Difference between revisions of "Lab 23 TF EIM"
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
= Gain measurements= | = Gain measurements= | ||
| − | + | 1.) Measure the gain as a function of frequency between 100 Hz and 2 MHz for three values of <math>R_2</math> = 10 k<math>\Omega</math>, 100 k<math>\Omega</math>, 1M<math>\Omega</math>. Keep <math>R_1</math> at <math>1k\Omega</math>. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | 2.)Graph the above measurements with the Gain in units of decibels (dB) and with a logarithmic scale for the frequency axis. | ||
=Impedance= | =Impedance= | ||
Revision as of 02:27, 13 April 2011
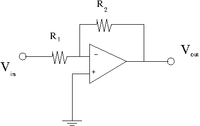
Inverting OP Amp
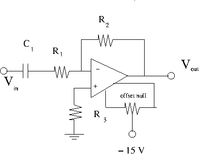
1. Construct the inverting amplifier according to the wiring diagram below.
Here is the data sheet for the 741 Op Amp
Use and as starting values.
Gain measurements
1.) Measure the gain as a function of frequency between 100 Hz and 2 MHz for three values of = 10 k, 100 k, 1M. Keep at .
2.)Graph the above measurements with the Gain in units of decibels (dB) and with a logarithmic scale for the frequency axis.
Impedance
Input Impedance
- Measure for the 10 fold and 100 fold amplifier at ~100 Hz and 10 kHz frequency.
Output Impedance
- Measure for the 10 fold and 100 fold amplifier at ~100 Hz and 10 kHz frequency. Be sure to keep the output () undistorted
and
Use the above equation and two measurements of , , and to extract and .
- measure for = 1 k, = 100 k, and=0 (grounded).
- measure for = 10 k, = 1 M, and=0 (grounded).
- You can now construct 2 equations with 2 unknowns and .
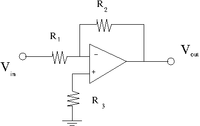
Now we will put in a pull up resistor R_3 as shown below.
Instead of the current we have the current
Use the same technique and resistors from the previous section to construct 2 equations and 2 unknowns and extract , keep =0.
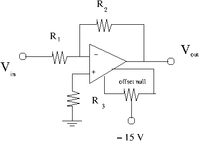
The offset Null Circuit
- Construct the offset null circuit above.
- Adjust the potentiometer to minimize with .
- Use a scope to measure the output noise.
Capacitors
- Revert back to the pull up resistor
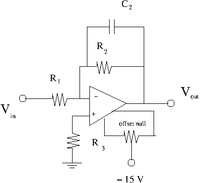
Capacitor in parallel with
- Select a capacitor such that when = 10 kHz.
- Add the capacitor in parallel to so you have the circuit shown above.
- Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage
- Measure the Gain as a function of the frequency and plot it.
Capacitor in series with R_1
- Select a capacitor such that when = 1 kHz.
- Add the capacitor in series to so you have the circuit shown above.
- Use a pulse generator to input a sinusoidal voltage
- Measure the Gain as a function of the frequency and plot it.
Slew rate
Measure the slew and compare it to the factory spec.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
- Set V_{in} = 0.
- Measure while changing