Difference between revisions of "Normalized and BKG subtracted data"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
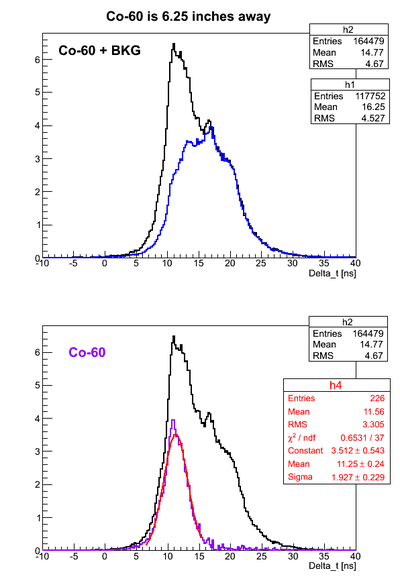
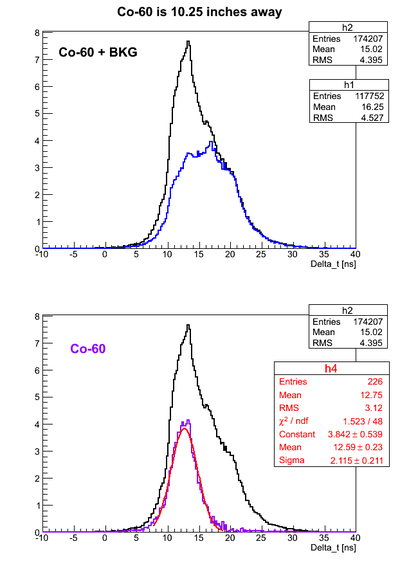
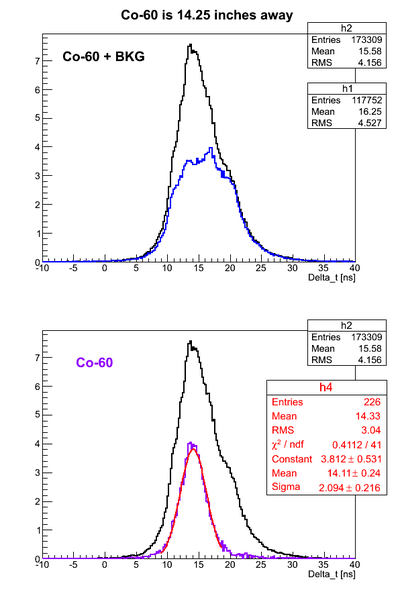
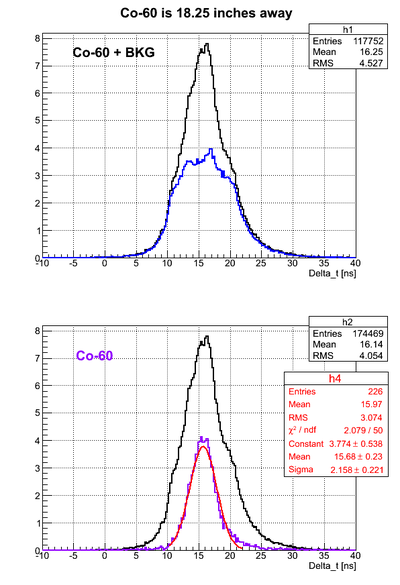
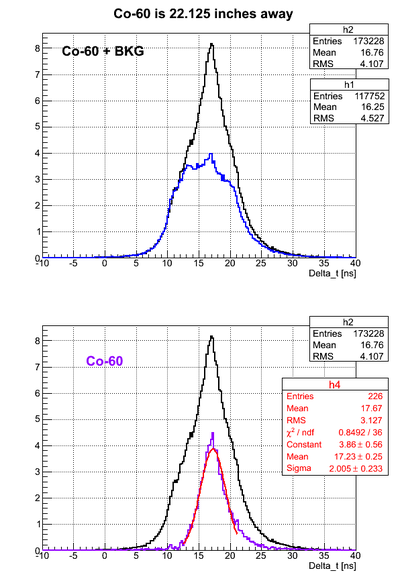
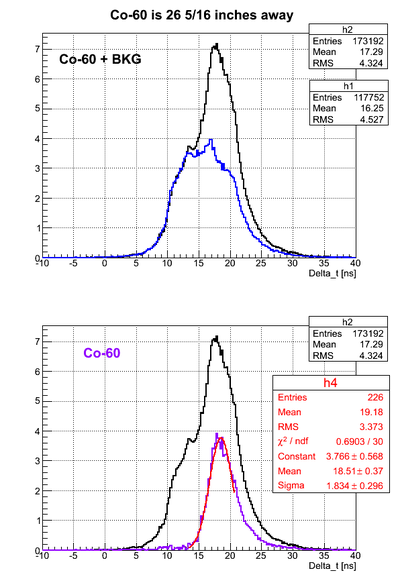
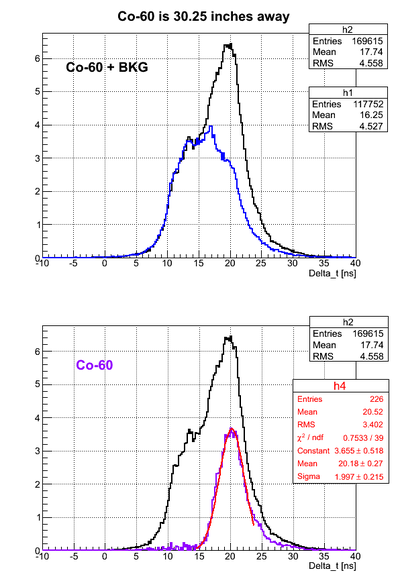
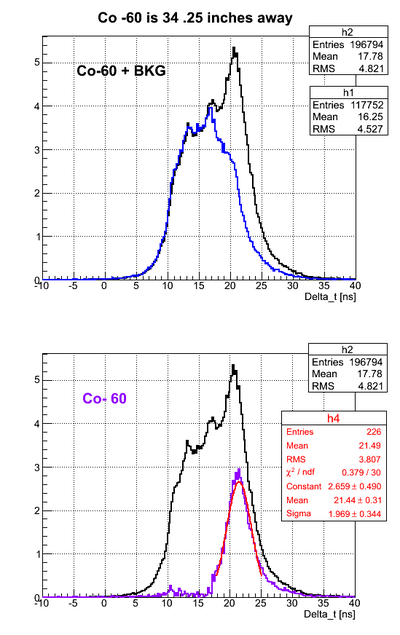
For all the timing spectra it was calculated K1(left)-K2(right). | For all the timing spectra it was calculated K1(left)-K2(right). | ||
| − | Co-60 was used as a source. 2" thick Pb brick with hole of a diameter ~5mm was used as a collimator. | + | Co-60 was used as a source. 2" thick Pb brick with a hole of a diameter ~5mm was used as a collimator. |
==Source is 15.85 cm away from the left PMT== | ==Source is 15.85 cm away from the left PMT== | ||
