Difference between revisions of "D2O bank"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[File:runTime_runNum.png | 600 px]] | [[File:runTime_runNum.png | 600 px]] | ||
| − | The thing is that the pair spectrometer is sensitive to the low energy background which may be present in the beam (e- beam finite size and, hence, scraping) so the value of the flux may be affected by low energy component. This thing may not be reflected in the number of neutrons detected by the neutron detectors. | + | The thing is that the pair spectrometer is sensitive to the low energy background which may be present in the beam (e- beam finite size and, hence, scraping) so the value of the flux may be affected by low energy component. This thing may not be reflected in the number of neutrons detected by the neutron detectors. So, it is arguable that the pair spectrometer can be used for the flux normalization procedure. |
==Neutron energy spectra== | ==Neutron energy spectra== | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 1 April 2013
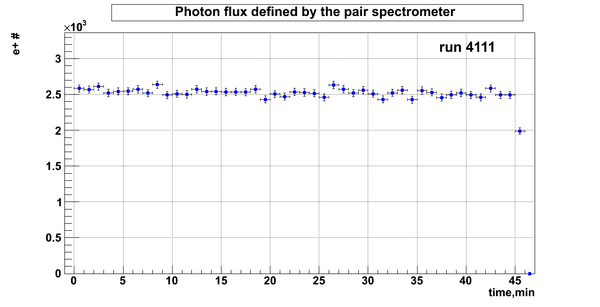
