Difference between revisions of "Forest UCM NLM GalileanTans"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:TF_UCM_GalileanTans_RefFrame.png | 200 px]] | [[File:TF_UCM_GalileanTans_RefFrame.png | 200 px]] | ||
| + | |||
[[File:TF_UCM_GalileanTans_RefFrame.xfig.txt]] | [[File:TF_UCM_GalileanTans_RefFrame.xfig.txt]] | ||
Revision as of 13:00, 20 August 2014
File:TF UCM GalileanTans RefFrame.xfig.txt
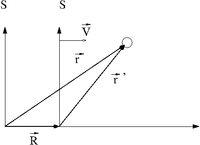
Assume that is a coordinate system moving at a CONSTANT speed with respect to a fixed coordinate system .
Let and describe the position an object in motion using two different coordinate systems and respectively.
represents a vector that locates the origin of the moving reference frame () with respect to the origin of reference from .
Using the definition of vector addition
Similarly
and
Newton's law of motion may be written as
If
- is moving at a constant velocity
Then
Newton's law hold in coordinate system which move at a constant velocity (an inertial reference frame). Accelerating reference frames are know as non-inertial reference frames and will be discussed later. (a coordinate system fixed to the Earth is a non-inertial reference frame since the Earth is rotating about its axis and moving in orbit about the Sun)