Gaseous Medium Physical Concepts
Related Physical Concepts
The gaseous medium inside a detector's chamber contains different physical processes as a particle arrives the gas. When the desired particles penetrate the gaseous medium, they directly or indirectly (neutron fission) ionize the gas. If the event happened in the active detection area of the detector, a drift electric field guides the primary and secondary electrons toward the GEM preamplifiers, These preamlifiers are placed to have a separation distance within a limit to not lose the electrons by keeping their diffusion to be a reason for their multiplication . An electron avalanches appear and the negative voltagge directs them toward the read out plate which collects the electrons to show them as negative pulses on the oscilloscope's screen. Electron recombination, deattachment and capture take place in every stage in the electron trip before they reach the readout plate. The output signal is important to measure the detector's performance by determining its efficiency, dead time, gain, spatial resolution and robustness.Theorretically, the detector output can be evaluated by solving Boltzmann equation that considers the effect of each physical process occured.
Ionization
Ionization is the liberation of an electron from the confines of a medium atoms or molecules. Also the minimum amount of energy required to liberate the electron is referred to as the ionization energy. When the ionizing particle get in the medium, it deposits its energy to free electrons, energy in excess of this ionization energy will appear in the form of kinetic energy carried by the free electrons. For instance, charged particles, like fission fragments, ionizes a gaseous medium and free electrons with kinetic energy that depends on the fragment energy deposition remained after ionization.
The ionization process depends stochastically on the ionization cross section which is usually determined by the ionizing particle energy, and mass( heavy or light in case of fission fragments), but it is observed that the amount of energy needed to have an ionization event in a gas is the same on average <ref name="Veenhof"> R. Veenhof, Internal Note/TPC, ALICE-INT-2003-29 version 1.0, 2003</ref>, regardless of the incident particle type or energy as shown in the following table for argon gas.
| Type of particle and its energy | 9 keV x-rays | 10 keV electrons | 40 keV electrons | x-rays Ar-37(K-capture)(5-25 keV) + beta | alpha 7.68 MeV | 340 MeV protons |
| Energy per ion-electron pair (eV) | 27.9 1.5 | 27.3 | 25.4 | 27.0 0.5 | 26.25 | 25.5 |
Ionization in fission chambers
Ionization by fission fragment is not the only source for a electrons and it is not the only ionization process in fission chamber. These chambers basically contain a neutoron fissinable material; it is a heavy radioisotope that decays and emits more than one type of the ionizing radiation by the radioisotope itself or by its daughters. For instance, using U-233, the source for the free electrons are fission fragments, alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays. More specific details about U-233 decay products is shown by the following tables.
| nuclide | Energy Minimum | Energy Maximum (keV) |
| U-233 | 25 | 1,119 |
| Ra-225 | 40 | 40 |
| Ac-225 | 10.5 | 758.9 |
| Fr-221 | 96.8 | 410.7 |
| At-217 | 140 | 593.1 |
| Bi-213 | 323.81 | 1,119.4 |
| Nuclides | energy (MeV) | half life |
| 0.357 | 14d. | |
| 1.426 | 46min. | |
| 1.981 | 2.2 min. | |
| 0.644 | 3.25h | |
| 1.893 | stable |
To count the free electrons produced by the fission fragments demands some modifications in the detector design which will be mentioned in details in the detector construction section .
They are other physical processes occur in the medium which are related to the gas mixture properties such as: photoionization, thermal ionization, deionization by attachment (negative ion formation) , photoelectric emission, electron emission by excited atoms or positive ion,penning ,and field emission <ref name="Kuffel"/>. The previos processes probably share in decreasing or increasing the number of free electrons in the medium, so evaluating the number of free electrons before amplification becomes sophisticated processes without a computer simulation.
Garfield simulates the ionization in the gas mixture cosidering all the former physical processes, it has the ability to simulate the electrons multiplication by GEM preaplifiers, it accepts external solutions for the electric field by other software packages like ANSYS, and it has more than one package such as Magboltz, HEED, and Imonte 4.5 that can be used for more precise simulations <ref name="Veenhof"/>.
