Difference between revisions of "Forest ModernPhysics"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
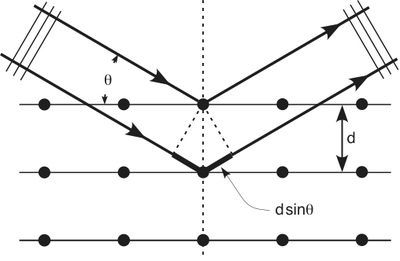
: <math>2 d sin \theta = n \lambda</math> | : <math>2 d sin \theta = n \lambda</math> | ||
| − | where <math>d</math> is the spacing between crystal planes, <math>\theta</math> is the reflected angle, and <math>\lambda</math> is the X-ray wavelength. The order of the diffraction maxima is given by <math>n</math>. | + | where <math>d</math> is the spacing between crystal planes, <math>\theta</math> is the reflected angle, and <math>\lambda</math> is the X-ray wavelength. The order of the diffraction maxima is given by <math>n</math>. The picture below should have a max in the center but the intensity is so high that it has been blocked in order to avoid washing out the picture. |
[[File:X-rayInterferencePattern.gif | 100px]] | [[File:X-rayInterferencePattern.gif | 100px]] | ||
Revision as of 03:07, 30 September 2009
Matter Waves (Wave Particle Duality)
Special relativity said that
if m=0
Plank said he could fit the Black Body radiation data assuming that that
where = Plank's constant
Combining the two we have
photons have momentum like a particle (mv)
Do particles reciprocate and behave like photons?
De Broglie's Hypothesis
If photons can behave like particles by having momentum
Then can a particle behave like a wave by having wavelength
or
de Broglie Hypothesis
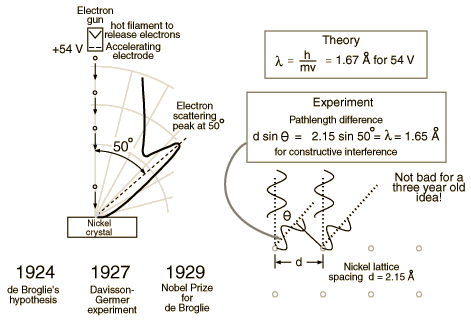
Davisson and Germer
We know that X-rays having a wavelength of make a diffraction pattern on an aluminum foil. The waves diffract around the obstacle and then constructively interfere according to
where is the spacing between crystal planes, is the reflected angle, and is the X-ray wavelength. The order of the diffraction maxima is given by . The picture below should have a max in the center but the intensity is so high that it has been blocked in order to avoid washing out the picture.
Another way to calculate
- What would be the energy of an electron with the same wavelength as the above X-ray?
relativistic total energy relation
- = 511.3 keV
relativistic kinetic energy
- Note classical physics may be used for electrons below 50 keV
Clinton Davisson and Lester Germer in 1927 published conclusive evidence for the diffraction of electron waves using 54 eV electrons impinging a crystal made of nickel.
One problem to overcome for the experiment was that such a low energy electron scatters in air. The had to do the experiment in a vacuum.
From hyperphysics: