Difference between revisions of "TF EIMLab13 Writeup"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
{| border="1" |cellpadding="20" cellspacing="0 | {| border="1" |cellpadding="20" cellspacing="0 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |V_{CC} || V_B || V_ E || R_E || | + | |V_{CC} || V_B || V_ E || R_E || R_B || I_E || I_B |
|- | |- | ||
| || || || || | | || || || || | ||
Revision as of 23:53, 8 March 2011
DC Bipolar Transistor Curves
Transistor circuit
1.) Identify the type (n-p-n or p-n-p) of transistor you are using and fill in the following specifications.
| Value | Description |
| Collector-Base breakdown voltage | |
| Emitter-Base Breakdown Voltage | |
| Maximum Collector Voltage | |
| Maximum Collector Current | |
| Transistor Power rating() | |
| DC current gain |
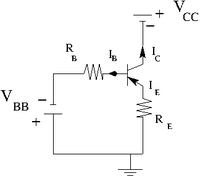
2.) Construct the circuit below according to the type of transistor you have.
Let R_E = 100 \Omega.
V_{CC} = variable power supply
V_{BE}= 1V.
I_B = 2 \mu A = 1V/500 k \Omega
- = 5 \mu A = 1V/200 k \Omega
- = 10 \mu A = 1V/100 k \Omega
3.) Measure the emitter current for several values of by changing such that the base current A is constant.
| V_{CC} | V_B | V_ E | R_E | R_B | I_E | I_B |
4.) Repeat the previous measurements for A. Remember to keep so the transistor doesn't burn out
5.) Graph -vs- for each value of and above. (40 pnts)
6.) Overlay points from the transistor's data sheet on the graph in part 5.).(10 pnts)
Questions
- Compare your measured value of or for the transistor to the spec sheet? (10 pnts)
- What is for the transistor?(10 pnts)
- The base must always be more _________(________) than the emitter for a npn (pnp)transistor to conduct I_C.(10 pnts)
- For a transistor to conduct I_C the base-emitter junction must be ___________ biased.(10 pnts)
- For a transistor to conduct I_C the collector-base junction must be ___________ biased.(10 pnts)