10^{12} $ & $3.1 \times 10^{10} $ & $3.1 \times 10^{9} $ & $3.6 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.5 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.3 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.7 \times 10^{7} $ & $4.0 \times 10^{5} $ & $646 $\\ $5.00 \pm 0.25$ & $3.8 \times 10^{12} $ & $2.7 \times 10^{10} $ & $2.7 \times 10^{9} $ & $3.1 \times 10^{8}$ & $2.2 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.2 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.2 \times 10^{7} $ & $3.6 \times 10^{5} $ & $566 $\\ $5.50 \pm 0.25$ & $3.0 \times 10^{12} $ & $2.2 \times 10^{10} $ & $2.2 \times 10^{9} $ & $2.6 \times 10^{8}$ & $1.9 \times 10^{8} $ & $1.0 \times 10^{8} $ & $5.6 \times 10^{7} $ & $3.3 \times 10^{5} $ & $533 $\\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:app-hrrl-par} \end{sidewaystable}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{4-Simulation/Figures/Transporation_Efficiency/Ef.eps} \caption{Predicted number of positrons transported. Black cube: positrons incident on DDNT1. Red cube: positrons entered Q4. Blue cube: positrons entered D1. Magenta cube: positrons exited D1. Black circle: positrons entered Q7. Red circle: positrons entered D2. Blue circle: positrons exited D2. Magenta circle: positrons incident on DT2UP. Black triangle: 511~keV photons detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode.} \label{fig:TransEff} \end{figure}
As shown in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par}, the positron energy distribution is divided into 10 bins. At detector DDNT1 (25.8~mm after T1), there are about $10^{12}$ positrons in each bin. At the entrance of Q4, the counts drop two orders of magnitude. This may be attributed to the solid angle that the entrance of Q4 makes, if one assumes T1 is a point source of positrons. The distance between T1 and the virtual detector DQ4 is $560$~mm and the radius of DQ4 is $24$~mm. The solid angle of the DQ4 is $\Omega_{\text{Q4}}=\frac{\pi r^2}{d^2}=\frac{\pi 24^2}{560^2}$~rad. Positrons make up a cone with a 45$^\circ$ half angle, which is $\Omega_{\text{beam}}=0.6\pi$~rad in solid angle. The ratio of the two solid angles, $\Omega_{\text{Q4}}/\Omega_{\text{beam}}$, is 1:160, $i.e.$ 1 out of 160 positrons make it from T1 to DQ4, assuming that the positron beam is isotropic inside the cone. However, the positron beam peaks at a smaller angle as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:DDNT1_results} (c) and (d) and as a result more positrons are transported from DDNT1 to DQ4, resulting in a ratio closer to 1:100. % for solid angle integrate sin(\theta)d\theta d\phi, theta=[0,90],phi=[0,360]. % $1.3 \times 10^{8} $ & $6.1 \times 10^{7} $ & $1.2 \times 10^{6} $ & $488 $\\
As an example to explain the beam loss along the beamline, the dipoles were set to transport $1.436 \times 10^9$ (one tenth of the number in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par}) 3~MeV positrons at the entrance of D1 as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:dipole-trans}. Beam energy distribution was plotted at the exit of D1, entrance of Q7, exit of Q7, entrance of D2, exit of D2, and at T2. $4.1 \times 10^8$ positrons entered and $4.6 \times 10^7$ exited D1, $2.7 \times 10^7$ entered and $2.5 \times 10^7$ exited Q7, $1.3 \times 10^{7} $ entered and $6.1 \times 10^{6} $ exited D2. At the end, $4.5 \times 10^{5}$ positrons reached T2. These positrons produced 256195 511~keV photon pairs inside T2 and 255861 escaped T2.
The distance between NaI detectors and the beamline center is 170~cm. The Pb shielding has a hole facing T2 with 2 inches diameter. Assuming positrons annihilated at the center of T2, the solid angle a NaI detector make is $\Omega=\frac{\pi r^2}{d^2}=\frac{\pi 25.4^2}{170^2}$~rad. The 511~keV photons created during the annihilation make a solid angle of $2\pi$~rad considering each side of T2 is facing one detector. The ratio of $2\pi$~rad to solid angle of T2 is about 90:1.
In a simulation with similar settings as in Table~\ref{tab:app-hrrl-par}, dipoles are set to bend 3~MeV positrons. As a result, $4.40041\times10^5$ 3~MeV positrons incident on T2 and created 254864 511~keV photon pairs ($i.e.$ 58\% of the positrons annihilated). Two 0.0254~mm thick stainless steel vacuum windows are placed 9~cm from T2 at two sides of the beamline. Detectors are placed in the front and back of vacuum windows to observe their affect on the photons (the detectors are placed 1~$\mu$m from the windows). 4330 511~keV photons went into the vacuum window and 4300 made it through. 0.7\% of photon pairs are lost when passing through the vacuum windows.
The left NaI detector detected 2897 511~keV photons and the right one detected 4100. The ratio of 511~keV photon pairs created in T2 to ones that made it to the right and the left NaI are 88:1 and 62:1 respectively. These are close to the ratios predicted by solid angle ratio 90:1. %The counts on the right detector is little higher than on left detector because the T2 is facing the left side. 1518 511~keV photon pairs are detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode. The ratio 511~keV photon pairs created to the ones detected in coincidence mode is 168:1. Counting photons in coincidence mode cut the rate by half. Note that these counts are given after considering detection efficiency of the system.
%The energy is 0.001 MeV (1 keV), in the figure at the exit of D1 the counts are from 2.8 MeV to 3.3 MeV, i.e. 500 keV, the amplitude of the peak is $8 \times 10^5$, $500 \times 8 \times 10^5 = 4 \times 10^8$, same as given above.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.70]{4-Simulation/Figures/Transporation_Efficiency/En2.eps} \caption{Positrons transported when dipoles are set to bend 3~MeV positrons.} \label{fig:dipole-trans} \end{figure}
\section{Quadrupole Triplet Collection Efficiency Study}
In this simulation, 5,475,869,400 positrons were generated at DDNT1 and transported to DD1 to study quadrupole triplet positron collection and transportation efficiency. Six quadrupole current settings of the triplet system were simulated as shown in Table~\ref{tab:triplet-eff}. For different quadrupole current settings, no significant differences were observed in the number of positrons, transverse beam profiles and momentum distributions. The ratio of positrons generated at DDNT1 to the ones that enter D1 is 1525:1.
