Difference between revisions of "Forest NucPhys I Nuclear Reactions"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
: a nuclear from projectile a is transfered to target X | : a nuclear from projectile a is transfered to target X | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Transfer_Reaction_Forest_NucPhys_I.png|200px]] |
[[Forest_NucPhys_I]] | [[Forest_NucPhys_I]] | ||
Revision as of 16:23, 6 April 2009
Nuclear Reactions
Types of Reactions
- elastic scattering
- X & Y and a & b are the same particles, momentum and energy are conserved, typically all are in their ground state
- In-elastic scattering
- If Y or b are in an excited state, energy is not conserved it is used to excite one of the exiting particles.
- knockout reaction
- a & b are the same but there are 3 total particles in the final state.
- e - + Mo-100 \rightarrow Mo-99 + n + e- = X(e,e'n)Y
- n + X \rightarrow Y + 3n = X(n,3n)Y
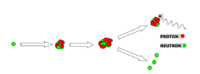
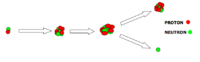
- Transfer Reaction
- a nuclear from projectile a is transfered to target X