Plotting Different Frames
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
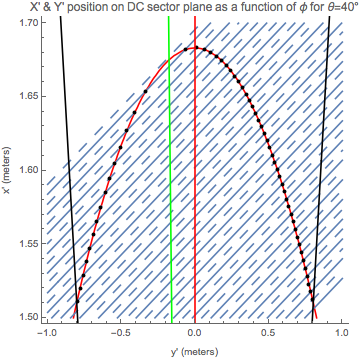
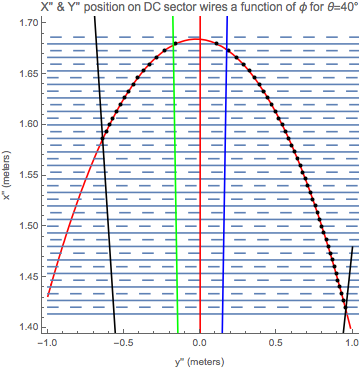
We can define different arrays to collect the coordinates in the different frames using a passive transformation. Assuming that the intersection of the ellipse and sense wires is in the y-x plane, we will have a positive rotation,
rFromYtoX = ( {
{Cos[6 \[Degree]], -Sin[6 \[Degree]], 0},
{Sin[6 \[Degree]], Cos[6 \[Degree]], 0},
{0, 0, 1}
} );
rFromXtoY = ( {
{Cos[6 \[Degree]], Sin[6 \[Degree]], 0},
{-Sin[6 \[Degree]], Cos[6 \[Degree]], 0},
{0, 0, 1}
} );
yxPoints = constant\[Theta];
constant\[Theta]yx = constant\[Theta];
constant\[Theta]yxRotated = constant\[Theta];
constant\[Theta]xyz = constant\[Theta];
constant\[Theta]xyzRotated = constant\[Theta];
RowLengths = Table[{Nothing}, {i, 1, 36}];
For[rows = 1, rows < 37, rows++,
RowLengths[[rows]] = Length[constant\[Theta][[rows]]];
For[columns = 1, columns < RowLengths[[rows]] + 1, columns++,
\[Theta] = rows + 4;
\[Phi] = constant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]];
constant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns]] = {y,
Sqrt[a^2 (1 - y^2/b^2)] - \[CapitalDelta]a};
constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows,
columns]] = {constant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 2]],
constant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 1]], 0};
If[constant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]] < 0,
constant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns,
1]] = -constant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 1]];
constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns,
2]] = -constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 2]];
];
constant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns]] =
rFromYtoX.{constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 1]],
constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 2]],
constant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 3]]};
constant\[Theta]yxRotated[[rows,
columns]] = {constant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns, 2]],
constant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns, 1]]};
yxPoints[[rows, columns]] = {y,
Sqrt[a^2 (1 - y^2/b^2)] - \[CapitalDelta]a,
constant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]],
constant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 2]]};
]
];
ClearAll[\[Theta], \[Phi]];
DesiredyxPoints = Desiredconstant\[Theta];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx = Desiredconstant\[Theta];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yxRotated = Desiredconstant\[Theta];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz = Desiredconstant\[Theta];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyzRotated = Desiredconstant\[Theta];
DesiredRowLengths = Table[{Nothing}, {i, 1, 36}];
For[rows = 1, rows < 37, rows++,
DesiredRowLengths[[rows]] =
Length[Desiredconstant\[Theta][[rows]]];
For[columns = 1, columns < DesiredRowLengths[[rows]] + 1,
columns++,
\[Theta] = rows + 4;
\[Phi] = Desiredconstant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns]] = {y,
Sqrt[a^2 (1 - y^2/b^2)] - \[CapitalDelta]a};
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows,
columns]] = {Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 2]],
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 1]], 0};
If[Desiredconstant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]] < 0,
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns,
1]] = -Desiredconstant\[Theta]yx[[rows, columns, 1]];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns,
2]] = -Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 2]];
];
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns]] =
rFromYtoX.{Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 1]],
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 2]],
Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyz[[rows, columns, 3]]};
Desiredconstant\[Theta]yxRotated[[rows,
columns]] = {Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns,
2]], Desiredconstant\[Theta]xyzRotated[[rows, columns, 1]]};
DesiredyxPoints[[rows, columns]] = {y,
Sqrt[a^2 (1 - y^2/b^2)] - \[CapitalDelta]a,
Desiredconstant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 1]],
Desiredconstant\[Theta][[rows, columns, 2]]};
]
];
ClearAll[\[Theta], \[Phi]]
The parameter's range changes from the DC frame with 0<t<2, since
In the frame of the wires, the x axis no longer is aligned with the semi-major axis, therefore for in the DC frame
In[153]:= ClearAll[X, \[Theta]];
\[Theta] = 40;
X = X /. Solve[(X + \[CapitalDelta]a)^2/a^2 == 1 && X > 0, X]
Out[155]= {1.68318}
This gives the (x' , y')=(1.68318, 0) in the DC frame for