\begin{sidewaystable} \centering \caption{Quadrupole Triplet System Collection and Transportation Efficiency Data.} \begin{tabular}{cccccccccccccc} \toprule Q4 & Q5 & Q6 & Entries & $x$ & $\sigma_{x} $ & y & $\sigma_{y}$ & $P_{x}$ & $\sigma_{P_{x}}$ & $P_{y}$ & $\sigma_{P_{y}}$ & $P_{z}$ & $\sigma_{P_{z}}$ \\ \midrule A & A & A & & mm & mm & mm & mm & MeV & MeV & MeV & MeV & MeV & MeV \\ \midrule -1 & 2 & -1 & 3587220 & -0.005 & 12 & 0.030 & 12 & $~~3.0 \times 10^{-5}$ & 0.0461 & -0.00216 & 0.04553 & 3.848 & 1.875 \\ -2 & 4 & -2 & 3591423 & -0.012 & 12 & 0.049 & 12 & $~~2.2 \times 10^{-5}$ & 0.0461 & -0.00211 & 0.04554 & 3.848 & 1.875 \\ 1 & -2 & 1 & 3591509 & -0.009 & 12 & 0.040 & 12 & $-1.5 \times 10^{-5}$ & 0.0462 & -0.00216 & 0.04557 & 3.849 & 1.876 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 & 3589854 & -0.005 & 12 & 0.034 & 12 & $-1.8 \times 10^{-5}$ & 0.0462 & -0.00216 & 0.04556 & 3.849 & 1.876 \\ 2 & -4 & 2 & 3592977 & -0.007 & 12 & 0.032 & 12 & $-3.3 \times 10^{-6}$ & 0.0462 & -0.00217 & 0.04549 & 3.849 & 1.876 \\ 2 & 4 & 2 & 3589495 & -0.004 & 12 & 0.033 & 12 & $~~3.0 \times 10^{-6}$ & 0.0462 & -0.00218 & 0.04554 & 3.849 & 1.875 \\ % & & & & & & & & & & & & & \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:triplet-eff} \end{sidewaystable}
\section{Error Study}
Systematic errors in positron counts were estimated by carrying out simulations with different magnet settings as shown in Table~\ref{tab:sim-error}. The magnet settings are indicated in top 3 rows of Table~\ref{tab:sim-error}. The energy of positrons being transported are given in the first column. The 511~keV photon pairs counted in coincidence mode ($i.e.$ the original counts was multiplied by 46.42\%) for different magnet settings are given in the corresponding columns below.
The uncertainty of the magnet power supply is 0.1~A. The Max/Min in the table refers to the Maximum/Minimum magnetic filed strength when the magnet coil current is at $I_{\text{max}}$/$I_{\text{min}}$, where $I_{\text{max}}$ = $I_{\text{def}} + 0.1$~A and $I_{\text{min}}$ = $I_{\text{def}} - 0.1$~A. Def refers to the default magnetic field strength of the magnet.
The average counts and fractional errors are shown in the last two columns of Table~\ref{tab:sim-error}. The fractional error in the 511~keV photon pair counts is calculated by dividing the standard deviation of counts by the counts in default magnet setting, $i.e.$ $\frac{\text{standard deviation of counts}}{\text{counts in defalt setting}}$. %The fractional error in the 511~keV photon pair counts is calculated by dividing the standard deviation of counts at different settings by the counts in default magnet setting, $i.e.$ $\frac{\text{standard deviation of counts}}{\text{counts in defalt setting}}$.
\begin{sidewaystable}
\centering
\caption{Systematic Error Study: Counts of 511~keV Photon Pairs for Different Magnet Settings.}
%\begin{tabular}{cccccccccccc}
\begin{tabular}{lllllllllllll}
\toprule
D1 & Max & Min & Max & Min & Max & Max & Min & Min & Def & & \\
Q7 & Def & Def & Def & Def & Max & Min & Min & Def & Def & & \\
D2 & Max & Min & Def & Def & Def & Def & Def & Def & Def & & \\
\midrule
Energy (MeV)& & & & & & & & & & Average & Fractional Error \\
\midrule
0.765~1.265 & 12 & 2 & 3 & 1 & 1 & 3 & 3 & 0 & 6 & 4 & 57.3 \% \\
1.25~-~1.75 & 95 & 75 & 70 & 86 & 85 & 92 & 129 & 86 & 97 & 90 & 17.6 \% \\
1.85~-~2.35 & 674 & 724 & 737 & 769 & 686 & 747 & 803 & 681 & 734 & 728 & 5.8 \% \\
2.25~-~2.75 & 781 & 755 & 753 & 759 & 772 & 963 & 794 & 763 & 794 & 793 & 8.3 \% \\
2.75~-~3.25 & 739 & 737 & 765 & 752 & 738 & 698 & 738 & 757 & 723 & 739 & 2.7 \% \\
3.25~-~3.75 & 713 & 699 & 747 & 712 & 707 & 751 & 718 & 705 & 716 & 719 & 2.5 \% \\
3.77~-~4.27 & 690 & 708 & 715 & 676 & 704 & 658 & 706 & 715 & 701 & 697 & 2.7 \% \\
4.25~-~4.75 & 627 & 666 & 634 & 646 & 635 & 675 & 637 & 653 & 646 & 646 & 2.5 \% \\
4.75~-~5.25 & 558 & 595 & 594 & 603 & 606 & 688 & 582 & 582 & 566 & 597 & 6.7 \% \\
5.25~-~5.75 & 513 & 536 & 535 & 522 & 525 & 535 & 518 & 544 & 533 & 529 & 1.9 \% \\
\bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:sim-error} \end{sidewaystable}
Experiment
\chapter{Experiment}
\section{Quadrupole Scanning Experiment} Quadrupole scanning method was used to measure the accelerator's emittance. The quadrupole current is changed to alter the strength and direction of the quadrupole magnetic field such that a measurable change in the beam shape is seen by the OTR system. Initially, the beam was steered by the quadrupole indicating that the beam was not entering along the quadrupole's central axis. Several magnetic elements upstream of this quadrupole were adjusted to align the incident electron beam with the quadrupole's central axis. First, the beam current observed by a Faraday cup located at the end of beam line was maximized using upstream steering coils within the linac nearest the gun. Second, the first solenoid nearest the linac gun was used to focus the electron beam on the OTR screen. Steering coils were adjusted to maximize the beam current to the Faraday cup and minimize the deflection of the beam by the quadrupole. A second solenoid and the last steering magnet shown in Figure~\ref{fig:app-hrrl-cavity}, both near the exit of the linac, were used in the final step to optimize the beam spot size on the OTR target and maximize the Faraday cup current. A configuration was found that minimized the electron beam deflection when the quadrupole current was altered during the emittance measurements.
