Difference between revisions of "Effects Due to Target Length"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "As the target material length is increased, the amount of multiple scattering increases. Since the majority of particles created in the CM frame are at large angles, this imp...") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[File:CompareTargetLength.png]] | [[File:CompareTargetLength.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This gives, for LH2 in a 5cm long target: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\rho_{target}\times l_{target}=\frac{70.85 kg}{1 m^3}\times \frac{1 mole}{2.02 g} \times \frac{1000g}{1 kg} \times \frac{6\times10^{23} atoms}{1 mole} \times \frac{1m^3}{(100 cm)^3} \times \frac{5 cm}{ } \times \frac{10^{-24} cm^{2}}{barn} =1.05\times 10^{-1} barns^{-1}</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\frac{1}{\rho_{target}\times l_{target} \times 6\times 10^6}=1.58\times 10^{-6} barns</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This gives, for LH2 in a 1cm long target: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\rho_{target}\times l_{target}=\frac{70.85 kg}{1 m^3}\times \frac{1 mole}{2.02 g} \times \frac{1000g}{1 kg} \times \frac{6\times10^{23} atoms}{1 mole} \times \frac{1m^3}{(100 cm)^3} \times \frac{1 cm}{ } \times \frac{10^{-24} cm^{2}}{barn} =2.10\times 10^{-2} barns^{-1}</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\frac{1}{\rho_{target}\times l_{target} \times 6\times 10^6}=7.94\times 10^{-6} barns</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This gives, for LH2 in a 1mm long target: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\rho_{target}\times l_{target}=\frac{70.85 kg}{1 m^3}\times \frac{1 mole}{2.02 g} \times \frac{1000g}{1 kg} \times \frac{6\times10^{23} atoms}{1 mole} \times \frac{1m^3}{(100 cm)^3} \times \frac{0.1 cm}{ } \times \frac{10^{-24} cm^{2}}{barn} =2.10\times 10^{-3} barns^{-1}</math></center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><math>\frac{1}{\rho_{target}\times l_{target} \times 6\times 10^6}=7.94\times 10^{-5} barns</math></center> | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 4 April 2018
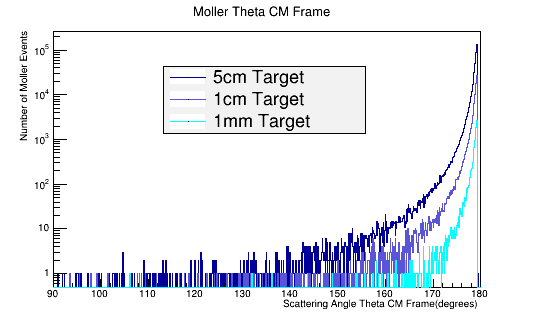
As the target material length is increased, the amount of multiple scattering increases. Since the majority of particles created in the CM frame are at large angles, this implies
This gives, for LH2 in a 5cm long target:
Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron:
This gives, for LH2 in a 1cm long target:
Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron:
This gives, for LH2 in a 1mm long target:
Using the number of incident electrons, for 1 Moller electron: