2n Neutron signal attenuation
Cf-252 source attenuation test
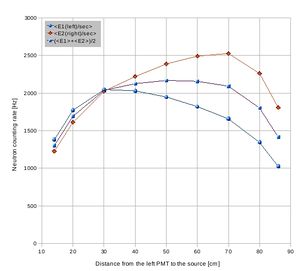
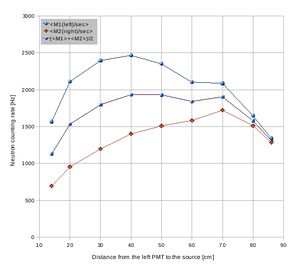
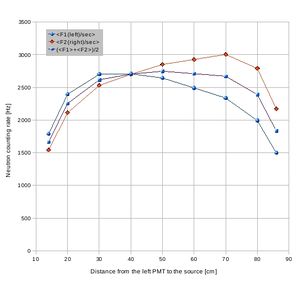
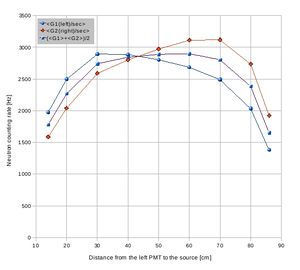
Cf-252 source was used to define the attenuation of a signal produced by neutrons in plastic scintillator. Cf-252 source was placed in different positions along the detector surface shielded with 2" of lead and counting rate of the two PMTs was observed via dual counter ORTEC 778. Cf-252 source was surrounded by borated poly to provide collimation of about 5 cm in diameter.
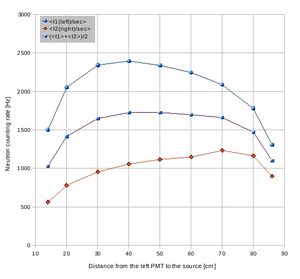
Would you add to the plot the sum of the rate from each end of the PMT.
In order to get it on the same scale you could divide by 2 or use a scale on the right side of the graph
Data with the counting rate from each tube added together.
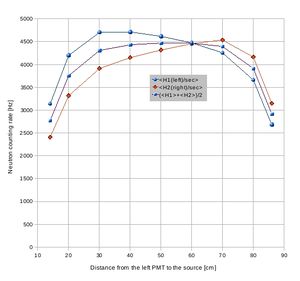
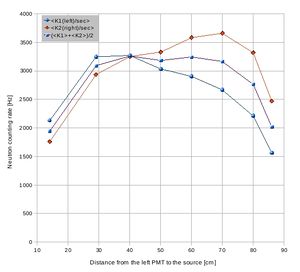
Detector E(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector M(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector F(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector G(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector H(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector K(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