The emittance measurement was performed using an electron beam energy of 15~MeV and a 200~ns long macro pulse of 40~mA current. The current in the first quadrupole after the exit of the linac was changed from $-$~5~A to $+$~5~A with an increment of 0.2~A. Seven measurements were taken at each current step in order to determine the average beam width and the variance. Background measurements were taken by turning the linac's electron gun off while keep the RF on. Background image and beam images before and after background subtraction are shown in Figure~\ref{bg}. A small dark current is visible in Figure~\ref{bg} (b) that is known to be generated when electrons are pulled off the cavity wall and accelerated.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{ccc} \centerline{\scalebox{0.42} [0.42]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f4.eps}}} \\ (a)\\ \centerline{\scalebox{0.42} [0.42]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f5.eps}}}\\ (b)\\ \centerline{\scalebox{0.42} [0.42]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/MOPPR087f6.eps}}}\\ (c) \end{tabular} \caption{Digital image from the OTR screen; (a) a beam with the dark current and background noise, (b) a background image taken after the RF was on but the gun is off, (c) a beam image when dark background was subtracted.} \label{bg} \end{figure}
The electron beam energy was measured using a dipole magnet downstream of the quadrupole used for the emittance measurements. Prior to energizing the dipole, the electron micro-pulse bunch charge passing through the dipole was measured using a Faraday cup located approximately 50~cm downstream of the OTR screen. The dipole current was adjusted until a maximum beam current was observed on another Faraday cup located just after the 45 degree exit port of the dipole. A magnetic field map of the dipole indicates that the electron beam energy was 15~$\pm$~1.6~MeV.
%\subsection{Data Analysis and Results} Images from the JAI camera were calibrated using the OTR target frame. An LED was used to illuminate the OTR aluminum frame that has a known inner diameter of 31.75~mm. Image processing software was used to inscribe a circle on the image to measure the circular OTR inner frame in units of pixels. The scaling factor can be obtained by dividing this length with the number of pixels observed. The result is a horizontal scaling factor of 0.04327~$\pm$~0.00016~mm/pixel and vertical scaling factor of 0.04204~$\pm$~0.00018~mm/pixel. Digital images from the JAI camera were extracted in a matrix format in order to take projections on both axes and perform a Gaussian fit. The observed image profiles were not well described by a single Gaussian distribution.
The profiles may be described using a Lorentzian distribution, however, the rms of the Lorentzian function is not defined. A super Gaussian distribution was used~\cite{sup-Gau}, because it has a sharper distribution than Gaussian and unlike Lorentzian the rms values may be directly extracted. The Chi-square for x and y profiles are $2.4 \times 10^7$ and $1.9 \times 10^7$ for super Gaussian fit and $2.6 \times 10^8$ and $9.1 \times 10^7$ Gaussian fit. The beam spot, beam projections and fits are shown in Figure~\ref{Gau-SupGaus-fits}. In Gaussian distribution, $\phi(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}x^2}$, the variable $x$ on exponent is raised to the 2nd power while in the super Gaussian it is raised to a power smaller than 2. For example, the beam projections shown in Figure~\ref{Gau-SupGaus-fits} were fitted with the super Gaussian distributions. The variable $x$ on exponents were raised to $0.9053$ ($x$-projection) and $1.0427$ ($y$-projection).
\begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/Gau_SupGau/Gau_ChiSqaure.eps}}} {\scalebox{0.42} [0.4]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/Gau_SupGau/SupGau_ChiSqaure.eps}}} \end{tabular} \caption{Gaussian and super Gaussian fits for beam projections. The beam images is background subtracted image and taken when quadrupole magnets are turned off. Left image is Gaussian fit and right image is super Gaussian fit.} \label{Gau-SupGaus-fits} \end{figure}
Figure~\ref{fig:par-fit} shows the square of the rms ($\sigma^2_{\textnormal{s}}$) $vs$ $k_1L$ for $x$ (horizontal) and $y$ (vertical) beam projections along with the parabolic fits using Eq.~\ref{fig:par-fit}. The emittance and Twiss parameters from these fits are summarized in Table~\ref{tab:results}. MATLAB scripts used to calculate emittance and Twiss parameters are given in appendix B. \begin{figure}[htbp] \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.295} [0.295]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/par_fit_x.eps}}} {\scalebox{0.295} [0.295]{\includegraphics{3-Apparatus/par_fit_y.eps}}} \end{tabular} \caption{Square of rms values and parabolic fittings.} \label{fig:par-fit} \end{figure}
\begin{table} \centering \caption{Emittance Measurement Results} \begin{tabular}{lcc} \toprule {Parameter} & {Unit} & {Value} \\ \midrule projected emittance $\epsilon_x$ & $\mu$m & $0.37 \pm 0.02$ \\ projected emittance $\epsilon_y$ & $\mu$m & $0.30 \pm 0.04$ \\ % normalized \footnote{normalization procedure assumes appropriate beam chromaticity.} emittance $\epsilon_{n,x}$ & $\mu$m & $10.10 \pm 0.51$ \\ %normalized emittance $\epsilon_{n,y}$ & $\mu$m & $8.06 \pm 1.1$ \\ $\beta_x$-function & m & $1.40 \pm 0.06$ \\ $\beta_y$-function & m & $1.17 \pm 0.13$ \\ $\alpha_x$-function & rad & $0.97 \pm 0.06$ \\ $\alpha_y$-function & rad & $0.24 \pm 0.07$ \\ micro-pulse charge & pC & 11 \\ micro-pulse length & ps & 35 \\ energy of the beam $E$ & MeV & 15 $\pm$ 1.6 \\ relative energy spread $\Delta E/E$ & \% & 10.4 \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:results} \end{table}
\section{Energy Scan}
The HRRL energy profile was measured when it was tuned to accelerate electrons to 12~MeV peak energy. A Faraday cup was placed at the end of the 45 degree beamline to measure the electron beam current when D1 was on and D2 was off. Dipole coil current for D1 was changed in 1~A increments. As the dipole coil current was changed, the energy of the electrons transported to the Faraday cup would change as described in Appendix A. Figure~\ref{fig:En-Scan} illustrates a measurement of the 12~MeV peak with a long low energy tail observed. The HRRL energy profile can be described by overlapping two skewed Gaussian fits~\cite{sup-Gau}. The fit function is given by \begin{equation} G(En)=A_{1}e^{\frac{-\left(En-\mu_{1}\right)^{2}}{2\left\{ \sigma_{1}\left[1+sgn\left(En-\mu_{1}\right)\right]\right\} ^{2}}}+A_{2}e^{\frac{-\left(En-\mu_{2}\right)^{2}}{2\left\{ \sigma_{2}\left[1+sgn\left(En-\mu_{2}\right)\right]\right\} ^{2}}}, \label{eq:skew-Gau} \end{equation} where $sgn$ is the sign function, that is defined as $$ sgn=\left\{ \begin{array}{ll}
\mbox -1\ & {(x<0)} \\
\mbox 0 \ & {(x=0)} \\
\mbox 1 \ & {(x>0)}.\\
\end{array}\right.