Diffusion
- Main differences between electrons and ions behavior in a gas <ref name="Mason">Mason, Edward A. and Earl W. MacDaniel. 1988. Transport Properties of Ions in Gases. John Wiley & Sons. </ref>
Haitham, here is a chance to get help with writing from the help center. Take the paragraph below to them and learn how to correct it.
H: Sure, but I need to add and edit some more to complete the idea then I will go there.
Studying diffusion and mobility of charged particles in a gas is classified in to two main groups, ion and electron diffusion and mobility. They are conceptually similar, but they have many differences. First, The ratio between the mass of the electrons and the gas atoms is very small, so with a few eV work done by the electric field, the electrons will gain a high velocity compared to that of the ions when are accelerated under the same electric field. Also, the probability of low energy electrons to make an interaction is higher than that of the low energy ions, the electron interactions are a supported with accurate calculations for the electron drift velocity. Electrons at low energy have the ability to produce vibrations and excitations in the gas atoms or molecules which are measured within the lab frame, but the low energy ions have very low cross sections for the most of the interactions with the gas atoms or molecules. When interactions happen, a complexity appears in measuring their products. Furthermore, calculations are simple for the velocity distribution for the electrons in many gases, since the ratio between a gas atom or molecule mass to the electron mass is very small. Producing electrons is simpler than producing ions in a gas; a number of interactions are resposible for producing electrons in gas, such as thermionic emission, photoemission, or a radioactive decay, on the other hand, creating an ion requires electron bombardment, photo-ionization or an electric discharge which requires more sophisticated conditions for the experiment, for instance , ions are not as sensitive as the electrons for the the non-uniformity of the electric field, electric potential and magnetic field. Finally, the existence of the impurities is always a concern; the ions lose most of their energy in the molecular level, but the electron energy loss within the atomic level in a pure gas, so the ionic velocity distribution is not affected by the existence of these impurities except for some cases related to a highly accurate ionic studies in gases.
Electron Diffusion
ion Diffusion
Townsend's Coefficients
Townsend's First Coefficient
Townsend's first Coefficient is defined as "the number of produced by an electron per unit length in the direction of the electric field"<ref name="Kuffel"/>.
- Townsend started his investigations about discharge after fundamental studies were known around 1899 about:
1- Conductivity production by x-rays.
2- Diffusion coefficients, mobility of ions and ion-electron recombinations.
- It was observed for an increment in Electric filed E and pressure P beyond the saturation current value, at some critical value of E and p, the current increases rapidly which will lead to a breakdown of the gap in the form of a spark <ref name="loeb"> L.B.Loeb, basics processes of gaseous electronics, University of California Press, 2nd edition, 1955. call number QC711 .L67 1955a </ref>.
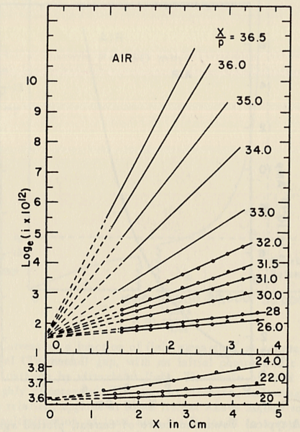
- Townsend studied the relationship between E/p as a function of x, where x is the separation distance between the plates. His study was based on the photoelectron emission from the cathode by ultraviolet light at high uniform electric field up to 30kV/cm and 1 atm pressure.
