Difference between revisions of "Lab 3 RS"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|0.1 ||5.0 ||5.0 ||1.0|| || | |0.1 ||5.0 ||5.0 ||1.0|| || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |1.0 ||4.2 ||4.2 ||1.0|| | + | |1.0 ||4.2 ||4.2 ||1.0||14.0 ||0.094 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |2.0 ||3.2 ||3.1 ||0.97|| | + | |2.0 ||3.2 ||3.1 ||0.97||14.0 ||0.188 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |5.0 ||1.8 ||1.6 ||0.89|| | + | |5.0 ||1.8 ||1.6 ||0.89||14.0 ||0.471 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |10.0 ||1.14 ||0.88 ||0.77|| | + | |10.0 ||1.14 ||0.88 ||0.77||11.0 ||0.628 |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |16.7 ||0.90 ||0.54 ||0.60|| | + | |16.7 ||0.90 ||0.54 ||0.60||8.5 ||1.049 |
|- | |- | ||
|20.0 ||0.88 ||0.48 ||0.54||8.0 ||1.005 | |20.0 ||0.88 ||0.48 ||0.54||8.0 ||1.005 | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
|125.0 ||0.74 ||0.07 ||0.095||1.8 ||1.413 | |125.0 ||0.74 ||0.07 ||0.095||1.8 ||1.413 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |200.0 ||0.75 ||0.04 ||0.053||0. | + | |200.0 ||0.75 ||0.04 ||0.053||0.9 ||1.005 |
|- | |- | ||
|333.3 ||0.76 ||0.03 ||0.039||0.25 ||0.523 | |333.3 ||0.76 ||0.03 ||0.039||0.25 ||0.523 | ||
Revision as of 22:32, 25 January 2011
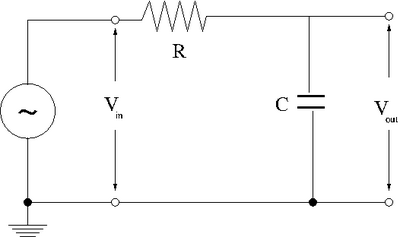
- RC Low-pass filter
1-50 kHz filter (20 pnts)
1. Design a low-pass RC filter with a break point between 1-50 kHz. The break point is the frequency at which the filter starts to attenuate the AC signal. For a Low pass filter, AC signals with a frequency above 1-50 kHz will start to be attenuated (not passed).
- To design low-pass RC filter I had:
2. Now construct the circuit using a non-polar capacitor.
3. Use a sinusoidal variable frequency oscillator to provide an input voltage to your filter.
4. Measure the input and output voltages for at least 8 different frequencies which span the frequency range from 1 Hz to 1 MHz.
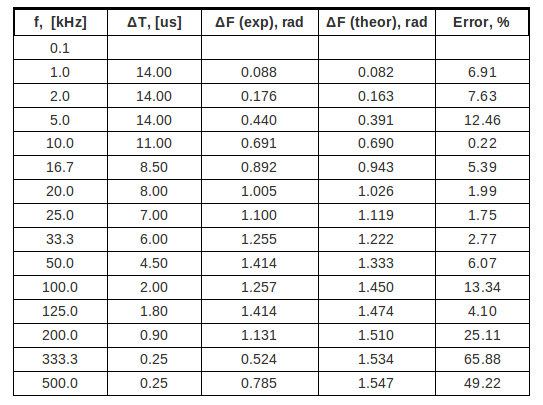
| 0.1 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 1.0 | 4.2 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 14.0 | 0.094 |
| 2.0 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 0.97 | 14.0 | 0.188 |
