TF EIMLab8 Writeup
Lab 8 The Diode Objective: Measure the current-voltage curve of a silicon diode.
Reverse current
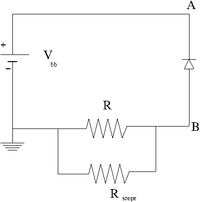
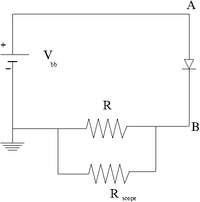
1.) Construct the circuit below using a DC power supply, a diode.
2.) attach an Oscilloscope set to 1M input impedence so the probe is located at point B. The oscilloscope's internal resistance will serve as a Resistor (R) to measure the voltage across the diode and calculate the current.
3.) Calculate the value of R needed to observe the current without burning up the diode. What is the max reverse voltage you will have.
P_{diode} = 0.5 Watts
V_{max} = 4.9 Volts
I_{rev}^{max} = 5 \mu A at V = 2 Volts
R = \frac{4.9}{5 \mu V} = 1 k\Omega
P = V I = 4.9 Volts \times 5 \mu A = 0.025 Wats
4.) Measure the diode reverse current as a function of the DC supply voltage. (30 pnts)
IN5230-B-T (4.7 Volt Zener Diode), The other diode is the IN5238B
Data sheet =>File:IN5230-B-T DataSheet.pdf
| V_Z | Z_Z (I_Z) | I_R (V_R) | Max Power |
| 4.7 | 19\Omega (20 mA) | 2\mu A (1 Volt) | 500 mW |
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Current (V/R) | Power |
| -2.5\pm 0.05 | 5 \pm 7 | 5/50 = 0 \pm 0.02 mA | |
| -4.4\pm 0.05 | 59\pm 10 mV | 0.59 \pm 0.1 mA | |
| -4.70 \pm 0.05 | 220 \pm 10 mV | 2.2 \pm 0.1 mA | 449 mW |
| -5.03 \pm 0.05 | 1050 \pm 15 | 10.5 \pm 0.2 mA | |
| -5.22 \pm 0.05 | 2280 \pm 50 | 22.8 \pm 0.5 mA | too much power |
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Current (V/R) | Power |
| 2.50 \pm 0.05 | 24 \pm 1 | 24/50 = 0.5 \pm 0.02 mA | 125 |
| 3.14 \pm 0.05 | 31.1 \pm 2 | 0.62 \pm 0.064 mA | |
| 4.07\pm 0.05 | 109 \pm 03 mV | 2.18 \pm 0.06 mA | |
| 4.46 \pm 0.05 | 274 \pm 3 mV | 5.4 \pm 0.06 mA | |
| 4.74 \pm 0.05 | 824 \pm 10 mV | 16.48 \pm 0.2 mA | 449 mW |
| 4.89 \pm 0.05 | 1860 \pm 10 | 37.2 \pm 0.2 mA | |
| 5.02 \pm 0.05 | 3880 \pm 10 | 77.6 \pm 0.2 mA |
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Keithley ammeter |
| 0.6 \pm 0.001 | 2 \pm 1 | 1.24 \pm 0.01 |
| 0.9 \pm 0.001 | 10 \pm 1 | 8.69 \pm 0.01 nA |
| 1.05 \pm 0.005 | 22 \pm 0.5 mV | 24.3 \pm 0.05 nA |
| 1.16 \pm 0.005 | 40 \pm 1 mV | 49.4 \pm 0.05 nA |
| 1.23 \pm 0.005 | 56 \pm 1 mV | 78.6 \pm 0.05 nA |
| 1.27\pm 0.005 | 68 \pm 1 mV | 98.2 \pm 0.005 nA |
| 1.30\pm 0.005 | 75 \pm 1 | 118.2 \pm 0.5 |
| 1.35 \pm 0.005 | 93 \pm 1 | 158.2 \pm 0.5 |
| 1.4 \pm 0.005 | 112 \pm 1 | 213.0 \pm 0.1 |
| 1.45 \pm 0.005 | 132 \pm 1 | 279.1 \pm 0.1 nA |
| 1.50 \pm 0.005 | 155 \pm 1 | 366 \pm 0.5 nA |
| 1.55 \pm 0.005 | 182 \pm 1 | 474 \pm 0.5 |
| 2.53 \pm 0.01 | 902 \pm 4 | 24 \pm .5 \times 10^{3} nA |
| 2.95 \pm 0.05 | 290 \pm 9 | 10 \pm 1 \times 10^{4} nA |
| 3.85 \pm 0.05 | 2240 \pm 20 | 83 \pm 1 \times 10^{4} |
| 4.62\pm 0.05 | 2900 \pm 6 | 8.0 \pm 0.5 \times 10^{6} |
| 5.5 \pm 0.05 | 3740 \pm 30 | NA |
| 6.4 \pm 0.05 | 4760 \pm 23 | |
| 7.4 \pm 0.05 | 5700 \pm 33 | |
| 9.84 \pm 0.05 | 8.04 \pm 30 |
4.) Fill in the blank. The reverse biased diode act as a constant _______________ source. (5 pnts)
Forward Current
- now swap the diode direction and repeat the measurement in the previous section.
