Difference between revisions of "Forest UCM NLM AtwoodMachine"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 73: | Line 73: | ||
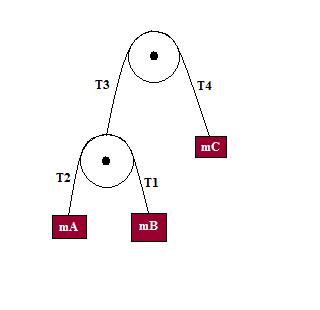
:<math>a_2=-a_r-a_3</math> : if <math>m_1</math> is accelerating upwards then <math>m_2</math> is accelerating downwards | :<math>a_2=-a_r-a_3</math> : if <math>m_1</math> is accelerating upwards then <math>m_2</math> is accelerating downwards | ||
| − | |||
[[Forest_UCM_NLM#Atwoods_Machine]] | [[Forest_UCM_NLM#Atwoods_Machine]] | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 22 August 2014
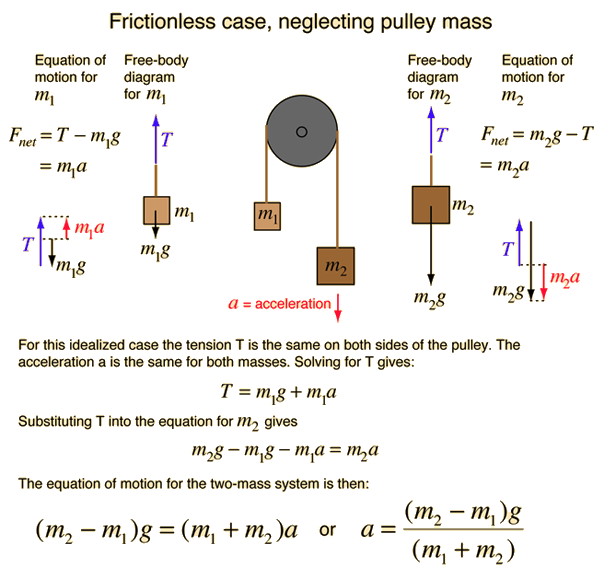
Simple Atwood's machine
Double Atwood's machine
The problem
Determine the acceleration of each mass in the above picture.
Step 1: Identify the system
- Each block is a separate system with two external forces; a gravitational force and the rope tension.
Step 2: Choose a suitable coordinate system
- A coordinate system with one axis that defines the posive direction as up is one possible orientation.
Step 3: Draw the Free Body Diagram
Step 4: Define the Force vectors using the above coordinate system
- for mass 1
- for mass 2
- for mass 3
If we know the mass of all the objects in the system then we are left with three unkown Tensions and three unknown acceleratios. In total we currently have 6 unkowns and 3 equations.
Using Newton's third law we know that reducing the unkowns to 5.
- We need 2 more equations!
External Forces on Lower pulley
Consider the external forces acting on the MASSLESS lower pulley
Now we have 4 unkwons and 3 equations
relative acceleration
let
- acceleration of with respect to the lower pulley
assuming that is moving upwards with respect to the earth
- : acceleration of lower pully as well as
similarly
- : if is accelerating upwards then is accelerating downwards