Lab 6 Pulses and RC Filters
Differentiator
1.) Adjust the pulse generator to output square pulses which at [math]\tau[/math] sec in time.
Possible capacitors
- [math]C_1 = 1 \times 10^{-6} F[/math]
- [math]C_2 = 10.24 \times 10^{-9} F[/math]
Possible Resistors
- [math]R_1 = 1 \times 10^3 \Omega[/math]
- [math]R_2 = 14.35 \times 10^{3} \Omega[/math]
- [math]R_1 C_1 = \tau_1 = (1 \times 10^3 \Omega ) (1 \times 10^{-6} F )= 0.001[/math] s
- [math]R_1 C_1 = \tau_2 = (14.35 \times 10^{3} \Omega)(10.24 \times 10^{-9} F )= 1.46 \times 10^{-4}[/math]
- [math]\omega_1 = 100 rad/sec \Rightarrow \nu_1 = 100/2\pi = 16 Hz[/math]
- [math]\omega_2 = 6805 rad/sec \Rightarrow \nu_2 = 1083 Hz[/math]
tek012
- [math]R_1 C_1 = \tau_2 = (1.46 \times 10^{-4}[/math]
2.)Construct the circuit below selecting an RC combination such that RC [math]\approx[/math] 1/10
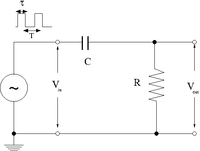
3.)Measure[math] V_{in}[/math] and [math]V_{out}[/math]. Sketch a picture comparing[math] V_{out}[/math] and [math]V_{in}[/math].
4.) Change the pulse width such that [math]RC = \tau[/math]
5.)Measure[math] V_{in}[/math] and [math]V_{out}[/math].Sketch a picture comparing[math] V_{out}[/math] and [math]V_{in}[/math].
6.) Change the pulse width such that[math] RC = 10 \tau[/math]
7.)Measure [math]V_{in} and V_{out}[/math].Sketch a picture comparing[math] V_{out}[/math] and [math]V_{in}[/math].
Questions
1.) What happens if than amplitude of [math]V_{in}[/math] is doubled.
2.) What happens if R is doubled and C is halved?
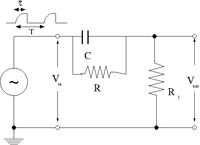
Integrator
To illustrate the integrator circuit we need to have an input pulse which looks like the output of the above differentiator circuit. In other words, input a pulse whose output is obviously the integral of the input pulse.
Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement

