Sadiq Proposal Defense
Emittance
What is Emittance
In accelerator physics, Cartesian coordinate system was used to describe motion of the accelerated particles. Usually the z-axis of Cartesian coordinate system is set to be along the electron beam line as longitudinal beam direction. X-axis is set to be horizontal and perpendicular to the longitudinal direction, as one of the transverse beam direction. Y-axis is set to be vertical and perpendicular to the longitudinal direction, as another transverse beam direction.
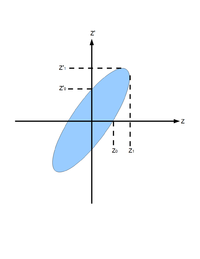
For the convenience of representation, we use to represent our transverse coordinates, while discussing emittance. And we would like to express longitudinal beam direction with . Our transverse beam profile changes along the beam line, it makes is function of , . The angle of a accelerated charge regarding the designed orbit can be defined as:
If we plot vs. , we will get an ellipse. The area of the ellipse is an invariant, which is called Courant-Snyder invariant. The transverse emittance of the beam is defined to be the area of the ellipse, which contains 90% of the particles
References
<references/>
Go back: Positrons