Go Back
LINAC parameters used in calculations
1) pulse width 50 ps
2) pulse current 50 A
3) repetition rate 300 Hz
4) energy 44 MeV
Counts Rate for U238 (1/2 mil of Ti radiadot)
Number of electrons/sec on radiator
[math] 50\ \frac{Coulomb}{sec} \times \frac{1\cdot e^-}{1.6\cdot 10^{-19}C} \times 50ps \times 300Hz = 0.47 \cdot 10^{13} \frac{e^-}{sec}[/math]
Number of photons/sec on target
bremsstrahlung
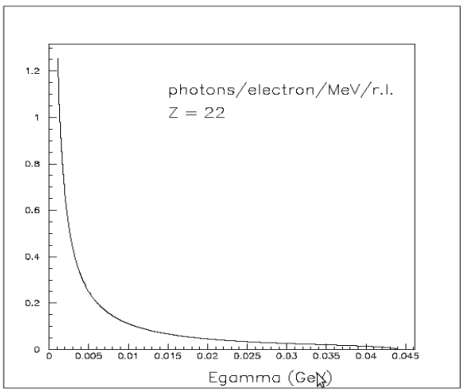
in (10,20) MeV region we have about
0.1 photons/electrons/MeV/r.l
radiation length
r.l.(Ti) = 3.59 cm
radiator thickness = 12.5 [math]\mu m[/math]
[math]\frac{12.5\ \mu m}{3.59\ cm} = 3.48 \cdot 10^{-4} \ r.l.[/math]
steps together...
[math]0.1\ \frac{\gamma 's}{(e^- \cdot MeV \cdot r.l.)} \times 3.48 \cdot 10^{-4} r.l. \times 10\ MeV \times 0.47 \cdot 10^{13} \frac{e^-}{sec}=1.64 \cdot 10^{9} \frac{\gamma}{sec}[/math]
Alex factor (GEANT4 calculation)
Collimation factor is
6.85 % of total # of photons
then, incident flux on target is
[math]1.64 \cdot 10^{9} \frac{\gamma}{sec} \cdot 6.85\ % = 1.12 \cdot 10^{8} \frac{\gamma}{sec}[/math]
Number of neutrons/sec
photonuclear cross section for [math]^{238}U(\gamma , F)[/math] reaction
J. T. Caldwell et all., Phys. Rev. C21, 1215 (1980):
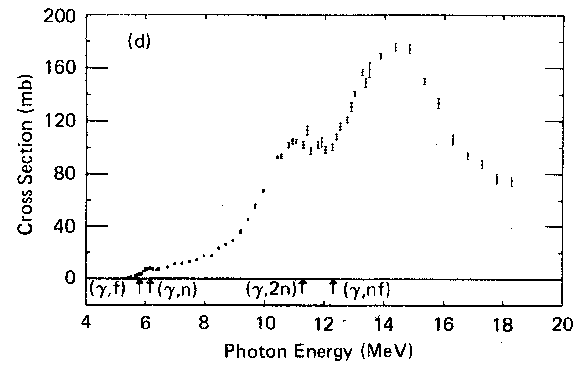
in (10,20) MeV region the average cross section, say, is:
130 mb
target thickness, [math]^{238}U[/math]
[math]\frac{19.1\ g/cm^3}{238.02\ g/mol} = 0.08\ \frac{mol}{cm^3} \times \frac{6.02\cdot 10^{23}\ atoms}{mol} = 0.48\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^3}[/math]
Let's target thickness = 1 mm:
[math]0.48\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^3} \times 0.1\ cm = 0.48\cdot 10^{22}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^2}[/math]
neutrons per fission
2.4 neutrons/fission
steps together...yeild
[math] Y = \frac{\gamma}{sec} \times t \times \sigma \times 2.4 = [/math]
[math] = 1.12 \cdot 10^{8} \frac{\gamma}{sec} \times 130\ mb \times 0.48\cdot 10^{22}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^2} \times 2.4 = 1.68 \cdot 10^{5}\ \frac{neutrons}{sec}[/math]
Worst Case Isotropic Neutrons
checking detector distance
we want:
the time of flight of neutron >> the pulse width
take the worst case 10 MeV neutron:
[math] E_{tot} = E_{kin} + E_{rest} = 10\ MeV + 938\ MeV = 948\ MeV [/math]
[math] \gamma = \frac{E_{tot}}{m_p} = \frac{948\ MeV}{938\ MeV} = 1.0107 [/math]
[math] \gamma^2 = \frac{1}{1 - \beta^2} \ \ \ \rightarrow \ \ \ \beta = 0.145\ c[/math]
take the neutron detector 1 meter away:
[math] t = \frac{1\ m}{0.145\ c} = \frac{1\ m}{0.145\cdot 3\cdot 10^8\ m/sec} = 23\ ns [/math]