$$ Where other variables defined as $\sigma_{1}=\frac{\sigma_{r,1}+\sigma_{l,1}}{2}$, $\sigma_{2}=\frac{\sigma_{r,2}+\sigma_{l,2}}{2}$, $E_{1}=\frac{\sigma_{r,1}-\sigma_{l,1}}{\sigma_{r,1}+\sigma_{l,1}}$, and $E_{2}=\frac{\sigma_{r,2}-\sigma_{l,2}}{\sigma_{r,2}+\sigma_{l,2}}$. The measurement results and fits are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:En-Scan} and in Table~\ref{tab:En-Scan_resluts}. \begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{3-Apparatus/En_Fit_Assym_Gau.eps} \caption{HRRL energy scan (dots) and fit (line) with two skewed Gaussian distribution.} \label{fig:En-Scan} \end{figure} \begin{table} \centering \caption{Fit Parameters for Two Skewed Gaussian.} \begin{tabular}{lclcc} \toprule {Parameter} & Notation & Unit & {First Gaussian} & {Second Gaussian} \\ \midrule amplitude & A & mA & ~2.14 & 10.88 \\ mean & $\mu$ & MeV & 12.07 & 12.32 \\ sigma left & $\sigma_L$ & MeV & ~4.47 & ~0.70 \\ sigma right & $\sigma_R$ & MeV & ~1.20 & ~0.45 \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:En-Scan_resluts} \end{table}
\section{The Positron Production Runs} The annihilation target T2 is insertable into the beamline and it was placed inside a 6-way cross that has horizontal sides sealed with 1~mil stainless steel windows. Positrons intercepting T2 thermalize, annihilate, and produce 511~keV photon pairs back-to-back. These photons are detected by two NaI detectors facing T2 and shielded with Pb bricks as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:HRRL-En-Scan}. The background was measured by retracting T2 thereby allowing positrons to exit the beamline and be absorbed by the beam dump.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{5-Experiment/Figures/PositronDetection/NaI_Setup4.png} \caption{Positron detection using T2 and NaI detectors.} \label{fig:HRRL-En-Scan} \end{figure}
As shown in Figure~\ref{fig:Dipole-in}, a 511~keV peak was observed (solid line) when T2 was in. A permanent dipole magnet was placed on the beamline after Q10 to deflect charged particles on the accelerator side preventing them from entering the shielded cell. The peak was not observed (dashed line) when T2 was in and the permanent magnet was used. The peak was also not observed (doted dashed line) when T2 and the permanent magnet were removed. Thus, one may argue that the observed peak is due to positrons annihilating in T2.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.35} [0.35]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/SweepingDipole/LNaI3.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.35} [0.35]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/SweepingDipole/RNaI3.png}}} \\ (a) Original spectrum on left NaI. & (b) Original spectrum on right NaI.\\ \end{tabular} \caption{Photon spectrum when a permanent dipole magnet is inserted along with T2 (dashed line), dipole out and T2 in (solid line), and dipole removed and T2 out (dotted dashed line). The positron energy incident on the T2 was $2.15\pm0.06$~MeV.} \label{fig:Dipole-in} \end{figure}
The normalized photon energy spectra observed by two NaI detectors are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} when T2 was both in (signal) and out (background) of the beamline. Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (c) and (d) illustrate the events observed when 511~keV photons were required in both detectors. The signal is indicated by the solid line and background by dashed line.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_L1/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_R1/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} \\ (a) Original spectrum on left NaI. & (b) Original spectrum on right NaI.\\ & \\ & \\ {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_L2/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.315} [0.315]{\includegraphics{5-Experiment/Figures/NaI_R2/r3735_sub_r3736_2.png}}} \\
(c) Spectrum with cut on left NaI. & (d) Spectrum with cut on right NaI.\\ & \\ \end{tabular} \caption{The time normalized spectra of photons. In the top row are original spectrum and in the bottom row are spectrum of incidents happened in the 511~keV peak coincidently in both detectors. The positron energy incident on the T2 was $3.00\pm0.06$~MeV.} \label{fig:in-out-runs} \end{figure}
%\begin{table} %\centering %\caption{Run Parameters of The Run No. 3735.} %\begin{tabular}{lll} %\toprule %{Parameter} & {Unit} & {Value} \\ %\midrule %run number & & 3735 \\ %repetition rate & Hz & 300 \\ %run time & s & 1002 \\ %pulses & & 301462 \\ %events & & 9045 \\ %e$^+$ Counts on NaI Detectors & & 256 $\pm$ 16\\ %\bottomrule %\end{tabular} %\label{tab:run3735} %\end{table}
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % \section{The Electron Beam Current Measurement}
A scintillator was placed between Q9 and Q10, as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:Scint_e-}, to monitor the electron beam current. The electron beam current was changed incrementally to measure the correlation between the scintillator and the accelerated electron beam. The beam current was measured using FC1 and the output was integrated using an oscilloscope. The scintillator output was measured by integrating the output of FC1 on an oscilloscope. As the electron beam current was decreased, the signal observed on the oscilloscope decreased and ADC measured less charge from the scintillator as shown in Figure~\ref{fig:ADC-CH9}. A linear fit to data resulted a linear relation \begin{equation} Q_{\text{e}^-}(i) = (0.0186 \pm 0.0028)i + 2.79 \pm 0.08~\text{C}, \end{equation} where $i$ is ADC channel number and Q is the accelerated electron beam charge. The fit is shown in Figure~\ref{fig:calb-fit}.
