Difference between revisions of "Lab 6 RS"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| − | [[File:Lab6 | + | [[File:Lab6 1_m1.png | 600 px]] |
| − | |||
==Adjust the pulse generator to output square pulses which at <math>\tau \approx</math> RC/10.== | ==Adjust the pulse generator to output square pulses which at <math>\tau \approx</math> RC/10.== | ||
Revision as of 16:19, 10 February 2011
Lab 6 Pulses and RC Filters
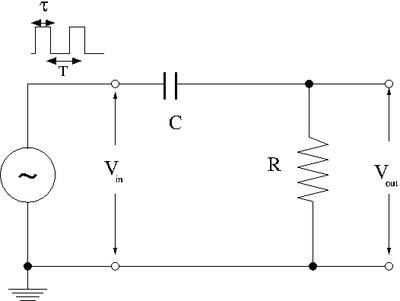
Differentiator
Construct the circuit below selecting an RC combination such that RC s
Adjust the pulse generator to output square pulses which at RC/10.
Measure and . Sketch a picture comparing and . ( 5 pnts.)
Change the pulse width such that RC
Measure and .Sketch a picture comparing and .( 5 pnts.)
Change the pulse width such that =10 RC
Measure and . Sketch a picture comparing and .( 5 pnts.)
Questions
What happens if the amplitude of is doubled.( 5 pnts.)
What happens if R is doubled and C is halved?( 5 pnts.)
The times constant becomes unchangeable so nothing is really happened
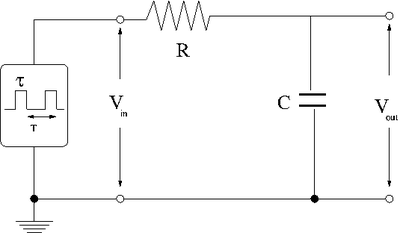
Integrator
Now repeat the above experiment with the resistor and capacitor swapped to form the low pass circuit below.
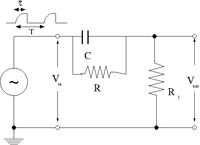
Pulse Sharpener
The goal of this section is to demonstrate how well the circuit below can sharpen an input pulse
1.) The first step is to create an input pulse which is rounded, similar to the output of the integrator circuit when RC = 10 . You can do this using a capacitor shorted across the output of the pulse generator. This will essential be coupled to the input impedance of the pulse generator and form a low pass circuit.
As a result the input voltage is given as
where
- = impedance of the function generator at output which produces V_{in}
- = capacitor shorting the function generator output to ground (not shown in the above picture)
2.) The output should be given by
where
3.) Make measurements of the rise time and . The rise time is defined as the time it take the pulse to go from 10% of its max value to 90% of its max value.( 5 pnts.)
4.) Compare the measurement of to what you expected based on your measured values of , and.( 15 pnts.)
Questions
1.) Qualitatify, why is ?( 10 pnts.)
2.) How is worse than ( 10 pnts.)