Detector I(1,2) neutron signal attenuation data sheet:
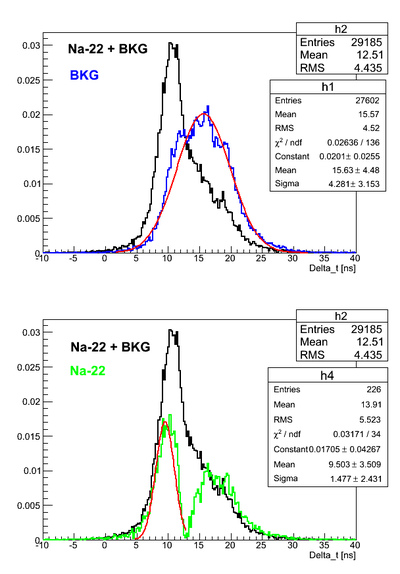
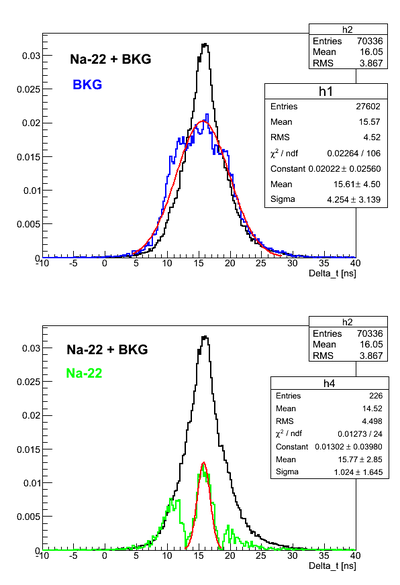
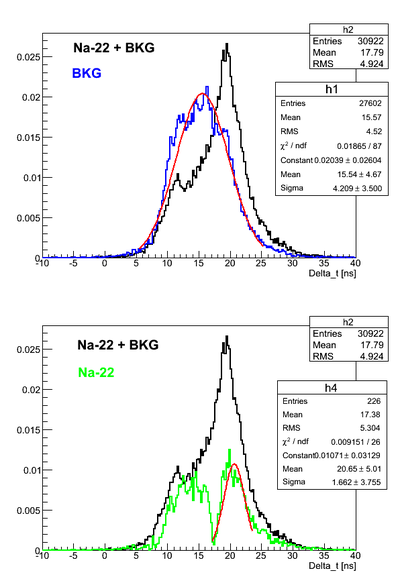
Na-22 source timing test
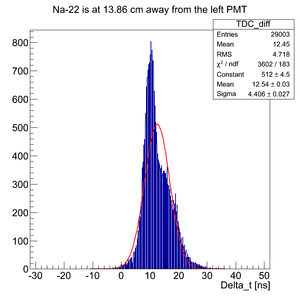
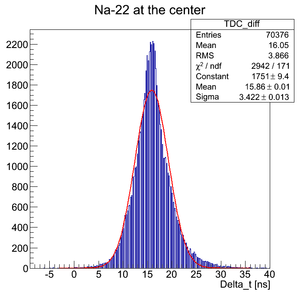
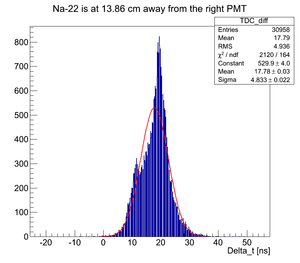
Here it was used Det K. DAQ was triggered on the coincidence signal from two PMTs and each PMT signal was delayed and connected to corresponding TDC channel. DAQ was configured to work in the common start mode. Na-22 source was moved over the detector surface.
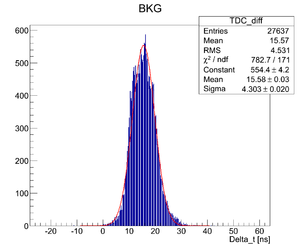
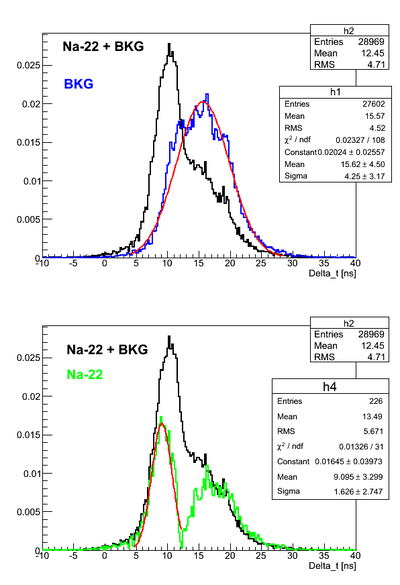
Raw spectra
As can be seen the BKG spectrum is not centered around zero time. That means that delays in the channels are different.
Normalized and BKG subtracted data
For all the timing spectra it was calculated K1(left)-K2(right).
The source is close to the left PMT (13.86 cm away):
The source is a bit further from the left PMT (17.64 cm away):
The source is at the center of the detector:
The source is close to the right PMT (13.86 cm away):
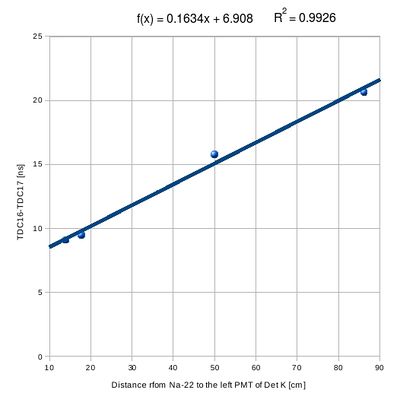
Calibration curve
Finally, using the mean values of the fitted Na-22 peaks the calibration curve can be plotted:
Hence, the slope is 0.1634 ns/cm or 6.12 cm/ns.