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.35]{5-Experiment/Figures/HRRL_line.eps} \caption{The electron beam monitor.} \label{fig:Scint_e-} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{5-Experiment/Figures/ScintilatorCalibration/ADC_CHAN3.eps} \caption{The photon flux detected using scintillator. The mean of the ADC channel decreased linearly as the electron beam current was decreased.} \label{fig:ADC-CH9} \end{figure}
\begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.50]{5-Experiment/Figures/ScintilatorCalibration/calb.eps} \caption{Fit for accelerator beam current $v.s.$ the ADC channel.} \label{fig:calb-fit} \end{figure}
\begin{table} \centering \caption{Scintillator Calibration Data.} \begin{tabular}{lll} \toprule {Run Number} & {Faraday Cup} & {Mean of ADC} \\ { } & {Charge Area (nVs)} & {Channel 9} \\ \midrule 3703 & $1201 \pm 10$ & $1126 \pm 0.8$ \\ 3705 & $777 \pm 110$ & $791.8 \pm 0.6$ \\ 3706 & $367.7 \pm 2.3$ & $242.1 \pm 0.3$ \\ \bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:scint_calb} \end{table}
When running in coincidence mode, the electron beam current is sampled by the scintillator only when a coincidence event occurs causing a trigger that gates the ADC and measures the scintillator output for that positron coincidence event. The charge measured by the ADC is the total charge of the electron pulses that created the positron events. The beam pulses are counted using a scaler. The total charge on T1 for the entire run is estimated using \begin{equation} Q_{\text{C}} = \left ( \overset{N}{\underset{i}{\sum}} 0.0186i\times(\text{bin~content}[i]) + 2.79 \right ) \times \frac{\text{(\# of beam pulses)}}{\text{(\# of events)}}. \label{eq:q_calc1} \end{equation} \noindent
\section{Positron Rate Estimation}
The background subtracted and normalized photon energy spectra were observed using two NaI detectors for $3.00 \pm 0.07$~MeV are shown in Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs}. Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (a) and (b) are the background subtracted spectrum with no coincidence or energy cut. Figure~\ref{fig:in-out-runs} (c) and (d) illustrate events observed in coincidence and within a energy window of $511\pm75$~keV for both detectors. The measured positron rate using NaI detectors in coincidence mode was 0.25~Hz. %The uncertainty of the power supplies used for dipoles is 0.1~A which creates 0.06~MeV uncertainty in energy of the beam bent by dipoles. \begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \begin{tabular}{cc} {\scalebox{0.8} [0.80]{\includegraphics[scale=0.40]{5-Experiment/Figures/subtract/whole/NaI_L/r3735_sub_r3736.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.8} [0.80]{\includegraphics[scale=0.40]{5-Experiment/Figures/subtract/whole/NaI_R/r3735_sub_r3736.png}}} \\ (a) & (b) \\ & \\ & \\ {\scalebox{0.8} [0.8]{\includegraphics[scale=0.40]{5-Experiment/Figures/subtract/511_peak/NaI_L/r3735_sub_r3736.png}}} & {\scalebox{0.8} [0.8]{\includegraphics[scale=0.40]{5-Experiment/Figures/subtract/511_peak/NaI_R/r3735_sub_r3736.png}}} \\ (c) & (d) \\
& \\
\end{tabular} \caption{Photon spectrum of NaI detectors after background subtraction. (a) and (b) are spectrum after background subtractions. (c) and (d) are the spectrum of events coincident in both detectors in 511~keV peaks.} \label{fig:pos_NaILR} \end{figure}
%The electron beam was transported to a phosphorous screen at the end of the 90 degree beamline to find the errors on the positron beam energy. The positron beam current was too low to be observed on phosphorous screen. %The beam centered on the phosphorous screen and then steered to the edge by changing current of D2 by 0.1~A. %The phosphorous screen is twice as large as T2 in horizantal direction.
\section{Positron to Electron Ratio} The ratios of positrons detected using NaI detectors in coincidence mode to the electrons impinging T1 at different energies are given in Table~\ref{tab:e+2e-} and Figure~\ref{fig:e+2e-}. A simulation was used to estimate the systematic error of the electron energy. The ratios errors are calculated by propagating the statistical errors of positron and electron rates. %error on total counts = sqt(total counts). Rate = Counts/time. Error on rates = sqrt(d(rate)/d(counts)^2*(error on the counts)^2)=sqrt((error on the counts)^2/time^2)=sqrt(counts/time^2)=sqrt(rate/time). \begin{table} \centering \caption{Positron to Electron Rate Ratio.} \begin{tabular}{lc} \toprule {Energy} & {Positron to Electron Ratio} \\ \midrule $1.02 \pm 0.03$ & $(0.19 \pm 0.19)\times10^{-16}$ \\ $2.15 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.69 \pm 0.24)\times10^{-16}$ \\ $3.00 \pm 0.07$ & $(8.25 \pm 0.96)\times10^{-15}$ \\ $4.02 \pm 0.07$ & $(4.20 \pm 0.80)\times10^{-15}$ \\ $5.00 \pm 0.06$ & $(0.62 \pm 0.16)\times10^{-16}$ \\
\bottomrule \end{tabular} \label{tab:e+2e-} \end{table} \begin{figure}[htbp] \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.72]{5-Experiment/Figures/Ratio/R.eps} \caption{The ratios of positrons detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode to the electrons impinging T1.} \label{fig:e+2e-} \end{figure}
%\subsubsection{Error on Ratio} % %Error on electron beam is derived from: % %Error on positron beam rate is derived from: $\sqrt{\frac{positron~rate}{run~time}}$ % %\subsubsection{Annihilation Target Angle} %Use simulation to determine how sensitive annihilation of positrons is to angle. % %What is the dependence of the annihilation target angle with the probability of a positron annihilating in the target and producing a photon that is detected by the NaI detector, % %What is the distribution of 511s as a function of angle phi when theta is 90 degrees? Are they uniformly produced? %\subsubsection{Energy cut systematics} % %How does the positron production efficiency change when you change the range of the 511 cut.
Conclusions and Suggestions
\chapter{Conclusions and Suggestions}
The HRRL cavity was moved to current location. New magnetic elements and diagnostic tolls were added to the beamline. The new HRRL beamline was successfully reconfigured to produce positrons while still can transport electrons to the experimental cell.
An OTR based diagnostic tool was developed and used to measure the beam emittance of the HRRL. The electron beam profile was not described well using a single Gaussian distribution but rather by a super Gaussian or Lorentzian distribution. The projected emittance of the HRRL was measured to be less than 0.4~$\mu$m as measured by the OTR based tool described above when accelerating electrons to an energy of 15~MeV.
Successfully constructed a positron detection system using two NaI detectors and the thin tungsten target placed in the 6-way cross. Successfully measured positrons at different energies (1 $-$ 5~MeV) in experiment. The ratio of positrons being detected on NaI detectors to electrons incident on T2 is on the order of $10^{-15}$ and the peak is observed around 3~MeV. %In the experiment, quadrapoles were optimized to only transport 2~MeV and due to the limited beam time and it could have diminished transportation efficiency for other energies. %Further experimental study is necessary to investigate the positron beam energy distribution.
