Forest NucPhys I Nuclear Reactions
Nuclear Reactions
Types of Reactions
- elastic scattering
- X & Y and a & b are the same particles, momentum and energy are conserved, typically all are in their ground state
- In-elastic scattering
- If Y or b are in an excited state, energy is not conserved it is used to excite one of the exiting particles.
- Note
- Elastic collisions are usually referred to as collisions and not nuclear reactions.
Direct Reactions
- knockout reaction
- a & b are the same but there are 3 total particles in the final state.
- n + X \rightarrow Y + 3n = X(n,3n)Y
- Transfer Reaction
- a nuclear from projectile a is transfered to target X
- Nuclear PhotoEffect
- projectile a ejects a nucleon from target X
- e - + Mo-100 \rightarrow Mo-99 + n + e- = X(e,e'n)Y
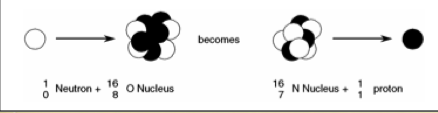
Capture
Compound reactions
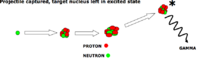
- Compound reaction
- projectiel a is captured by target X forming an intermediate state which then decays, possibly through multiple excited nuclear states/species, to Y and b
This is typically a low energy reaction in which particle Y doesn't leave the target material but the intermediate state may be surmised at through the detection of particle b.