IN5230-B-T (4.7 Volt Zener Diode)
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Keithley ammeter |
| 0.922 \pm 0.005 | 1780 \pm 40 | 17.80 \pm 0.4 mA |
| 0.953 \pm 0.005 | 2800 \pm 40 | 28.0 \pm 0.4 |
| 1.00 \pm 0.005 | 4280\pm 50 | 42.8 \pm 0.5 |
| Bias Volts | V_{scope} (1 M\Omega)(mV) | Keithley ammeter |
| 0.850 \pm 0.005 | 1740 \pm 20 | 1740/50 = 34.8 mA |
| 0.872 \pm 0.005 | 3090 \pm 20 | |
| 0.883 \pm 0.005 | 4230\pm 35 | |
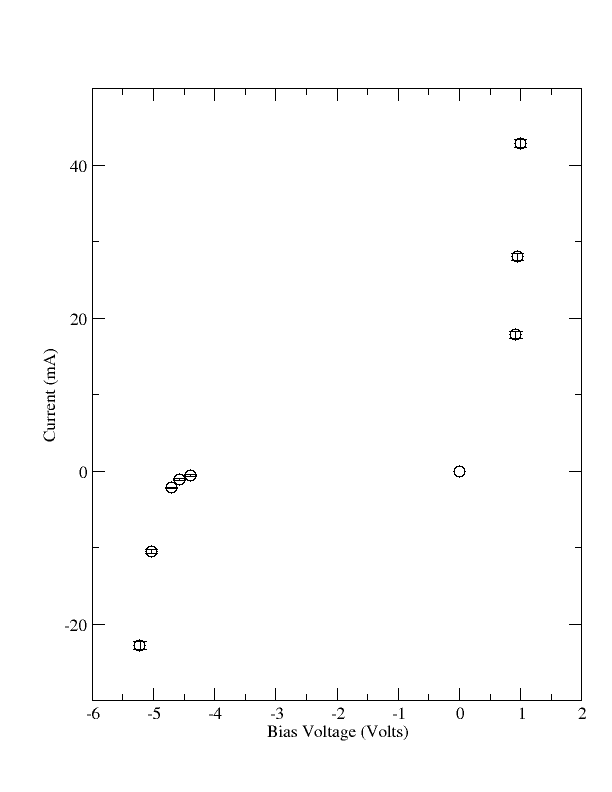
Graph
- Plot the diode current (on the ordinate) versus the diode voltage (on the abscissa)for both the reverse and forward bias measurements. (50 pnts)
Questions
- The reverse biased diode acts like a constant _____DC Voltage_______. (10 pnts)
- The forward biased diode has a very __________ resistance. A reverse biased diode has a very ____________ resistance.(10 pnts)
- The approximate DC forward resistance for diode #___________ is _________ when the forward current is _______________.(10 pnts)
- The approximate DC reverse resistance for diode #___________ is _________ when the forward current is _______________.(10 pnts)
- The silicon diode #___________ has an approximate turn on voltage of ___________.(10 pnts)