Difference between revisions of "Forest UCM Energy CentralForce"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
:<math>df = f(x+dx) -f(x) = \frac{df}{dx} dx</math> | :<math>df = f(x+dx) -f(x) = \frac{df}{dx} dx</math> | ||
| − | in three | + | in three dimensional cartesian coordinates this may be written in terms of the gradient as |
| − | :<math>df = \vec \nabla f \cdot d \vec r</math> | + | :<math>df = \frac{df}{dx} dx + \frac{df}{dy} dy + \frac{df}{dz} dz =\vec \nabla f \cdot d \vec r</math> |
| − | + | ||
| + | To determine the gradient in sperical coordinates on just compares the two equations | ||
| + | |||
| + | :<math>\frac{df}{dr} dr + \frac{df}{d \theta} d\theta + \frac{df}{d\phi} d\phi =\vec \nabla f \cdot d \vec r</math> | ||
| + | ::<math>\vec \nabla f \cdot d \vec r = \left . \vec \nabla f \right |_r dr</math> | ||
comparing terms of the above with | comparing terms of the above with | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 27 September 2014
A central force is defined as a force depends only on separation distance
ie
Coulomb force and gravitation force.
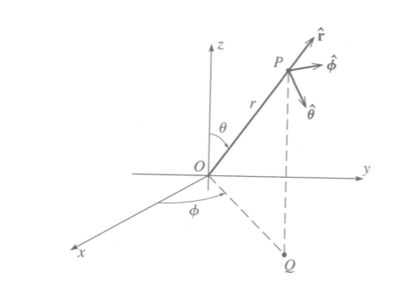
Spherical Coordinates
Forest_UCM_NLM_Ch1_CoordSys#Spherical
Gradient in spherical coordinates
The differential change of in spherical coordinates occurs in three directions.
In the radial direction
In the polar angle direction
In the aximuthal angle direction
The differential force of the displacement vector in spherical coordinates is
The derivative may be represented as
in three dimensional cartesian coordinates this may be written in terms of the gradient as
To determine the gradient in sperical coordinates on just compares the two equations
comparing terms of the above with