Simulation results indicate that the transportation efficiency varies for different energies. Higher energies has better transportation efficiency. While simulation results agree with experiment in that the peak energy distribution is around 3~MeV, it predicts higher positron to electron ratio as shown in the Fig~\ref{fig:e+2e-exp-sim}. %Beam loss
Experimental results show quadrupole magnets are not efficient in collecting positrons, since positrons have large angular distribution. Solenoid might be better option to improve the collection efficiency of the positrons. Placing the solenoid close the production target would increase the positron transportation efficiency since it can capture more positrons. %7. Experimental results show quadrupole magnets are not efficient in collecting positrons, since positrons have large angular distribution. Solenoid might be able to improve the collection efficiency of positrons~\cite{kim-bindu-solenoid} and should be placed as close the production target as possible for better efficiency.
\begin{figure} \centering \includegraphics[scale=0.80]{6-Conclusion/Figures/Overlay_Exp-Sim-Ratio/R1.eps} \caption{Ratio of positrons detected to electrons in experiment and simulation.} \label{fig:e+2e-exp-sim} \end{figure}
List of Figures
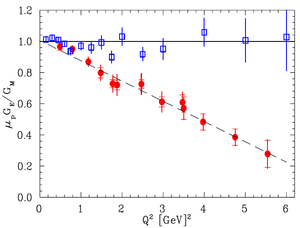 1.1 Form factor ratio, obtained by Rosenbluth Technique (hollow square) and results from Recoil Polarization Technique [5]. . . . . 3
1.1 Form factor ratio, obtained by Rosenbluth Technique (hollow square) and results from Recoil Polarization Technique [5]. . . . . 3
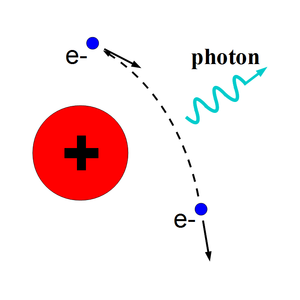 1.2 Photon generation from Bremsstrahlung processes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.2 Photon generation from Bremsstrahlung processes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
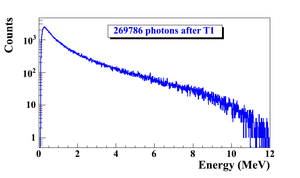 1.3 Simulated Bremsstrahlung photon energy right after a tungsten foil. . . . . . 5
1.3 Simulated Bremsstrahlung photon energy right after a tungsten foil. . . . . . 5
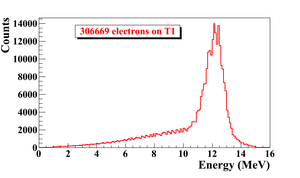 1.4 Simulated electron energy distribution right before a tungsten foil. . . . . . . 6
1.4 Simulated electron energy distribution right before a tungsten foil. . . . . . . 6
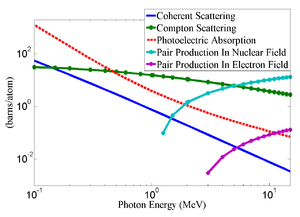 1.5 Cross section for each type of photon interaction with tungsten as function of photon energy [10]. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.5 Cross section for each type of photon interaction with tungsten as function of photon energy [10]. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
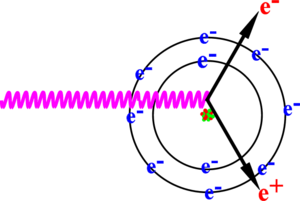 1.6 Pair production. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.6 Pair production. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
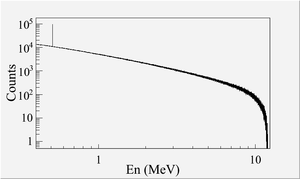 1.7 Photon spectrum of 12 MeV mono energy 10 million electrons impinge on a 1.016 mm thick tungsten target. . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.7 Photon spectrum of 12 MeV mono energy 10 million electrons impinge on a 1.016 mm thick tungsten target. . . . . . . . . . . 8
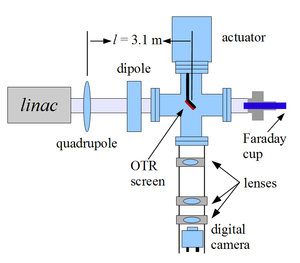 1.8 Apparatus used to measure the beam emittance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.8 Apparatus used to measure the beam emittance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
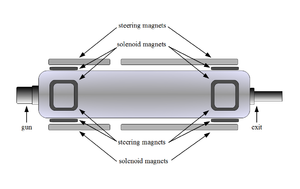 2.1 HRRL cavity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.1 HRRL cavity. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
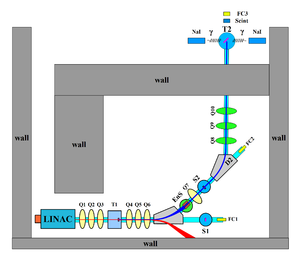 2.2 HRRL beamline layout and parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.2 HRRL beamline layout and parts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
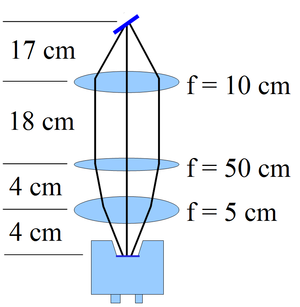
 2.3 The OTR Imaging system. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.3 The OTR Imaging system. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
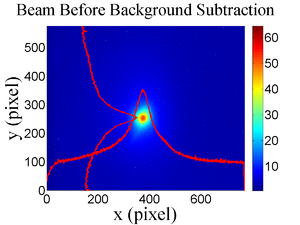
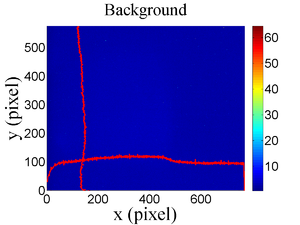
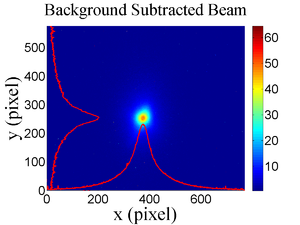 2.4 Background subtracted to minimize impact of dark current; (a) a beam with the dark current and background noise, (b) a background image, (c) a beam
