Sadiq Thesis
Introduction
Positron
Positron is the antimatter of electron. Positrons have same mass as electron ( ), carries positive charge, and it is noted as "".
Positrons predicted by Paul Dirac in 1928, <ref name="Dirac1928"> The Quantum Theory of the Electron, P. A. M. Dirac, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A February 1, 1928 117 778 610-624;</ref>, and experimentally observed by Dmitri Skobeltsyn in 1929 and by Carl D. Anderson in 1932 <ref name="e+_discover"> General Chemistry, Taylor and Francis. p. 660. </ref>. Anderson also coined the term positron and he won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1936.
<ref name="name"> BOOK_Gernal, Auther, Month_Year,issue,page </ref>
Positron Beamline History
Theory
positron creation from Bremsstrahlung
Positron rate prediction
Apparatus
HRRL Positron Beamline
Beam properties
Emittance Measurement
Energy Spread Measurement
Current, rep-rate
Radiation Footprint
Positron detection
DAQ setup
Data Analysis
Signal extraction
For 3 MeV and on detector show all the steps
- Raw counts target in and out (calibrated energy)
- Normalized counts
- background subtracted
- Integral (zoomed in and with error)
Example of error propagation for the above
Raw counts target in and out
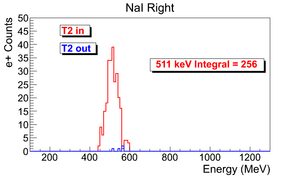
| run in | run out | NaI Left: image with cut | NaI Right: image with cut | 3735 | 3736 | 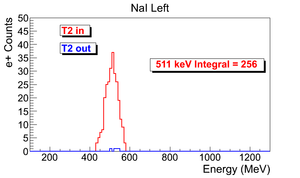
|
|
Reprate = 300 Hz
Run time = 1002 s
Pulses = 301462
Events = 9045 (Hz)
e+ rate NaI Left = 256 +- 16 (Hz).
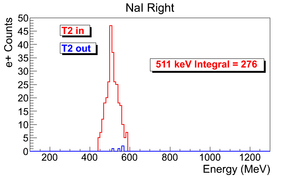
| run in | run out | NaI Left: image with cut | NaI Right: image with cut | 3737 | 3736 | 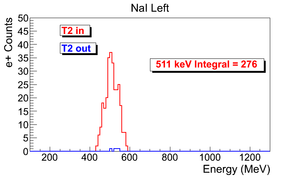
|
|
Reprate = 300 Hz
Run time = 1094 s
Pulses = 329368
Events = 15361 (Hz)
e+ rate NaI Left = 276 +- 16.6132 (Hz).
Background subraction
Sources of Systematic Errors
Efficiency measurement
acceptance, quad collection efficiency,
Conclusion
References
<references/>