Difference between revisions of "NSF-MRI 2013"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=Proj Summary= | =Proj Summary= | ||
| − | + | Each proposal must contain a summary of the proposed project not more than one page in length. | |
The Project Summary consists of an overview, a statement on the intellectual merit of the proposed activity, and a statement on the broader impacts of the proposed activity. | The Project Summary consists of an overview, a statement on the intellectual merit of the proposed activity, and a statement on the broader impacts of the proposed activity. | ||
Revision as of 02:08, 7 February 2013
Title
MRI: The Development of an Instrument for Isotope Production and Photon Activation Analysis (MRI Track 2)
Proj Summary
Each proposal must contain a summary of the proposed project not more than one page in length. The Project Summary consists of an overview, a statement on the intellectual merit of the proposed activity, and a statement on the broader impacts of the proposed activity.
%\centerline{{\bf PIs}: Tony Forest, Alan Hunt, Phil Cole, Valeriia Starovoitova
Project Description
\section{Introduction}
In June of 2012, the Idaho Accelerator Center received a grant from the state of Idaho as part of the Idaho Global Entrepreneurial Mission (IGEM) program. One of the proposed objectives was to research the use of an electron accelerator to produce copper isotopes for use in medical diagnostic procedures. Preliminary results of the work sponsored by this research have indicated that the production of copper isotopes strongly depends on the alignment of incident radiation to the sample. While a sample size of 2 cm is predicted to produce the highest number of isotopes per volume, a misalignment of more than a centimeter may reduce the amount of isotopes produced by a factor of at least two. A strong need now exists for a system to monitor the spatial distribution of the photons used to irradiate the samples. There is also a need to transport samples into and out of the radiation area. Based on these results, we propose to develop an instrument, that qualifies for the MRI category ``Track 2, that will be used to produce isotopes and perform Photon Activation Analysis (PAA) services.
a.) Information
\section{Information about the Proposal (a)}
\subsubsection{Instrument Location and Type (a.1)}
Physical location: Idaho Accelerator Center, Pocatello, ID
Instrument type: MRI-61
\subsubsection{Justification for Submission as a Development (Track 2) Proposal (a.2)} (1 page)
The proposed instrument will be developed by combining several instruments from different vendors as well as the "in house" construction of a remote transport system for sample placement. What may appear at first glance as an upgrade to an existing instrument is actually the development of the instrument specifically designed for Isotope production and Photon Activation Analysis. Preliminary results indicate that the "off-the-shelf" medical linac that we currently have acquired can be developed into an instrument that is more efficient, stable, and effective at providing the service of isotope production and photon activation analysis. A key ingredient to the instrument will be an in-house designed and constructed transport system that will remotely position samples at an optimum location for irradiation. The Idaho Accelerator Center's on staff engineers and its machine shop will be used to manufacture the infrastructure used to mount stepper motors and control systems for the transport system. The second key component is a beam control and feedback system that will allow operators to deliver a constant flux of photons to the specified sample location. The remote transport system and the photon flux monitor each represent a development instrument. A instrument for Isotope production and PAA can be developed by combining each of two instruments above with an electron accelerator. The development of this instrument will require the design and fabrication talents of engineers as well as the quality control and measurement expertise of scientists.
We propose to acquire and install the equipment for a photon beam monitoring system and a conveyor system to transport irradiation samples into and out of the radiation cell. This equipment, when combined with our existing facility, will increase our isotope production effiicency by at least two fold and reduce the systematic errors involved in PAA by ???????????
Matching support from the IGEM project will be used to design and install a conveyor system while the MRI will purchase the system components.
The conveyor, commonly referred to as a rabbit, will transport samples into the irradiation region and then to a shielded container (lead pig) after irradiation.
The transportation system is a necessity due to the high activity isotopes that may be produced.
When used as an instrument for PAA, the transportation system will eliminate the step of shutting the accelerator off in order to change to the control sample thereby risking a change in the experimental conditions whose uniformity is essential for meaningful measurements.
Once calibrated, the photon monitoring system would allow users to irradiate sample with a known amount of radiation.
\\
b.) Research Activities
\section{Research Activities to be Enabled (b)} ( 4 pages) The research activities to be enabled by the proposed instrument can be grouped into two categories; Isotope production and Photon Activation Analysis.