| 5.0 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 0.89 | 14.0 | 0.471 |
| 10.0 | 1.14 | 0.88 | 0.77 | 11.0 | 0.628 |
| 16.7 | 0.90 | 0.54 | 0.60 | 8.5 | 1.049 |
| 20.0 | 0.88 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 8.0 | 1.005 |
| 25.0 | 0.82 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 7.0 | 1.099 |
| 33.3 | 0.78 | 0.28 | 0.36 | 6.0 | 1.255 |
| 50.0 | 0.76 | 0.18 | 0.24 | 4.5 | 1.413 |
| 100.0 | 0.75 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 2.0 | 1.256 |
| 125.0 | 0.74 | 0.07 | 0.095 | 1.8 | 1.413 |
| 200.0 | 0.75 | 0.04 | 0.053 | 0.9 | 1.005 |
| 333.3 | 0.76 | 0.03 | 0.039 | 0.25 | 0.523 |
| 200.0 | 0.76 | 0.03 | 0.039 | -0.25 | -0.785 |
| 1000.0 | 0.78 | 0.06 | 0.077 | -0.25 | -1.570 |
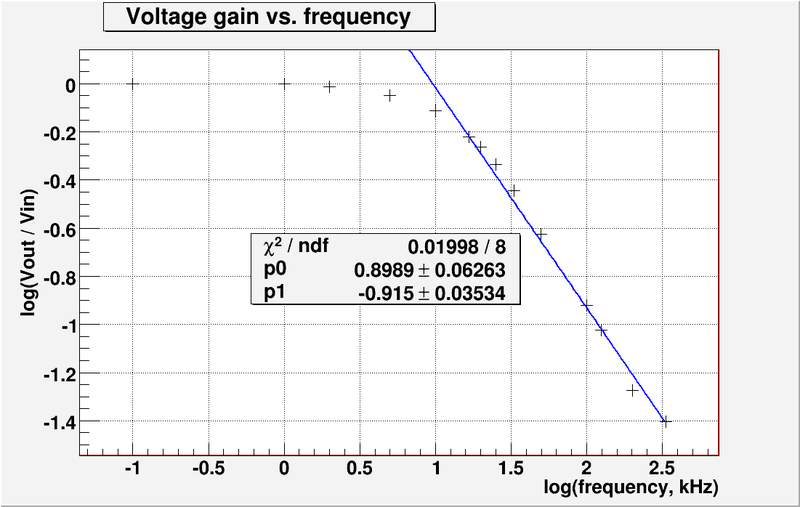
5. Graph the -vs-
phase shift (10 pnts)
- measure the phase shift between and as a function of frequency . Hint: you could use as an external trigger and measure the time until reaches a max on the scope .
See table above, columns #5 and #6.
Questions
1. Compare the theoretical and experimentally measured break frequencies. (5 pnts)
- Theoretical break frequency: 12.1 kHz
- Experimentally measured break frequency: 9.59 kHz
Q: The above was read off the graph? Why not use fit results? A: The fit was made by using GIMP Image Editor. I do not have so much experience with ROOT. But I will try to do it. Thank you for comment. A1: The fit was done by ROOT
- The fit line equation from the plot above is .
- From intersection point of line with x-axis we find:
- The error is:
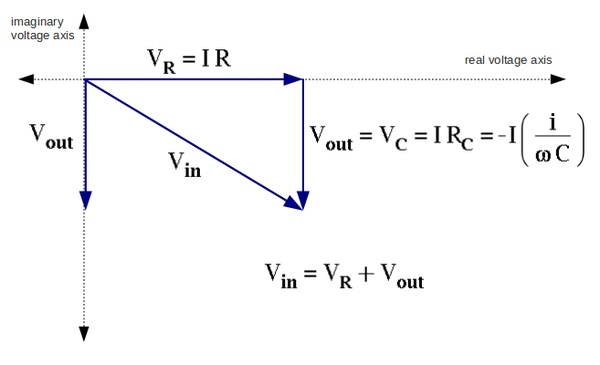
2. Calculate and expression for as a function of , , and . The Gain is defined as the ratio of to .(5 pnts)
We have:
Dividing second equation into first one we get the voltage gain:
And we are need the real part:
3. Sketch the phasor diagram for ,, , and . Put the current along the real voltage axis. (30 pnts)
4. Compare the theoretical and experimental value for the phase shift . (5 pnts)
The experimental phase shift is
The theoretical phase shift is
5. what is the phase shift for a DC input and a very-high frequency input?(5 pnts)
6. calculate and expression for the phase shift as a function of , , and graph -vs . (20 pnts)