image when dark background was subtracted. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2.4 Background subtracted to minimize impact of dark current; (a) a beam with the dark current and background noise, (b) a background image, (c) a beam
image when dark background was subtracted. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
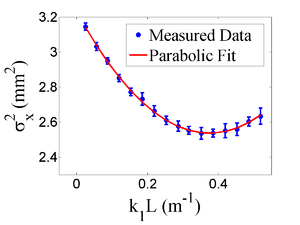
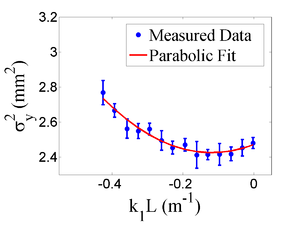 2.5 Square of rms values and parabolic fittings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2.5 Square of rms values and parabolic fittings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
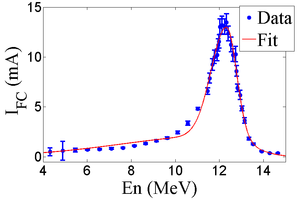 2.6 HRRL energy scan (blue dots) and fit (red line) with two skewed Gaussian distribution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
2.6 HRRL energy scan (blue dots) and fit (red line) with two skewed Gaussian distribution. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
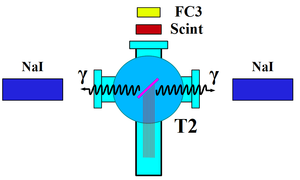 2.7 Positron Detection System. T2 (pink) is 45 degree placed with horizontal plane, then rotated towards left detector 45 degree. . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.7 Positron Detection System. T2 (pink) is 45 degree placed with horizontal plane, then rotated towards left detector 45 degree. . . . . . . . . . . 26
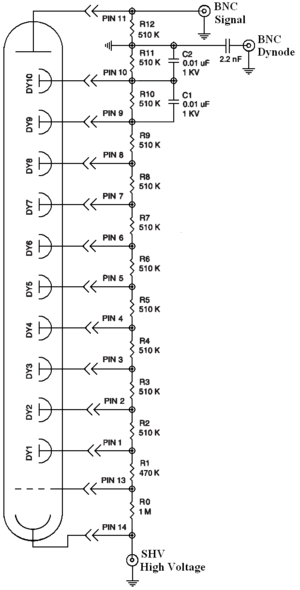 2.8 Modified PMT base design. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2.8 Modified PMT base design. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
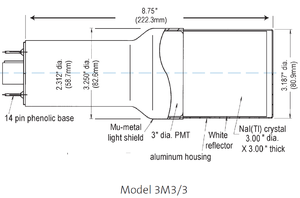 2.9 NaI crystal dimension. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.9 NaI crystal dimension. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
 2.10 NaI crystals and new bases. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.10 NaI crystals and new bases. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
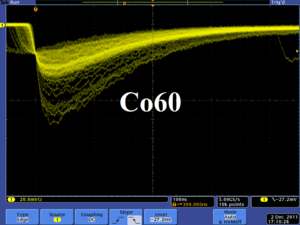 2.11 Pulses from Co-60 source observed on the scope. The amplitude is about 60 mV. The rise time is larger than 50 ns, and the fall time is larger than 700 ns. . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . 30
2.11 Pulses from Co-60 source observed on the scope. The amplitude is about 60 mV. The rise time is larger than 50 ns, and the fall time is larger than 700 ns. . . . . . . . .. . . . . . . . . 30
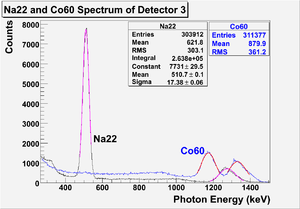 2.12 Calibrated NaI spectrum of Na-22 and Co-60 sources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.12 Calibrated NaI spectrum of Na-22 and Co-60 sources. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
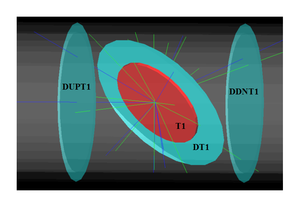 3.1 T1 is positron production target with same geometry and material as real target. DUPT1 is virtual detector located upstream to sample incoming electron
beam. DDNT1 is down stream virtual detector; DT1 is a virtual detector that is placed right after T1 with same angle as T1. . . . . . . . . 34
3.1 T1 is positron production target with same geometry and material as real target. DUPT1 is virtual detector located upstream to sample incoming electron
beam. DDNT1 is down stream virtual detector; DT1 is a virtual detector that is placed right after T1 with same angle as T1. . . . . . . . . 34
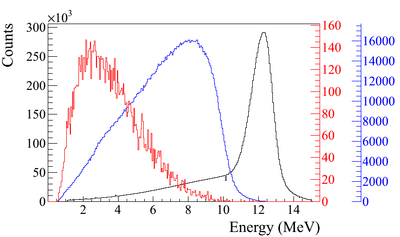 3.2 Energy distribution of positrons detected on virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . 35
3.2 Energy distribution of positrons detected on virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . 35
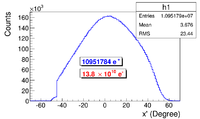
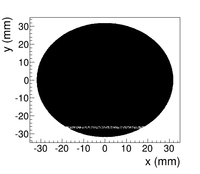
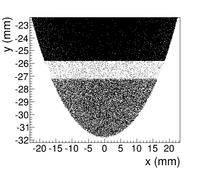 3.3 Transverse spacial and angular distribution of positrons on the virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . . . . . . 36
3.3 Transverse spacial and angular distribution of positrons on the virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . . . . . . 36
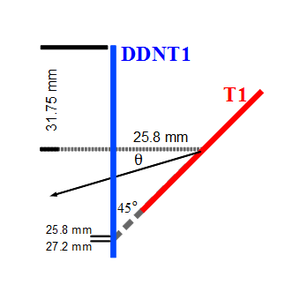 3.4 Geometry of the target T1 and the virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . . . . . . 37
3.4 Geometry of the target T1 and the virtual detector DDNT1. . . . . . . . . . 37
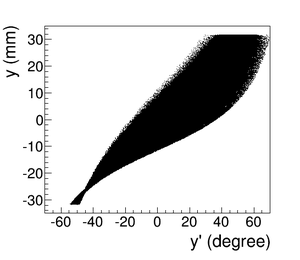
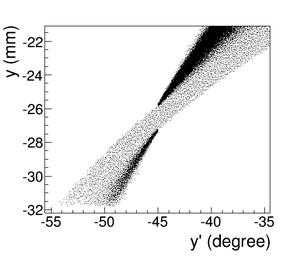 3.5 Positron beam distribution Y divergence vs. Y spacial distribution on DDNT1. 37
3.5 Positron beam distribution Y divergence vs. Y spacial distribution on DDNT1. 37
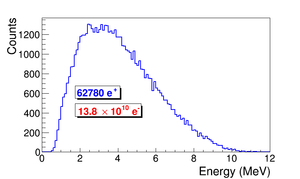 300 px
