Alpha Ionization
Alpha Particles ionization simulation using GEANT4
GEANT4 simulates the ionization of alpha particles in Ar/CO2 90/10 gas. Geant4 can simulate the ionization process for the alpha particles, but unfortunately the value of the step function of the step function that determines the number of delta electrons is very low even by decreasing the cut to 1 nm. Also Range of alpha particles in Ar/CO2 gas is not accurate and does not match the projected ranges using srim File:Alpha range ArCo2.txt, the following table shows the maximum range of the alpha particles that are emitted from the U-233, and the ranges calculated by srim.
| Alpha Energy (MeV) | G4 Range (cm) | Srim Range (um) |
| 1.0 | 0.56599 | 129.49 |
| 2.0 | 1.1467 | 255.91 |
| 3.0 | 1.9024 | 417.27 |
| 4.0 | 2.8012 | 612.45 |
| 5.0 | 3.8425 | 839.91 |
Based on the previous table, GEANt4 failed to calculate the expected alpha range for most energy, in addition to underestimating the number of alpha's delta electrons emitted through that range.
Calculating the number of the delta electrons without using GEANT4
there is Another way to Calculate the number of delta electrons without using GEANT4. It starts by calculating the average energy loss by the alpha and average energy loss per unit length in Ar/CO2 gas using Bethe-Block equation,then using the the following equation:
to calculate the actual energy loss by ionization , where represents random landau number. By dividing the energy loss by the minimum energy for producing a pair of ion/electron W, it gives the number of electrons emitted by ionization.
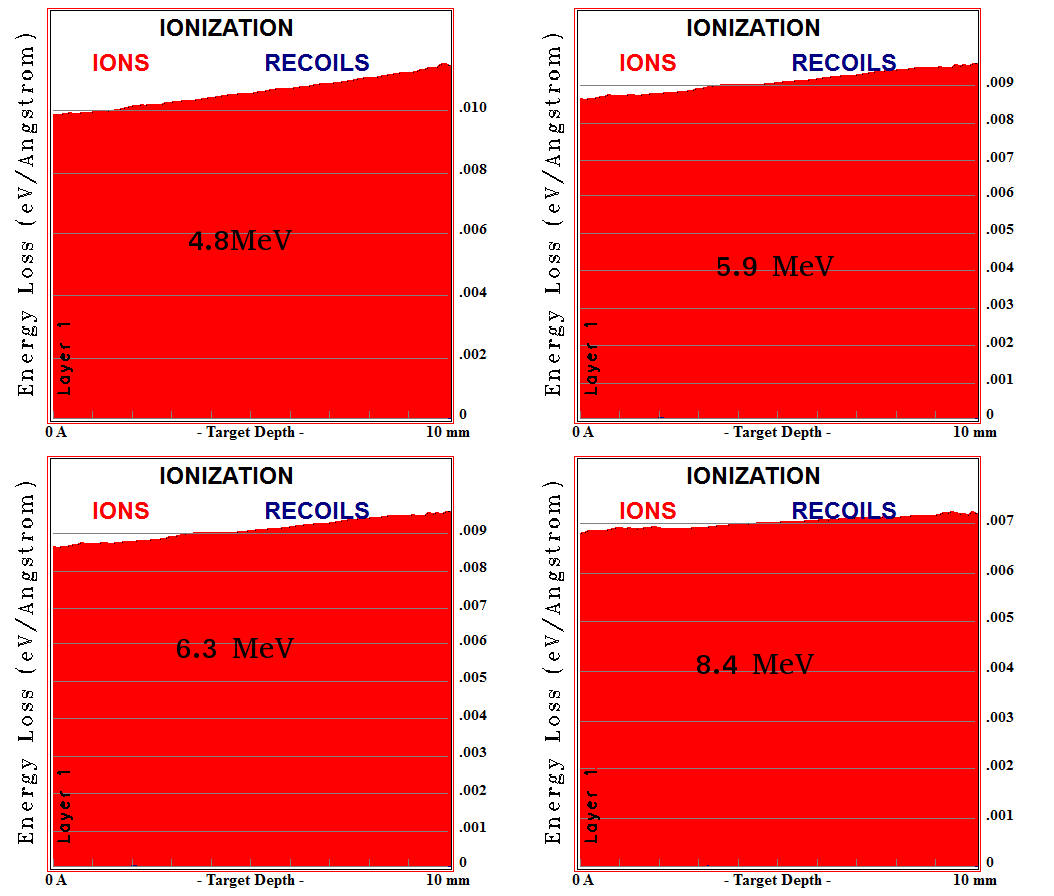
Srim can simulate the motion of an alpha particle in Ar/CO2 gas by considering the change in the stopping power per unit length, it also can show the ionization energy loss as shown in the following figure:
The figure shows the ionization energy loss of 999 alpha particles as they pass through a 0.85 mm Ar/CO2 gas. integrating the area under the curve, then dividing by (W*1000) will give the number of delta electrons produced by an alpha particle.