Difference between revisions of "B-field calculation"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
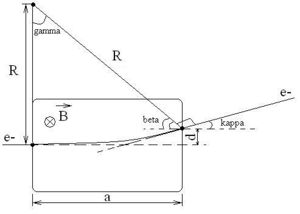
<math>d = R \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa)) = \frac{a \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa))}{sin(\kappa)}</math> | <math>d = R \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa)) = \frac{a \cdot (1 - cos(\kappa))}{sin(\kappa)}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B(T) = \frac{p_e (\frac{MeV}{c})\cdot 0.33\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot sin(\kappa)}{a(m)}</math> | ||
<math>B(T) = \frac{4.67\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot sin(\kappa)}{a(m)}</math> | <math>B(T) = \frac{4.67\cdot 10^{-2}\cdot sin(\kappa)}{a(m)}</math> | ||