- He plotted different values for E/p, he found that the slope of the line is which is "the number of the new electrons created by single electron in 1 cm path in the filed direction in a gas at appropriately high E/p" <ref name="loeb"/> . Townsend plotted against the distance of separation x, he concluded the following equation
to calculate (the slope) for different values of E/p as shown in the figure:
- Townsend studied as a function of E/p for a given gas, he founded ,for different values of p,
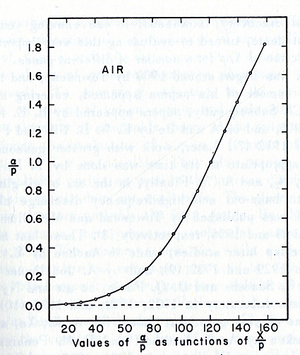
experimentally is different from expected value calculated, but the plots met in values when it represented the relationship between /p as a function of E/p as shwon in the figure below.
- The relationship between /p and E/p is shown below. However, the equation can not predict all the values of /p accurately for different values of E/p, i.e having a single analytical function to fit the experimental results for a gas does not exist, because /p is dependent on the number of electrons produced which changes as the average energy distribution of the ionizing electrons changes <ref name="loeb"/>.
- Theoretical evaluation of as a function of E/p
- The first attempt was done by Townsend when the experimental data were limited by the to the high E/p.
Gas Quenching
Rewrite the first two sentences so quenching is more clearly described.
Gas quenching is a non-ionizing process occurs when a gas molecules with large cross sections for excitation and vibration states decreases a charged particle energy to create any ionization when the charged particle passes through. Usually, the gas mixture ,contains the ionization event, consists mostly of gas atoms as a main source of electrons and the quenching gas, when the free electrons are scattered after the ionization, their energy is decreased by quenching so the number of secondary electrons becomes less, Consequently, a higher voltage is required to get a gain from this mixture than a medium only has a non-quenching gas<ref name="Sharma"> A.Sharma,F. Sauli, first Townsend coefficients measurements for argon gas european organization for nuclear research (1993) </ref >.
Not only does the quenching process decreases the electron energy, but also decreases the positive ions energy (produced by ionization) when the ions collide with these gas molecules and emits a photon or more from these positive ions. These photons represent the energy loss in a form other than the ionization which is called argon escape peak in case of using Argon gas.
Gas quenching experimentally can be measured by evaluating Townsend first coefficients A,B for different gas mixtures. The following table represents the Townsend first coefficients' values for different ratio of Ar/CO2 gas mixtures<ref name="Sharma"/>:
| Percentage of CO2 | 3.7 | 22.8 | 87.2 | 100 |
| A | 5.04 | 221.1 | 158.3 | 145.1 |
| B | 90.82 | 207.6 | 291.8 | 318.2 |
| 16.2 | 21.6 | 32.9 | 36.4 |
The electric field pressure ratio in the last row is the upper limit of the reduced electric field which Townsend's equation fits considering E as a uniform electric field.
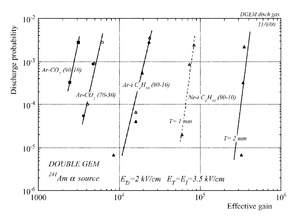
Why 90/10 Ar/CO2 Mixture and why Garfield <ref name="Veenhof"/>
Decreasing the discharge in THGEM
GEm and THEGM preamplifiers are designed to be rebust, economical, and to get the maximum gain with the least discharge effect.
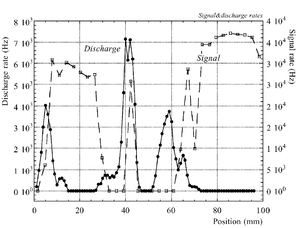
The discharge effect is when you experimentally start observing sparks coming from the detector. Whenever discharge becomes phenomenon to study then the probability of discharge is used. The probability of discharge is defined as the ratio between the observed frequency of the breakdown and source rate <ref name="bachmann"/>.The discharge rate and the source rate can be represented as function of position as shown in the figure.
Producing these sparks refers to many reasons,it is obviously observed when a highly ionizing ion passes through the gaseous chamber and produces enough free electrons to break down the rigidity of surrounding gas by having an avalanche size exceeds Raether limit ( electron-ion pairs) when separating the electrodes vertically with small a distance <ref name="bachmann"> Bachmann et al NIM A 479 (2002) 294-308 </ref > .