3.6 Positron beam energy distribution detected on the downstream of T2. . . . . 38
300 px
3.6 Positron beam energy distribution detected on the downstream of T2. . . . . 38
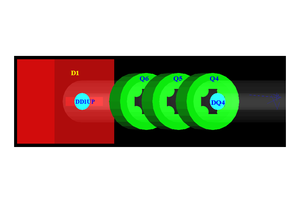 3.7 Step 2 setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.7 Step 2 setup. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
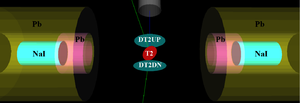 3.8 T2 and virtual detectors located upstream (DT2UP) and downstream (DT2DN) of T2. NaI dettectos and Pb shielding. . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.8 T2 and virtual detectors located upstream (DT2UP) and downstream (DT2DN) of T2. NaI dettectos and Pb shielding. . . . . . . . . . . 40
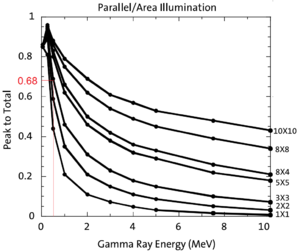 3.9 NaI detector eficiency [21]. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
3.9 NaI detector eficiency [21]. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
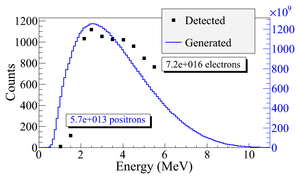 3.10 Positrons generated detected on virtual detector DDNT1 and 511 keV counts
detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode (100 % eficiency assumed). . 42
3.10 Positrons generated detected on virtual detector DDNT1 and 511 keV counts
detected by NaI detectors in coincidence mode (100 % eficiency assumed). . 42
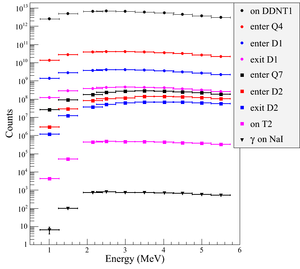 3.11 Predicted number positrons of transported. Black circle: positrons after T1. Red circle: positrons enter Q4. Blue circle: positrons enters D1. Magenta
circle: positrons reaches T2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . 42
3.11 Predicted number positrons of transported. Black circle: positrons after T1. Red circle: positrons enter Q4. Blue circle: positrons enters D1. Magenta
circle: positrons reaches T2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . 42
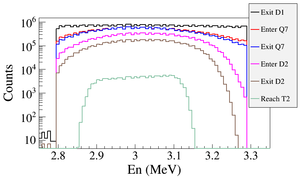 3.12 Beam transported when dipoles are set for 3 MeV positrons. . . . . . . . . . 45
3.12 Beam transported when dipoles are set for 3 MeV positrons. . . . . . . . . . 45
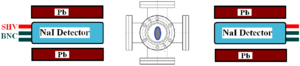 4.1 Positron detection using T2 and NaI detectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4.1 Positron detection using T2 and NaI detectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
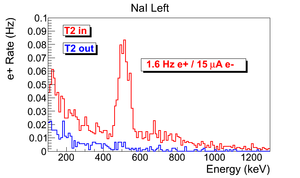
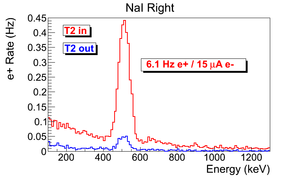
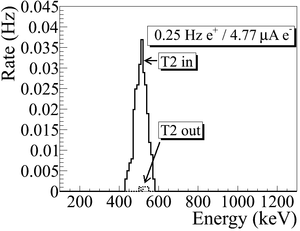
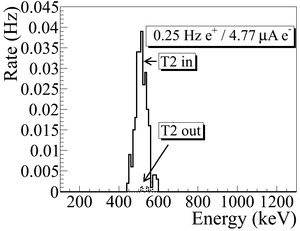 4.2 T2 in run (red) and T2 out background run (blue) time normalized spectrum. Top row shows original spectrum and bottom row shows incidents only happen
in 511 keV peak coincidently on both detectors. . . . . . . . . . . . 50
4.2 T2 in run (red) and T2 out background run (blue) time normalized spectrum. Top row shows original spectrum and bottom row shows incidents only happen
in 511 keV peak coincidently on both detectors. . . . . . . . . . . . 50
 4.3 Electron beam monitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . 52
4.3 Electron beam monitor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .. . . . 52
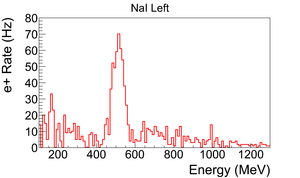
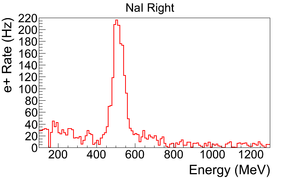
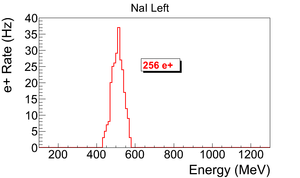
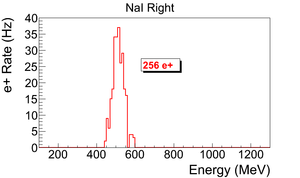 4.4 Electron beam monitor ADC signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
4.4 Electron beam monitor ADC signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
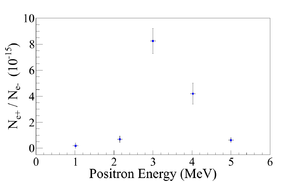 4.5 Ratio of positrons detected to electrons in experiment. . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
4.5 Ratio of positrons detected to electrons in experiment. . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
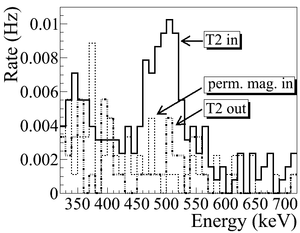
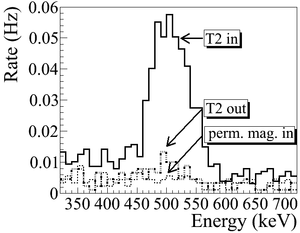 Photon spectrum when permanent dipole magnet in and T2 in (dashed line), dipole out and T2 in (bold dashed line), and dipole in and T2 out (solid line). The positron energy incident on the T2 was $2.15\pm0.06$~MeV.
Photon spectrum when permanent dipole magnet in and T2 in (dashed line), dipole out and T2 in (bold dashed line), and dipole in and T2 out (solid line). The positron energy incident on the T2 was $2.15\pm0.06$~MeV.
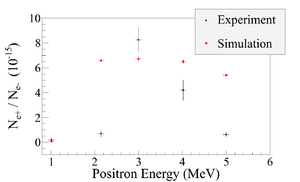 5.1 Ratio of positrons detected to electrons in experiment and simulation. . . . . 58
5.1 Ratio of positrons detected to electrons in experiment and simulation. . . . . 58