23 ns >> 50 ps <= time resolution is good
geometrical factor
taking real detector 3" x 2" => S is about 40 cm^2
1 meter away
fractional solid angle = [math]\frac{40\ cm^{2}}{4 \pi\ (100\ cm)^{2}} = 3.2 \cdot 10^{-4}[/math] <= geometrical acceptance
Yield
the yield per second:
[math]1.68 \cdot 10^{5}\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} \times 3.2 \cdot 10^{-4} = 53.8\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} [/math]
the yield per pulse:
[math] 53.8\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} \times \frac{1\ sec}{300\ pulses} = 0.18\ \frac{neutrons}{pulse} [/math]
- 53.8 neutrons/sec (1/2 mil of Ti and without detector efficiency) <= this experiment is do able
- 0.18 neutrons/pulse (1/2 mil of Ti and without detector efficiency) <= good for stopping pulse
Counts Rate for U238 (1/2 mil of Al converter)
radiation length
r.l.(Al) = 8.89 cm
radiator thickness = 12.5 [math]\mu m[/math]
[math]\frac{12.5\ \mu m}{8.89\ cm} = 1.41 \cdot 10^{-4} \ r.l.[/math]
Calibration factor
The only difference from calculations above is:
1) radiation length:
1.41 (1/2 mil Al) / 3.48 (1/2 mil Ti) = 0.40
Yield (without detector efficiency)
- 53.8 neutrons/sec * 0.40 = 21.5 neutrons/sec (1/2 mil of Al)
- 0.18 neutrons/pulse * 0.40 = 0.07 neutrons/pulse (1/2 mil of Al)
Counts Rate for Deuteron (12.5 µm Ti converter)
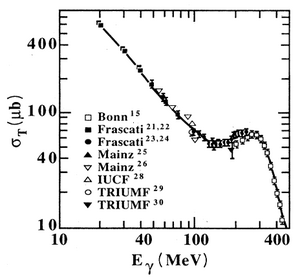
photonuclear cross section for [math] ^2H(\gamma , n) [/math] reaction
A. De Graeva et all., Phys. Rev. C45, 860 (1992):
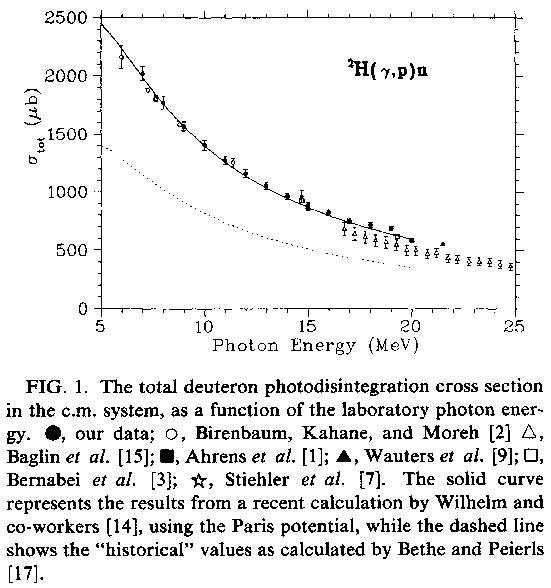
in (10,20) MeV region the average cross section, say, is:
1000 μb
target thickness, [math] D_2O [/math]
take [math]D_2O[/math], liquid (20°C):
[math] \frac{1.1056\ g/mL}{20.04\ g/mol} = 0.055\ \frac{mol}{cm^3} \times \frac{6.02\cdot 10^{23}\ molecules}{mol} = 0.33\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{molecules}{cm^3} [/math]
[math] 0.33\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{molecules}{cm^3} \times \frac{2\ deuterons}{molecule} = 0.66\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{deuterons}{cm^3} [/math]
Let's target thickness = 10 cm:
[math]0.66\cdot 10^{23}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^3} \times 10\ cm = 66\cdot 10^{22}\ \frac{atoms}{cm^2}[/math]
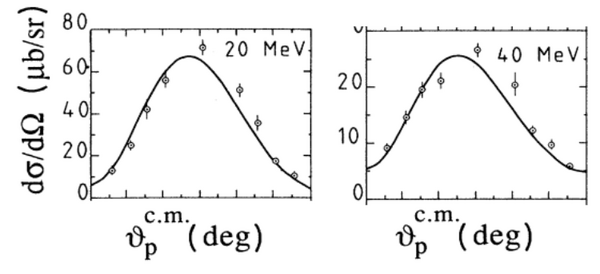
angular distribution of neutron
P. Rossi et all., Phys. Rev. C40, 2412 (1989):
relativistic kinematics
An Introduction to Nuclear and Subnuclear Physics. Emilio Segre (1964)
[math] \tan(\Theta_i) = \frac{1}{\overline{\gamma}} \frac{\sin\Theta_i^*}{\overline{\beta} (E_i^*/p_i^*) + \cos\Theta_i^*}[/math]