Temperature, humidity, and gas flow externally affect the probability of the transition from the proportional multiplication to a discharge at a given potential, the effect clearly appears in absence of the amplification internal effects as the design quality and the history of the electrodes <ref name="bachmann"/>.
In case of heavily ionizing ions like alpha particles, an increase in gain causes the probability of discharge to increase, but the increment in the probability of discharge can be decreased by choosing an appropriate gap between the THGEM cards <ref name="bachmann"/>. As a result, achieving a maximum gain for an incident particle on a chamber with a specific gas mixture ,under a voltage applied on the THGEM cards, requires an appropriate distance that increases with increment of the ionization rate, i.e an alpha particle requires a bigger gap between the THGEM cards than that of a gamma ray to avoid the discharge effect.(can be experimentally proven).
Experimetally, GEM and THGEM have similarities in factors that increases discharge in radiation harsh environment. Being charge preamplifiers requires a high voltage provided by a voltage divider network which does not have resistors of order of hundred Mohm. Setting the power supply to the maximum current limit causes a discharge,indeed high network resistors up to hundreds of Mohm may limit the effect fo the returning current which will casue less discharge in the GEM or THGEM. Generally, the HV-circuit divides the voltage for triple GEM based detector in away that the voltage difference between the top and bottom of of the first preamplifer is 10% more than the second, and the second preamplifer is 10% more in voltagethan the third one to avoid the discharge effect throught the detector operaion.
The discharge probability is independent on gap voltage between two successive preamplifiers but adding 50 pF capacitor "lower the threshold considerably to the charge propagation". The charge propagation relies on the capacitance of GEM. Having the GEM with independently powered sectors reduces "the probability of energetic discharge propagation to the readout plate.
In some gases, The highest gain value ,in presence of heavily ionizing radiation, is affected by the gap between the THGEM cards due to the photon feedback mechanics.<ref name="Bachmann"> Nucl. Inst. and meth. 479 (2002) 294-308 </ref>.
Photon feedback: emission and re-absorption of the photons in the gas or in the metal's surface.
Reminders
- Basic definitions<ref name="Petrovic"> Z Lj Petrovi´c, S Dujko J. Phys. D
- Appl. Phys. 42 (2009) 194002 </ref>
1- Enhanced electron conductivity: effect shows an increase in the electron drift velocity in a system encounters inelastic collisions with small probability for drift velocity in all directions when it is directed by an electric field.
2- Negative differential conductivity: An effect is observed when the increase in electric field density ratio leads to a decrease in the drift velocity. "NDC was found to be favoured by increasing momentum transfer and decreasing inelastic cross sections and the balance of different processes affecting it can be put into a condition which is relatively accurate". it observed in argon mixtures.
- Physical parameter and its eefect on the detector properties
| physical parameter | Effect on the detector properties <ref name="Veenhof"/> |
| Electron drift velocity | Dead time |
| Electron transverse diffusion | Spatial resolution (momentum resolution), transverse resolution should match the response function (signal width) |
| Townsend Coefficient | Gain which improves the resolution |
| Attachment Coefficient | Losing the information about an ionization, affects the position information and dE/dx identification |
| Gas breakdown | Discharge at that voltage |
| Ion mobility | Determine the rate of collecting the electrons (if the space charge is eliminated), the signal duration in the readout plate |
| Ionization rate | Affect the spatial resolution, dE/dx identification |
Boundary Element Method (BEM)
Boundary Element Method is used to solve Laplace or Poisson Equation, a function u(x,y,z) is solved on the domain boundary and the function partial derivatives are evaluated by integrating on the number of elements on the boundary.<ref name="Kuffel"> Kuffel, W. S. Zaengl, J. Kuffel, High voltage engineering: fundamentals, Biddle Ltd, 2nd edition, 2000 </ref>.
<references/>