Revision as of 23:22, 14 September 2012
For all the timing spectra it was calculated K1(left)-K2(right).
Co-60 was used as a source. 2" thick Pb brick with a hole of a diameter ~5mm was used as a collimator.
Source is 15.85 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 26.035 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 36.2 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 46.35 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 56.2 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 66.82 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 76.83 cm away from the left PMT
Source is 87 cm away from the left PMT
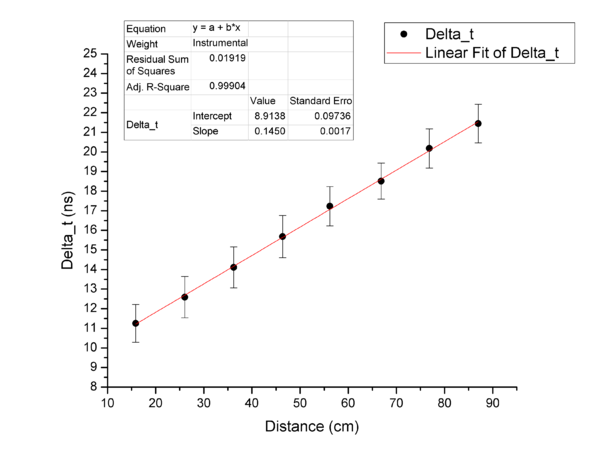
Final calibration curve
The whole width of a single error bar represents the value of one sigma in time difference spectrum for BKG subtracted data.
Hence, the slope is 0.1450 ns/cm or 6.89 cm/ns.