Difference between revisions of "Conversion TDC to Energy"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [http://wiki.iac.isu.edu/index.php/PhotoFission_with_Polarized_Photons_from_HRRL Go Back] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
= Method 1: = | = Method 1: = | ||
Latest revision as of 06:18, 5 February 2009
Method 1:
Calculation
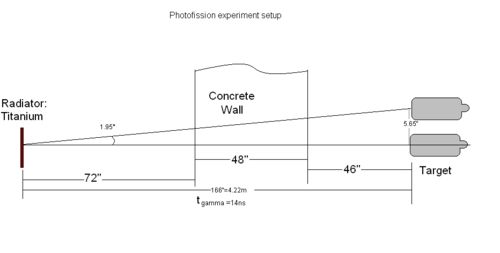
When electron beam hit the radiator, TDC start to count. It will take gamma 14 ns to reach the target. Then after some time , neutron arrive to the detectors.
Let's call the the total time from electron beam hit the radiator to neutron to be detected is . So,
where d is the distance between detector and target, v is speed of neutron. So,
where should be in the unit of nano second.
Data
For data go to link:
http://inca.iac.isu.edu/~setiniyaz/photofis/Method1/
or click on:
File:Method 1 unpolarized top.pdf
File:Method 1 unpolarized side.pdf
Method 2: Using time difference in two peaks
Calculation
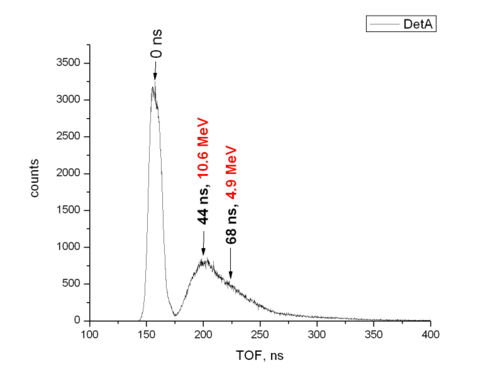
If we assume gamma flash is coming from target, then by time difference in gamma peak and neutron peak, we can tell the energies in neutrons.
: Neutron time of flight
: Gamma time of flight
d: Distance between detector and target.
d for polarized case: = 91.25 inches = 231.775 cm.
d for unpolarized top detector: =96.25 inches = 244.745 cm.
d for unpolarized side detector: =91.39 inches = 232.131 cm.
)
=>
=
={1- }
=939.5656*{1- } (MeV)
Where d is geven above.
Data
For data go to Link below:
http://inca.iac.isu.edu/~setiniyaz/photofis/TDCtoMeV/
or click on:
File:Method 2 unpolarized top.pdf
File:Method 2 unpolarized side.pdf
Energy vs Channel
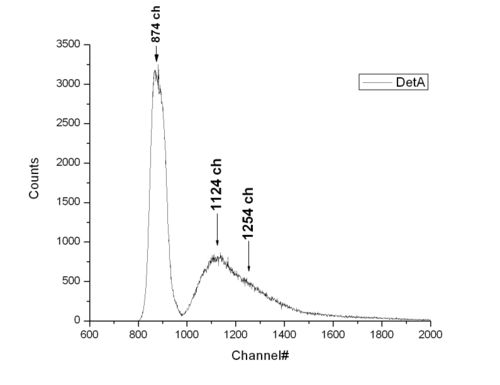
We calibrated ADC [[1]] and using those data we can tell energy of neutron by its relative channel number difference from gamma peak.
There a two scale for ADC. One is 2000 ns, the other one is 5000ns.
For 2000 ns scale:
File:Method 2 polarized 2000 channels.pdf
For 5000 ns scale:
File:Method 2 polarized 5000 channels.pdf
Example Analysis
Channel difference in two peaks is about 260 channels. This corresponds to 47 ns, which is 9.5 MeV neutron kinetic energy.
4.9 MeV neutrons come 68 ns later, which corresponds to 380 channels difference.