\subsection{current isotope crisis}
In fiscal year 2011, the Department of Energy's Isotope program had a budget of \$48.5 million that was used to send about 450 shipments of isotopes to over 150 industrial users and 100 researchers. ~\cite{FY2013CongBudgetOff} The Isotope Production Facility (IPF) at Los Alamos National Laboratory, the Brookhaven Linac Isotope Producer (BLIP) at Brookhaven National Laboratory, and processing facilities at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORL) are the three primary facilities for isotope production.
\subsection{accelerator based isotope production}
\subsection{interdisciplinary research enabled by the device}
will provide a means to more effectively produce isotopes and perform Photon Activation Analysis. The Idaho Accelerator Center has a history of irradiating materials for outside users across disciplines from Biology to Archaeology. The production of isotopes, currently being pursued to provide medical sources, may also find consumers in industry. PAA has been demonstrated as a useful tool in several IAC research projects already. We believe a facility providing this service will find customers in fields ranging from Archaeology to mining and even coffee producers.
c.) Description
\section{Description of Research Instrumentation and Needs (c)} (6 pages)
The proposed instrument will be composed of hardware used to position and monitor the incident radiation and a device to transport samples in and out of the radiation environment. Beam position monitors will be purchased to monitor the incident electron beam from the IAC accelerator on the radiator target. The position of the electrons on the radiator target effects the quality of the photons produced to irradiate samples. A set of photon detectors (CVD diamond films) will be purchased and placed strategically around the beam line in order to tune the accelerator such that the photon flux is centered on the target. A data acquisition system will be purchased to monitor this radiation flux. A conveyor system will be designed and installe to transport samples into and out of the radiation area.
\subsection{CVD detectors}
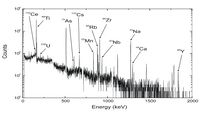
The chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of polycrystalline diamond onto films has become an industry that currently provides "off-the-shelf" detectors among other applications.
GSI shows a signal output of about 2 ns when hit with a 200 MeV/u C-12 atom.
\subsection{Transport System}
\subsection{BPM monitors}
\subsection{permanent deflecting magnet}
d.) Impact
\section{Impact on Research and Training Infrastructure (d)} ( 2 pages)
The proposed instrument will be a facility for performing isotope production research and training accelerator physicists. The research on copper isotopes is well underway and quickly approaching a point where production for consumption is likely. The production of other isotopes for industry and research will also be under investigation using this device. The goal will be for the instrument to be self sustaining and a means of training students.
The instrument will be an opportunity to train students in the operation of an electron accelerator as well as the techniques for isotope production and PAA. Graduate students, once trained, would operate the accelerator as a means of supporting their studies at ISU.
e.) Management
\section{Management Plan (e)} ( 2 pages)
The IAC has a well established record of managing a facility that attracts researchers who purchase beam time. This proposal seeks to expand the services that the IAC can provide. The components used to develop this instrument may be considered ``off the shelf. The accelerator expertise of the IAC and the detector development expertise of the PI will be relied upon to construct a working instrument. The track records of both entities are quite sound for this project. The long term operations and maintenance plan will rely on the instruments ability to attract customers. The growth of demand for medical isotopes and the continued warning of an isotop production crisis by the Department of Energy is a strong indication that the instrument will be in demand should its ability to produce isotopes become well established.
References
\begin{thebibliography}{99} %--- Tony's ---- \bibitem{Zhang04}X.~Zheng {\it et al.}, Phys.~Rev.~Lett.~92 (2004) 012004.
\bibitem{FY2013CongBudgetOff} FY2013 Cngressionl Budget (http://science.energy.gov/~/media/budget/pdf/sc-budget-request-to-congress/fy-2013/Cong_Budget_2013_IsoptopeProductionandDistributionProgramFunding.pdf)
\end{thebibliography}
Bio Sketeches
Budget
\section{Budget}
\begin{table}[h]
\begin{center}
\begin{tabular}{ccc}
\multicolumn{1}{c}{Cost} &
\multicolumn{1}{c}{Match} &
\multicolumn{1}{c}{Description} \\
\hline\hline
50,000 & N & 4 electron Beam Position Monitors\\ 20,000 & N & CVD diamond detectors \\ 28,000 & N & Data Acquisition System \\ 50,000 & N & Conveyor system for isotope samples \\ 22,000 & Y & end station \\ 50,000 & Y & Professional \& Technical Services \\ \hline \end{tabular} \caption{Budget: Total expenses = \$220,000, Available Match \$72,000 (33 \%)} \end{center} \label{table:Projects} \end{table}