Difference between revisions of "Lab 3 TF EIM"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
=Questions= | =Questions= | ||
| − | # | + | #Compare the theoretical and experimentally measured break frequencies. (5 pnts) |
| − | #Calculate | + | #Calculate an expression for <math>\frac{V_{out}}{ V_{in}}</math> as a function of <math>\nu</math>, <math>R</math>, and <math>C</math>. The Gain is defined as the ratio of <math>V_{out}</math> to <math>V_{in}</math>.(5 pnts) |
#Sketch the phasor diagram for <math>V_{in}</math>,<math> V_{out}</math>, <math>V_{R}</math>, and <math>V_{C}</math>. Put the current <math>I</math> along the real voltage axis. (30 pnts) | #Sketch the phasor diagram for <math>V_{in}</math>,<math> V_{out}</math>, <math>V_{R}</math>, and <math>V_{C}</math>. Put the current <math>I</math> along the real voltage axis. (30 pnts) | ||
| − | # | + | #Calculate an expression for the phase shift <math>\theta</math> as a function of <math>\nu</math>, <math>R</math>, <math>C</math> and graph <math>\theta</math> -vs <math>\nu</math>. (20 pnts) |
#Compare the theoretical and experimental value for the phase shift <math>\theta</math>. (5 pnts) | #Compare the theoretical and experimental value for the phase shift <math>\theta</math>. (5 pnts) | ||
# what is the phase shift <math>\theta</math> for a DC input (the limit as frequency goes to zero) and a very-high frequency input?(5 pnts) | # what is the phase shift <math>\theta</math> for a DC input (the limit as frequency goes to zero) and a very-high frequency input?(5 pnts) | ||
Revision as of 18:57, 29 January 2015
- RC Low-pass filter
1-50 kHz filter (20 pnts)
1.) Design a low-pass RC filter with a break point between 1-50 kHz. The break point is the frequency at which the filter starts to attenuate the AC signal. For a Low pass filter, AC signals with a frequency above 1-50 kHz will start to be attenuated (not passed).
2.)Now construct the circuit using a non-polar capacitor.
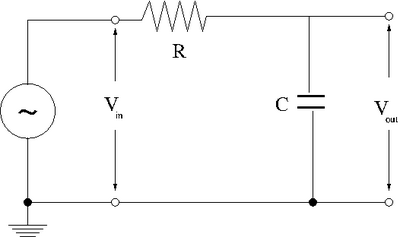 3.)use a sinusoidal variable frequency oscillator to provide an input voltage to your filter.
4.)Measure the input and output voltages for at least 8 different frequencies which span the frequency range from 1 Hz to 1 MHz.
3.)use a sinusoidal variable frequency oscillator to provide an input voltage to your filter.
4.)Measure the input and output voltages for at least 8 different frequencies which span the frequency range from 1 Hz to 1 MHz.
| Hz | Volts | Volts | |
5.) Graph the -vs-
phase shift (10 pnts)
- measure the phase shift between and as a function of frequency . Hint: you could use as an external trigger and measure the time until reaches a max on the scope .
Questions
- Compare the theoretical and experimentally measured break frequencies. (5 pnts)
- Calculate an expression for as a function of , , and . The Gain is defined as the ratio of to .(5 pnts)
- Sketch the phasor diagram for ,, , and . Put the current along the real voltage axis. (30 pnts)
- Calculate an expression for the phase shift as a function of , , and graph -vs . (20 pnts)
- Compare the theoretical and experimental value for the phase shift . (5 pnts)
- what is the phase shift for a DC input (the limit as frequency goes to zero) and a very-high frequency input?(5 pnts)