Difference between revisions of "Geometry (44 MeV LINAC exit port)"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
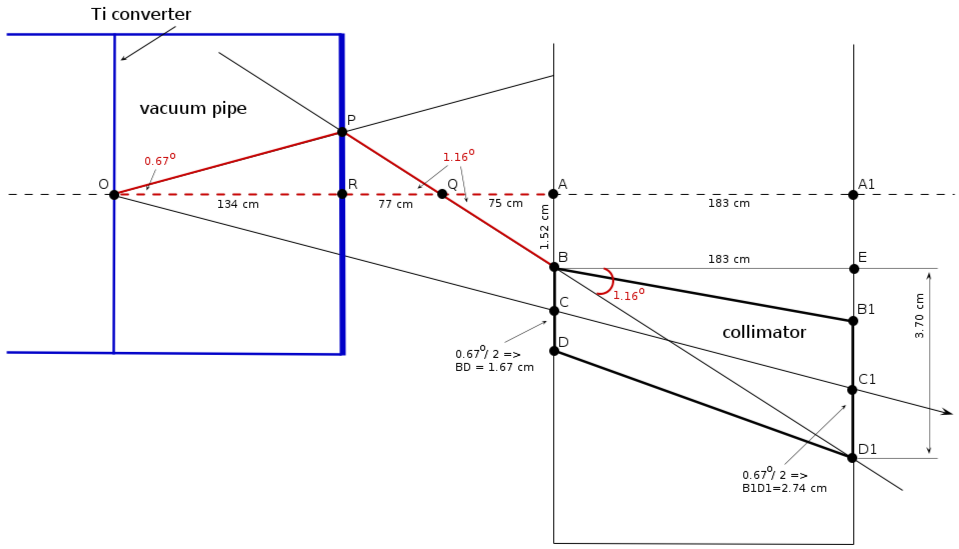
<math> OR\ \tan (0.67^o) = (211 - OR)\ \tan (1.16^o) \Rightarrow</math><br> | <math> OR\ \tan (0.67^o) = (211 - OR)\ \tan (1.16^o) \Rightarrow</math><br> | ||
| − | <math> OR = 211 | + | <math> OR = 211 cm \frac{tan (1.16^o)}{tan (0.16^o) + tan (0.67^o)} = 134\ cm</math> |
| + | |||
| + | RQ = OQ - RQ = (211-134) cm = 77 cm | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> PR = 134/ /tan (0.67^{grad}) = 1.57\ cm</math> | ||
4) minimal distance: | 4) minimal distance: | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 25 May 2010
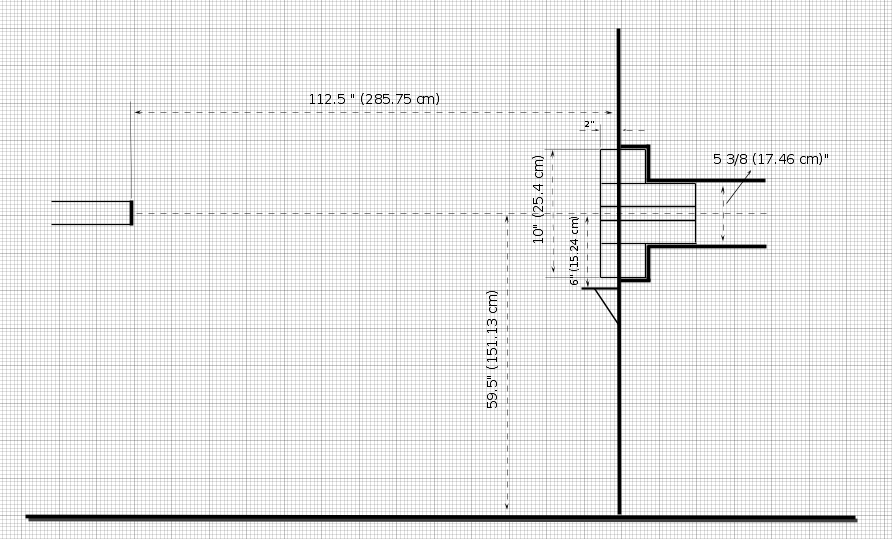
Some measurements of 90 experimental degree exit port
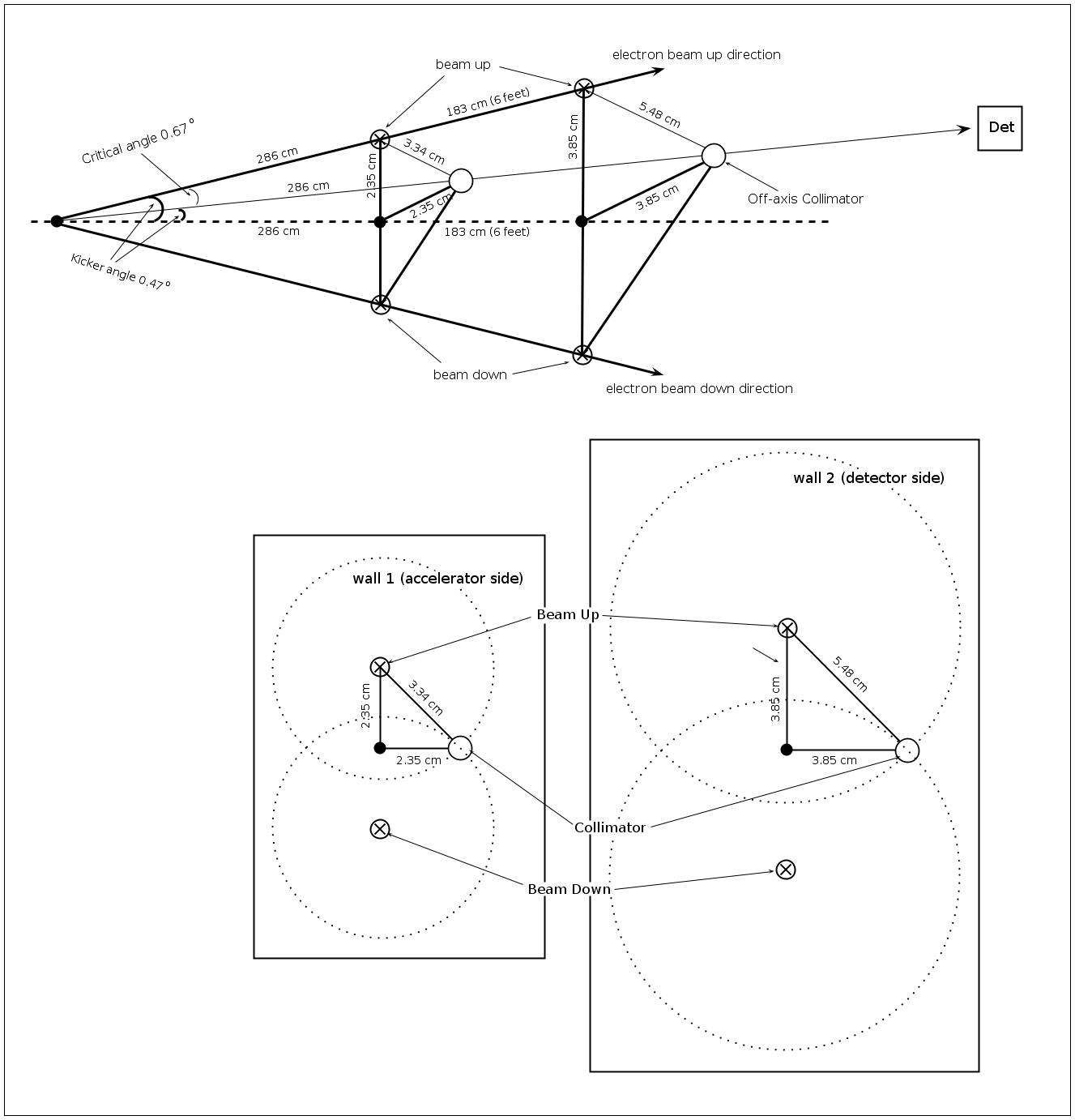
Critical angle and displacement calculations
Kicker angle and displacement calculations
1 foot = 30.48 cm
accelerator's side wall
detector's side wall
Off-axis collimation geometry
Vacuum pipe location (only the kicker angle)
collimator location
1) center position
(wall 1)
(wall 2)
2) assume diameter is
(wall 1)
(wall 2)
collimator critical angle
AB = AC - BD/2 = (2.35 - 1.67/2) cm = 1.52 cm
A1D1 = A1C1 + B1D1/2 = (3.85 + 2.74/2) cm = 5.22 cm
ED1 = A1D1 - AB = (5.22 - 1.52) cm = 3.70 cm
from triangle :
minimal distance from the wall
1) from triangle QAB:
3) from triangles OPR and QPR:
OQ = OA - QA = (286 - 75) cm = 211 cm
RQ = OQ - RQ = (211-134) cm = 77 cm
4) minimal distance:
OR = 134 cm (vacuum pipe length)
RA = OA - OR = (286 + 134) cm = 152 cm (from the wall to the pipe)
collimator and pipe geometry
Vacuum pipe location (kicker angle + multiple scattering angle)
1) take multiple scattering angle
4) minimal distance:
RA = RQ + QA = (31 + 75) cm = 106 cm (from the wall to the vacuum pipe)
OR = OA + RA = (286 + 106) cm = 180 cm (vacuum pipe length)