Difference between revisions of "CrossTalk"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
=Detector physics= | =Detector physics= | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| − | Neutron energy deposition from collisions with hydrogen and carbon are converted to electron equivalent light output by MCNP-POLIMI. Neutron collisions that all occur | + | Neutron energy deposition from collisions with hydrogen and carbon are converted to electron equivalent light output (MeVee) by MCNP-POLIMI. Neutron collisions that all occur within a pulse collection time of 10 ns of each other are converted to MeVee and cumulated. If the cumulative light output exceeds 0.03 MeVee then it is considered a detection. The value 0.03 MeVee was chosen because it corresponds to a mean neutron energy deposit of 0.2 MeV. |
==Detectpor responce== | ==Detectpor responce== | ||
Revision as of 21:39, 18 July 2016
Go back MCNP simulations
Geometry
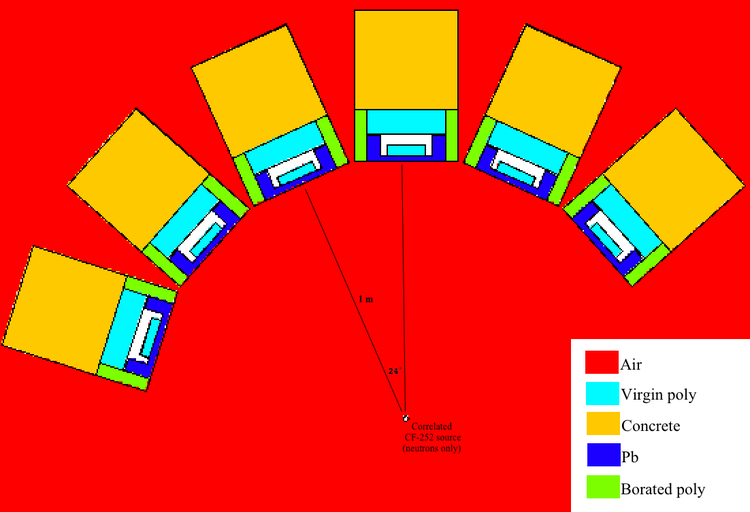
An array of 6 detectors are placed radially at a distance of 1 meter from an uncorrelated 252-CF source. The image below shows a top down view of the simulation geometry. The detector setups have a vertical extent of 30".
Detector physics
Summary
Neutron energy deposition from collisions with hydrogen and carbon are converted to electron equivalent light output (MeVee) by MCNP-POLIMI. Neutron collisions that all occur within a pulse collection time of 10 ns of each other are converted to MeVee and cumulated. If the cumulative light output exceeds 0.03 MeVee then it is considered a detection. The value 0.03 MeVee was chosen because it corresponds to a mean neutron energy deposit of 0.2 MeV.
Detectpor responce
The electron equivalent (MeVee) conversion functions for neutrons were measured for plastic (BC 420) scintillators as a function of neutron energy deposit, . For deposit on hydrogen the measurements fit the following quadratic function:
and for deposit on carbon:
A light output of 0.03 MeVee corresponded to an average neutron energy deposition of 0.2 MeV in the scintillator.
Go back MCNP simulations