where
asterisks are quantities referred to CM
barred quantities refer to the velocity of the CM
[math] E^* = \left[(m_1+m_2)^2 + 2T_1m_2\right]^{1/2}[/math]
[math] \overline{\gamma} = \frac{E}{E^*} = \frac{m_1 + m_2 + T_1}{E^*}[/math]
[math] \overline{\beta} = \frac{p}{E} = \frac{p_1}{m_1 + m_2 + T_1}[/math]
[math] E_3^* = \frac{E^{*2} + m_3^2 - m_4^2}{2E*}[/math]
[math] E_4^* = \frac{E^{*2} + m_4^2 - m_3^2}{2E*}[/math]
[math] |p_3^*| = |p_4^*| = \left( E_3^{*2} - m_3^2 \right)^{1/2} = \left( E_4^{*2} - m_4^2 \right)^{1/2}[/math]
calculations
| [math]T_{\gamma}[/math]
|
[math]\Theta_{LAB}[/math]
|
[math]\Theta_{CM}[/math]
|
[math]\sigma_{T}[/math]
|
[math]d \sigma / d \Omega\left(\Theta_{CM}\right)[/math]
|
[math]\Omega_{Det}=\frac{A}{r^2}[/math]
|
[math]\frac{d \sigma / d \Omega \times \Omega_{Det}}{\sigma_{T}}[/math]
|
| 20 MeV |
[math]90^o[/math] |
[math]94.38^o[/math] |
[math]600\ \mu b[/math]
|
[math]63\ \mu b/sr[/math] |
[math]40\cdot 10^{-4}\ sr[/math] |
[math]4.2\cdot 10^{-4}[/math]
|
| 40 MeV |
[math]90^o[/math] |
[math]96.06^o[/math] |
[math]350\ \mu b[/math]
|
[math]23\ \mu b/sr[/math] |
[math]40\cdot 10^{-4}\ sr[/math] |
[math]2.6\cdot 10^{-4}[/math]
|
geometrical factor
taking average for 20 and 40 MeV photons
geometrical acceptance = [math]\frac{(4.2\cdot 10^{-4} + 2.6\cdot 10^{-4})}{2} = 3.4\cdot 10^{-4}[/math]
Calibration factor
The only differences from calculations above are:
1) cross section correction:
1000 μb (D) / 130 mb (238U) = 1/130
2) target thickness correction:
[math] \frac{66\cdot 10^{22}\ atoms/cm^2\ (D)}{0.48\cdot 10^{23}\ atoms/cm^2\ (^{238}U)} = 66/0.48 [/math]
3) neutrons per reaction correction:
1 neutron (D) / 2.4 neutrons(238U) = 1/2.4
4) geometrical factor correction:
[math] \frac{3.4\cdot 10^{-4}\ (D)}{3.2\cdot 10^{-4}\ (^{238}U)} = 1.06 [/math]
total calibration factor is:
[math]\frac{1}{130} \times \frac{66}{0.48} \times \frac{1}{2.4} \times \frac{3.4}{3.2} = 0.468[/math]
Yield
saying all other factors is the same =>
the yield per second :
[math] 53.8\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} \times 0.468 = 25.2\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} [/math]
the yield per pulse:
[math] 23.7\ \frac{neutrons}{sec} \times \frac{1\ sec}{300\ pulses} = 0.08\ \frac{neutrons}{pulse} [/math]
Summary
| converter
|
target
|
neutrons/sec
|
neutrons/pulse
|
| 1/2 mil Ti |
[math]^{238}U[/math] |
53.8 |
0.18
|
| 1/2 mil Al |
[math]^{238}U[/math] |
21.5 |
0.07
|
| 1/2 mil Ti |
[math]D_2O[/math] |
25.2 |
0.08
|
| 1/2 mil Al |
[math]D_2O[/math] |
10.1 |
0.03
|
Go Back