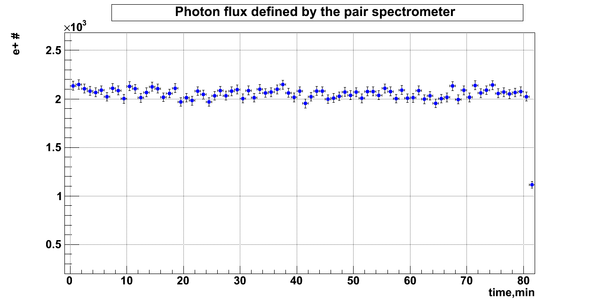
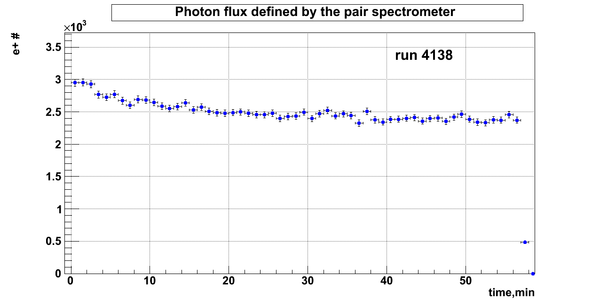
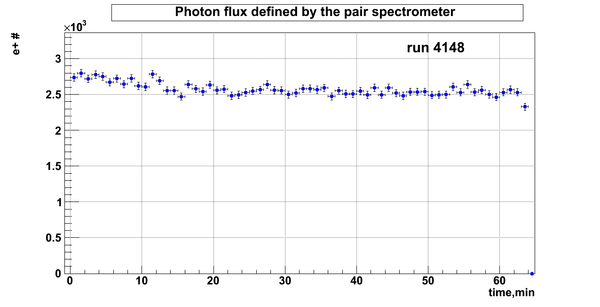
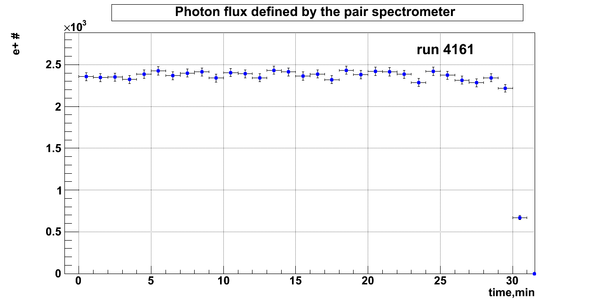
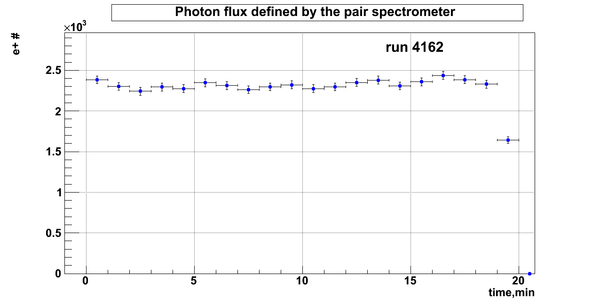
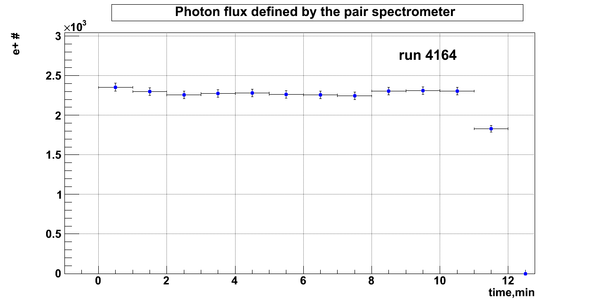
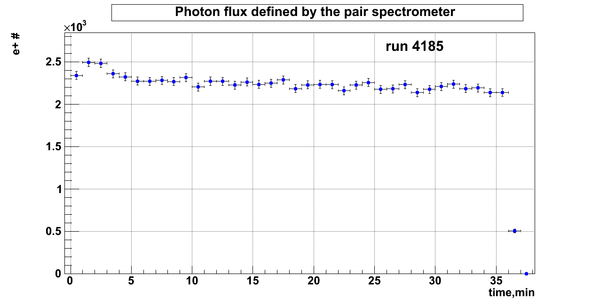
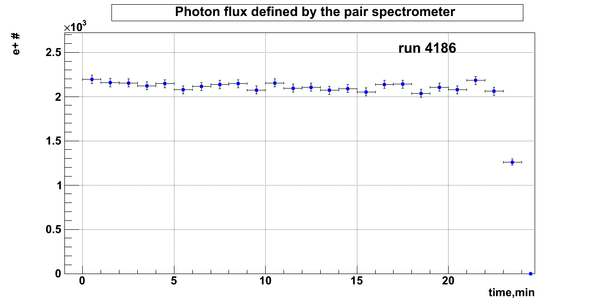
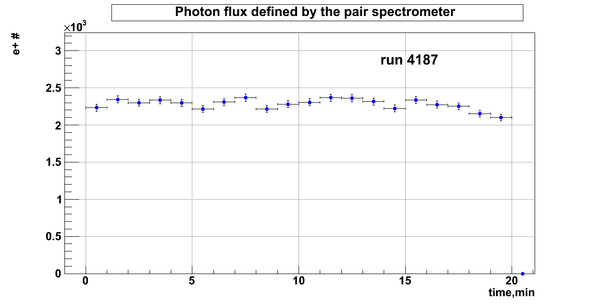
Relative photon flux
Normalization?
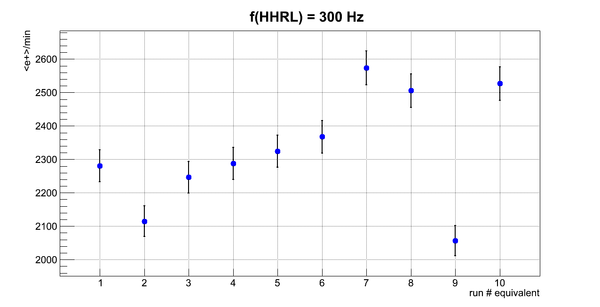
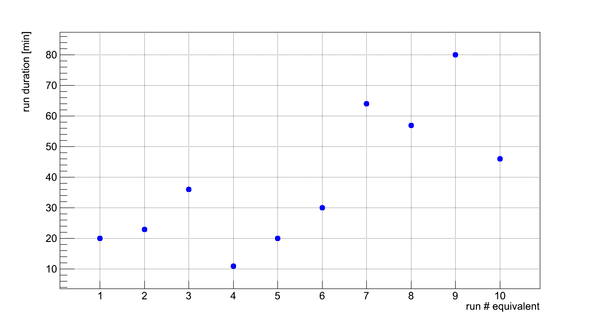
Flux fluctuation over the runs:
run # equivalent 1 corresponds to run 4187, 2 - 4186, 3 - 4185, 4 - 4164, 5 - 4162, 6 - 4161, 7 - 4148, 8 - 4138, 9 - 4126, 10 - 4111.
The thing is that the pair spectrometer is sensitive to the low energy background which may be present in the beam (e- beam finite size and, hence, scraping) so the value of the flux may be affected by low energy component. This thing may not be reflected in the number of neutrons detected by the neutron detectors. So, it is arguable that the pair spectrometer can be used for the flux normalization procedure.
