Forest IonizationChambers
An ionization chamber is essentially a gas filled volume which has one or more wires suspended inside with a voltage bias used to collect any ions or liberated electrons within the volume.
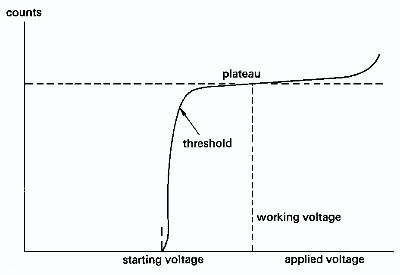
There are 4 basic operating regions which are determined by the amount of the voltage across the wire(s).
- recombination
- ionization
- proportional (plataue)
- Geiger-Muller
Recombination
Until the voltage reaches a high enough value (threshold), the liberated electrons produces will recombine with the gas before reaching the wire.
Ionization
Once the voltage is increased beyond the above threshold, the ions/ electrons make it to the cathode/anode and produce an electronic pulse on the wire (cathode). The voltage is high enough to attract all of the electron-ion pairs. The pulse height (signal) out of the chamber is independent of the voltage at this point.
quick definitions
- Anode
- Current IN, positively charged electrode
- Cathode
- Current OUT, negatively charged electrode
The flow of electrons is from the cathode to the anode.
Proportional
At a certain voltage though the electron-ions pairs gain enough kinetic energy that they can start to ionization the chamber gas as well. Now the pulse height (signal) out of the chamber depends on the Voltage on the wire.