Lab 8 TF EIM
Lab 8 The Diode Objective: Measure the current-voltage curve of a silicon diode.
Reverse current
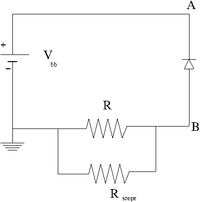
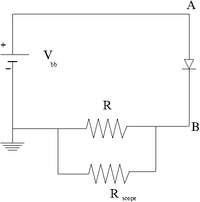
1.) Construct the circuit below using a DC power supply, a diode.
2.) Attach an Oscilloscope with internal resistance . The scope will measure the voltage drop across R and thus the current will be given by this voltage difference divided by R.
3.) Determine a value for R which will allow you to measure a current of at least 10 mA (prefeferably 50 mA) at the diodes reverse bias cut off voltage.
4.) Measure the diode reverse current as a function of the DC supply voltage. (30 pnts)
| Bias Voltage | V_{scope} | Current (V/R) | Diode power | R power |
5.) Fill in the blank. The reverse biased diode act as a constant _______________ source. (5 pnts)
Forward Current
- now swap the diode direction and repeat the measurement in the previous section.
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Current (V/R) | Power |
Graph
- make the same measurements in parts 1 and 2 above for a germanium diode.
- Plot the diode current (on the ordinate) versus the diode voltage (on the abscissa)for both diodes on the same graph. (50 pnts)
Questions
- The reverse biased diode acts like a constant ____________. (10 pnts)
- The forward biased diode has a very __________ resistance. A reverse biased diode has a very ____________ resistance.(10 pnts)
- The approximate DC forward resistance for diode #___________ is _________ when the forward current is _______________.(10 pnts)
- The approximate DC reverse resistance for diode #___________ is _________ when the forward current is _______________.(10 pnts)
- The silicon diode #___________ has an approximate turn on voltage of ___________.(10 pnts)