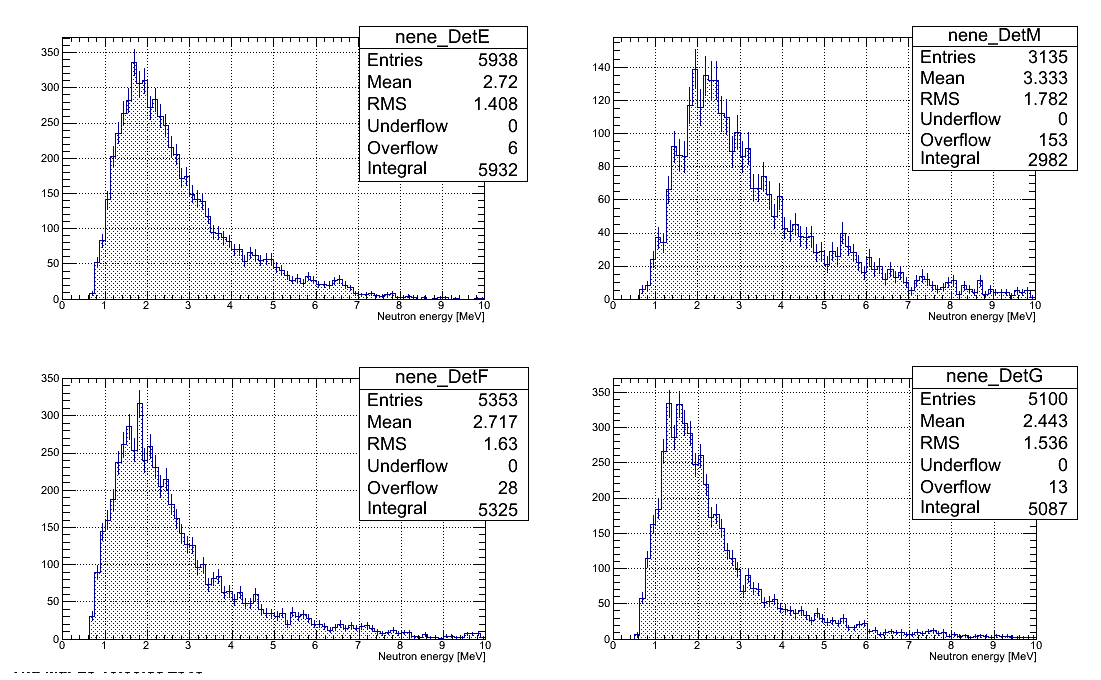
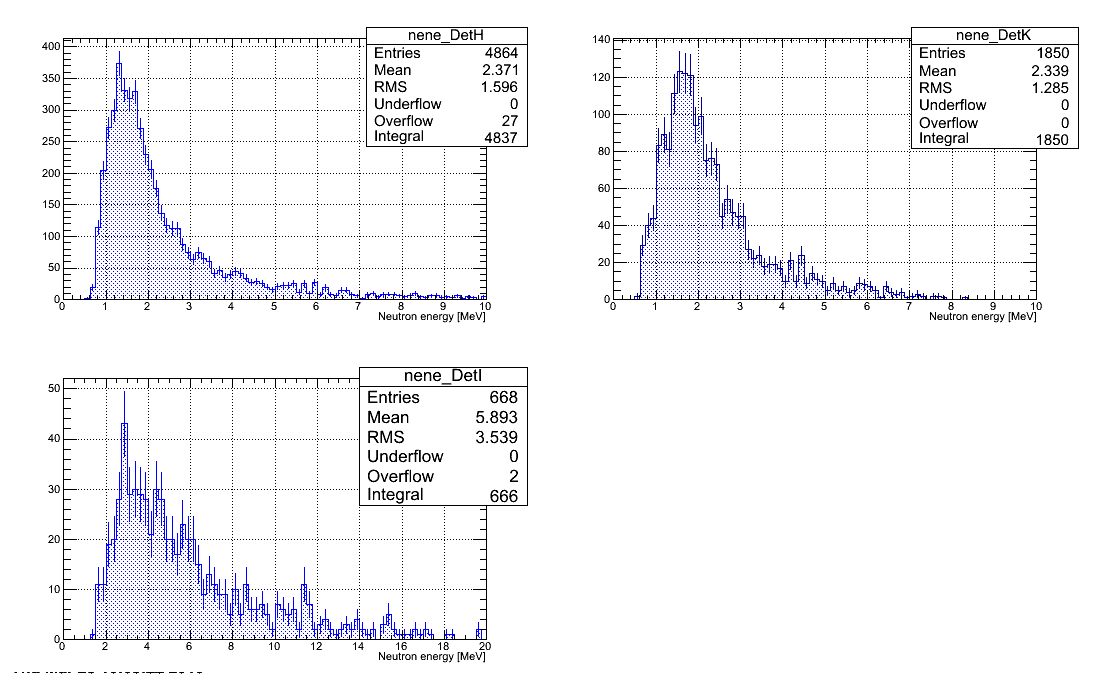
Neutron energy spectra
Neutron energy spectra restored from all the runs with D2O target are plotted below. Statistical error bars only presented.