Difference between revisions of "TF EIM Chapt3"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
| − | ;Bandwith: The most common definition for the Bandwidth of this circuit is the frequency range over which the output decreases by 3 dB | + | ;Bandwith: The most common definition for the Bandwidth of this circuit is the frequency range over which the output decreases by 3 dB. This correspond to the frequency at which the circuits power is cut in half from the resonance frequency. |
| + | |||
| + | :<math>P = I^2 R</math> | ||
| + | :<math>P_{1/2} = (\sqrt{2}I)^2 R</math> | ||
[[File:TF_EIM_BandWidthDef_LC.gif | 200 px]] | [[File:TF_EIM_BandWidthDef_LC.gif | 200 px]] | ||
[[Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement]] | [[Forest_Electronic_Instrumentation_and_Measurement]] | ||
Revision as of 05:56, 2 February 2011
gain
Loop Theorem
or
- Notice
- When then the AC signal is attenuated.
Looking at the Voltage divider aspect of the circuit
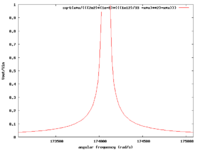
| and and R=200 |
|
| rad/s or Hz |
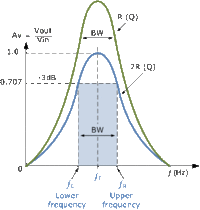
Q and Bandwidth
In the above circuit
The inductors reactance at this resonance frequency is
- Bandwith
- The most common definition for the Bandwidth of this circuit is the frequency range over which the output decreases by 3 dB. This correspond to the frequency at which the circuits power is cut in half from the resonance frequency.